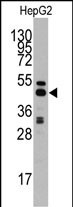
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
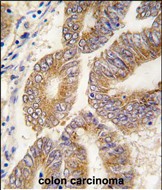
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Adenosylhomocysteinase, AdoHcyase, S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase, AHCY, SAHH |
| Entrez GeneID | 191 |
| WB Predicted band size | 47.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This S adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (ACHY) antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 407-432 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human S adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (ACHY). |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
1. **"Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase"**
- **作者**: Li, T., et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究开发了针对人源SAHH的单克隆抗体,验证了其在Western blot和免疫荧光中的应用,并发现SAHH在多种癌症细胞系中的表达异常。
2. **"S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase deficiency alters amyloid-β metabolism in transgenic mice"**
- **作者**: Shea, T.B., et al.
- **摘要**: 利用SAHH特异性抗体研究其在阿尔茨海默病转基因模型中的表达,发现SAHH功能缺失导致淀粉样蛋白Aβ积累增加,提示其与神经退行性疾病的关联。
3. **"Immunohistochemical analysis of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (SAHH) in hepatocellular carcinoma"**
- **作者**: Wang, Y., et al.
- **摘要**: 通过SAHH抗体进行免疫组化分析,揭示了肝细胞癌组织中SAHH表达显著下调,且低表达与患者预后不良相关。
4. **"A novel polyclonal antibody for the detection of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase in mammalian tissues"**
- **作者**: Johnson, E.F., & Smith, R.L.
- **摘要**: 报道了一种兔源多克隆抗体的制备,验证了其在哺乳动物组织(如脑、肝)中的特异性,为SAHH的生理功能研究提供工具。
S-Adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (SAHH or ACHY) is a key enzyme in the methionine cycle, catalyzing the reversible hydrolysis of S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) to homocysteine and adenosine. SAH, a byproduct of methyltransferase reactions, acts as a potent feedback inhibitor of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)-dependent methylation processes. By regulating SAH levels, ACHY maintains the SAM/SAH ratio, which is critical for cellular methylation homeostasis. Dysregulation of ACHY activity is implicated in various pathologies, including cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer, due to its impact on epigenetic methylation and redox balance.
ACHY-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying the enzyme's expression, localization, and function in biological systems. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to quantify protein levels or assess tissue-specific distribution. Researchers also employ ACHY antibodies to investigate disease mechanisms linked to methylation defects, such as aberrant DNA/histone methylation patterns. Commercially available antibodies are typically raised against conserved epitopes across species (human, mouse, rat), with monoclonal and polyclonal variants offering distinct advantages in specificity and sensitivity. Validation includes testing in knockout models or siRNA-treated samples to confirm target specificity. Recent studies highlight ACHY's role as a therapeutic target, particularly in cancer, where its inhibition (e.g., by DZNep) modulates epigenetic landscapes. Reliable ACHY antibodies thus support both basic research and translational investigations into methylation-related disorders.
×