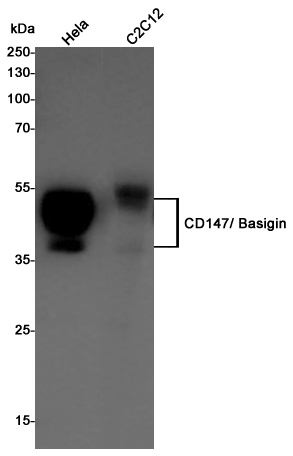
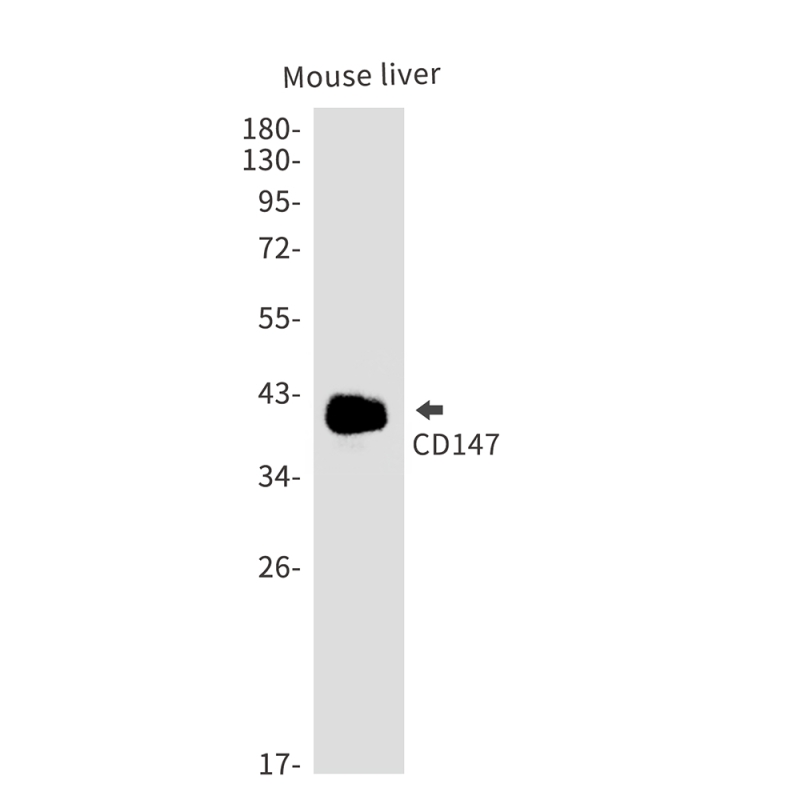
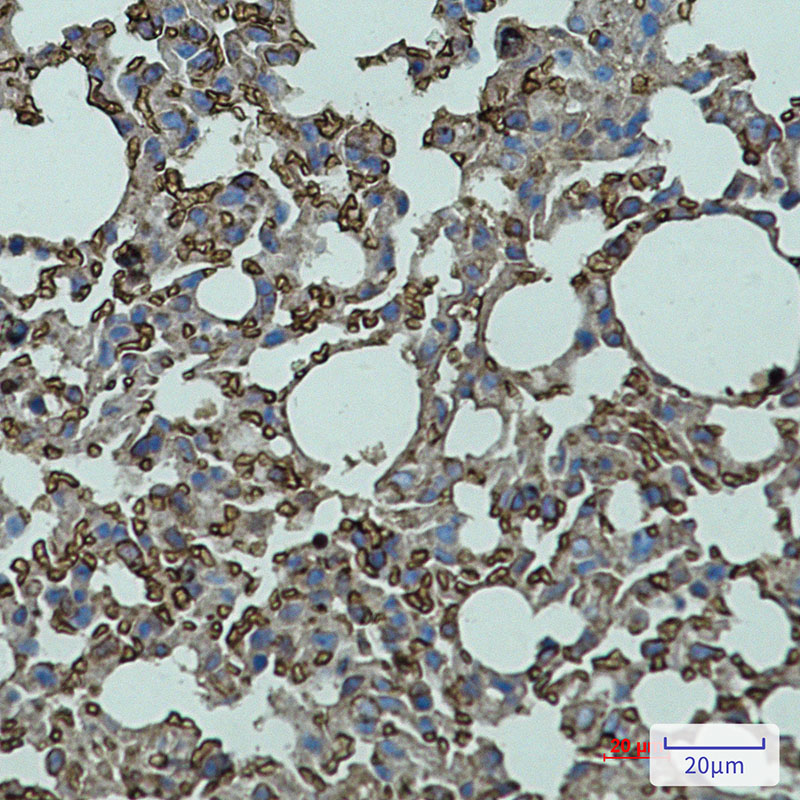
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HT-7; CD147; EMMPRIN; AI115436; AI325119 |
| Entrez GeneID | 12215 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 42 kDa; Observed MW: 38-58 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of mouse CD147 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD147抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(虚构示例,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*CD147 Antibody HAb18 Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis via Inhibition of MMP-9 Secretion*
**作者**:Zhang Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种靶向CD147的单克隆抗体(HAb18),通过阻断CD147与金属蛋白酶(MMPs)的相互作用,抑制肝癌细胞的侵袭和转移,为肝癌治疗提供了潜在策略。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD147 in Tumor Microenvironment: A Novel Therapeutic Approach*
**作者**:Biswas C. et al.
**摘要**:文章揭示了CD147在肿瘤微环境中促进血管生成和免疫逃逸的作用,并证明其抗体可通过抑制肿瘤-基质细胞相互作用显著延缓多种癌症的进展。
3. **文献名称**:*CD147 as a Binding Receptor for SARS-CoV-2 and Anti-CD147 Antibody for COVID-19 Therapy*
**作者**:Pushkarsky T. et al.
**摘要**:研究发现CD147是新冠病毒(SARS-CoV-2)入侵宿主细胞的潜在受体,使用抗CD147抗体可有效阻断病毒感染,提示其在COVID-19治疗中的应用价值。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed等数据库查询。)
CD147 antibody targets CD147. a transmembrane glycoprotein also known as Basigin (BSG) or EMMPRIN. CD147 is widely expressed in various cell types, including immune cells, endothelial cells, and tumor cells. It plays critical roles in intercellular communication, tissue remodeling, and inflammatory responses by regulating matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) production, lymphocyte trafficking, and cellular adhesion. Structurally, it contains two immunoglobulin-like domains and interacts with integrins, cyclophilins, and monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs), influencing metabolic reprogramming in cancer.
CD147 antibodies have garnered attention in research and therapeutics due to their involvement in pathological conditions. In oncology, CD147 is overexpressed in many cancers (e.g., breast, liver, pancreatic), promoting tumor invasion, metastasis, and chemoresistance by stimulating MMP secretion and angiogenesis. Antibodies blocking CD147 inhibit these processes, showing potential in preclinical models. Additionally, CD147 serves as a receptor for SARS-CoV-2 entry, spurring interest in neutralizing antibodies for COVID-19. In autoimmune diseases, CD147 modulates T-cell activation and cytokine release, making it a target for immunomodulation.
Current studies focus on developing humanized or monoclonal CD147 antibodies for clinical use. Challenges include optimizing specificity to avoid off-target effects and understanding isoform-specific functions (e.g., Basigin vs. Emmprin). Despite hurdles, CD147 antibodies represent a promising avenue for targeted therapy and diagnostics in cancer, infectious diseases, and inflammation.
×