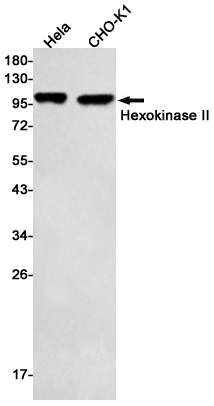
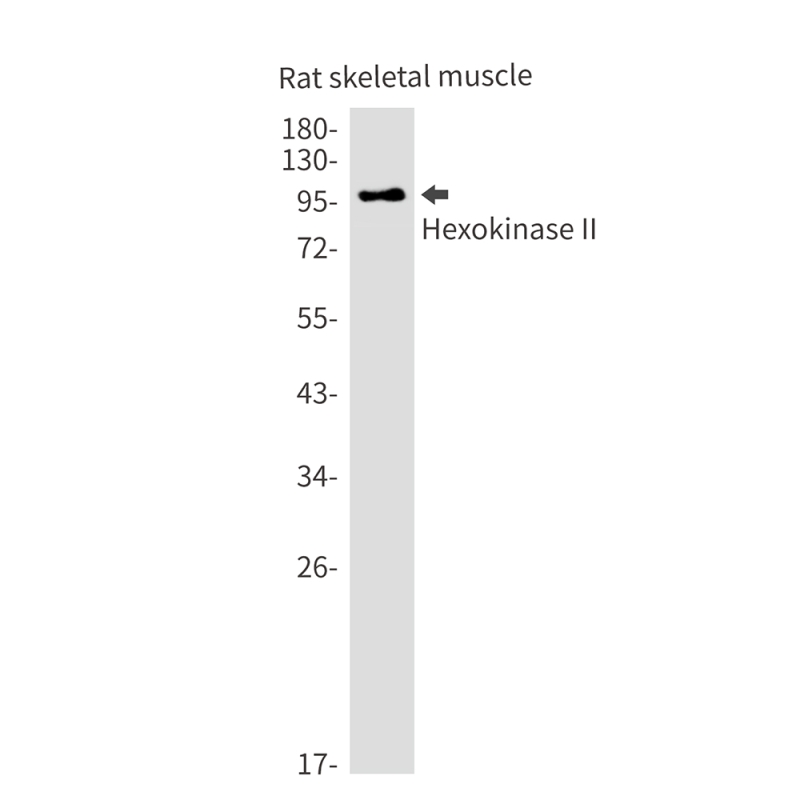
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| Aliases | HKII; HXK2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3099 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 102 kDa; Observed MW: 102 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat,Hamster |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human Hexokinase II |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Hexokinase II(HK2)抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Hexokinase 2 as a therapeutic target in cancer*
**作者**:Roberts DJ, Miyamoto S
**期刊**:*Trends in Pharmacological Sciences* (2015)
**摘要**:该综述讨论了HK2在肿瘤代谢重编程中的核心作用,指出使用HK2特异性抗体检测其在癌细胞线粒体膜上的过表达,并验证其作为化疗增敏靶点的潜力(抗体用于Western blot和免疫组化分析)。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Mitochondrial binding of hexokinase II inhibits Bax-induced cytochrome c release and apoptosis*
**作者**:Pastorino JG, et al.
**期刊**:*Journal of Biological Chemistry* (2002)
**摘要**:通过抗HK2抗体(克隆号:C64G5)研究HK2与线粒体的结合如何抑制Bax介导的细胞色素c释放,揭示HK2在调控细胞凋亡中的双重功能(抗体用于免疫沉淀和亚细胞定位分析)。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting hexokinase 2 enhances response to radio-chemotherapy in cervical cancer*
**作者**:Liu Y, et al.
**期刊**:*Molecular Cancer Therapeutics* (2016)
**摘要**:利用HK2特异性抗体(兔多克隆,Abcam ab209847)验证HK2在宫颈癌组织中的高表达,并证明其沉默可通过抑制糖酵解增强放化疗敏感性(抗体用于免疫荧光和流式细胞术)。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Hexokinase 2 is required for tumor initiation and maintenance in a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma*
**作者**:Patra KC, et al.
**期刊**:*Cancer Cell* (2013)
**摘要**:通过抗HK2抗体(Cell Signaling Technology #2867)在小鼠肺癌模型中证实HK2在肿瘤发生中的必要性,并揭示其通过mTORC1通路驱动增殖(抗体用于免疫印迹和免疫组化,且验证了抗体特异性)。
---
**注**:以上文献均涉及HK2抗体的实验应用,涵盖癌症机制、治疗靶点及代谢调控研究,抗体用途包括蛋白检测、定位分析和功能验证。
Hexokinase II (HK2) is a key enzyme in glycolysis, catalyzing the first step by phosphorylating glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. It is highly expressed in energy-demanding tissues, such as skeletal muscle and heart, and plays a critical role in cancer metabolism. HK2 is overexpressed in many tumors, where it supports the Warburg effect—a metabolic shift favoring aerobic glycolysis for rapid ATP production and biomass synthesis. This isoform uniquely localizes to mitochondria, interacting with voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC) to evade apoptosis and promote cell survival, making it a potential therapeutic target in oncology.
Antibodies against HK2 are essential tools for studying its expression, subcellular localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to assess HK2 levels in cancer models, metabolic studies, and drug development research. Commercial HK2 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice using peptide antigens derived from conserved regions of the human HK2 protein. Validation often includes knockout cell lines or tissue-specific expression patterns to confirm specificity. Researchers also employ these antibodies to explore HK2’s role in diseases beyond cancer, such as diabetes and cardiovascular disorders, where metabolic dysregulation is implicated. Reliable HK2 antibodies thus serve as critical reagents for advancing understanding of cellular metabolism and targeted therapies.
×