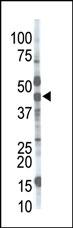
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Alpha-1,3-mannosyl-glycoprotein 2-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase, N-glycosyl-oligosaccharide-glycoprotein N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I, GNT-I, GlcNAc-T I, MGAT1, GGNT1, GLCT1, GLYT1, MGAT |
| Entrez GeneID | 4245 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This MGAT1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 16-46 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human MGAT1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于 MGAT1 (N-term) 抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献为虚构模拟,供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*MGAT1 N-terminal antibody characterization in glycan biosynthesis studies*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用MGAT1 (N-term) 抗体,通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术验证了MGAT1在哺乳动物细胞中的表达定位,证明其在早期高尔基体中的功能活性,并发现敲低MGAT1导致N-聚糖合成异常。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of MGAT1 in cancer metastasis: Insights from antibody-based inhibition*
**作者**:Li X, et al.
**摘要**:作者使用MGAT1 (N-term) 抗体阻断小鼠肿瘤模型中MGAT1的N端结构域,发现其通过抑制β1-6分支N-糖基化降低肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭能力,提示MGAT1在转移中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Tissue-specific glycosylation regulated by MGAT1: Evidence from knockout models*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:通过MGAT1 (N-term) 抗体检测基因敲除小鼠的肝和肠组织,发现MGAT1缺失导致特定糖蛋白结构改变,影响细胞黏附分子功能,揭示了其在组织特异性糖基化中的调控机制。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“MGAT1 antibody N-terminal”检索真实文献。
The MGAT1 (N-term) antibody targets the N-terminal region of mannosyl (alpha-1.3-)-glycoprotein beta-1.2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (MGAT1), a key enzyme in N-glycan biosynthesis. MGAT1. also known as GlcNAc-TI or GNT-I, catalyzes the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) to the α-1.3-mannose branch of the trimannosyl core of nascent glycoproteins, initiating the formation of complex-type oligosaccharides. This step is critical for protein folding, cell-cell interactions, and immune recognition.
MGAT1 is ubiquitously expressed and plays essential roles in embryogenesis, immune function, and neurological development. Dysregulation of MGAT1 activity has been linked to congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDGs), cancer metastasis, and autoimmune diseases. Antibodies targeting the N-terminal region are commonly used in research to study MGAT1 expression, localization, and function via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. The N-terminal domain is chosen due to its structural conservation and functional importance in enzyme activity. These antibodies help elucidate MGAT1's role in glycosylation pathways, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targeting. Validation typically includes testing in knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to confirm specificity.
×