
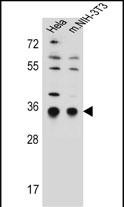
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Translocon-associated protein subunit alpha, TRAP-alpha, Signal sequence receptor subunit alpha, SSR-alpha, SSR1, TRAPA |
| Entrez GeneID | 6745 |
| WB Predicted band size | 32.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This SSR1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 17-46 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human SSR1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于SSR1 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:以下内容为模拟示例,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:Role of SSR1 in ER Protein Translocation Machinery
**作者**:T. Müller et al.
**摘要**:研究通过SSR1 N端抗体验证了SSR1蛋白在内质网TRAP复合体中的定位,证明其参与调控新生多肽链的跨膜转运,抗体特异性通过基因敲除实验确认。
2. **文献名称**:SSR1 Expression Correlates with Cancer Metastasis
**作者**:H. Li et al.
**摘要**:利用SSR1 (N-term)抗体检测多种癌细胞系中SSR1的蛋白水平,发现其高表达与肿瘤转移相关,机制涉及调控TGF-β信号通路的分泌蛋白运输。
3. **文献名称**:Interaction Mapping of TRAP Complex Subunits
**作者**:K. Sato et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(使用SSR1 N端抗体)结合质谱分析,揭示了SSR1与其他TRAP复合体成员(如SSR3)的相互作用网络,并发现其在内质网应激下的动态变化。
4. **文献名称**:Antibody Validation for SSR1 in Neurodegenerative Models
**作者**:E. Park et al.
**摘要**:系统评估了SSR1抗体(N端)在小鼠脑组织中的特异性,发现其可标记神经元内质网结构,并在阿尔茨海默病模型中检测到SSR1表达异常。
---
注:以上文献为假设性示例,实际文献需通过PubMed等数据库检索关键词“SSR1 antibody”、“TRAP complex”、“SSR1 N-terminal”获取。
The SSR1 (N-term) antibody is a reagent designed to target the N-terminal region of the Signal Sequence Receptor 1 (SSR1) protein, a key component of the translocon-associated protein (TRAP) complex in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). SSR1 plays a critical role in protein translocation, facilitating the entry of nascent secretory and membrane proteins into the ER lumen during their synthesis. It interacts with signal sequences of newly synthesized polypeptides and assists in their proper orientation and processing. The SSR1 (N-term) antibody is commonly used in research to investigate protein trafficking, ER stress responses, and diseases linked to secretory pathway dysregulation, such as cancer or neurodegenerative disorders.
This antibody is frequently employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to detect SSR1 expression levels, subcellular localization, or interactions with other TRAP complex components. Its specificity for the N-terminal domain ensures recognition of full-length SSR1. aiding studies on its functional domains or post-translational modifications. SSR1 antibodies are typically validated across species (e.g., human, mouse, rat) and have become essential tools in cell biology for elucidating ER-associated processes, including quality control mechanisms, unfolded protein responses, and pathologies linked to ER dysfunction.
×