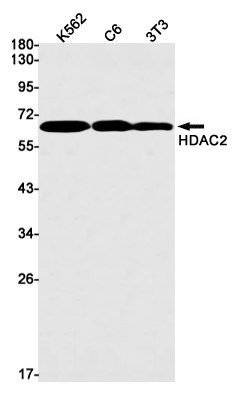
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
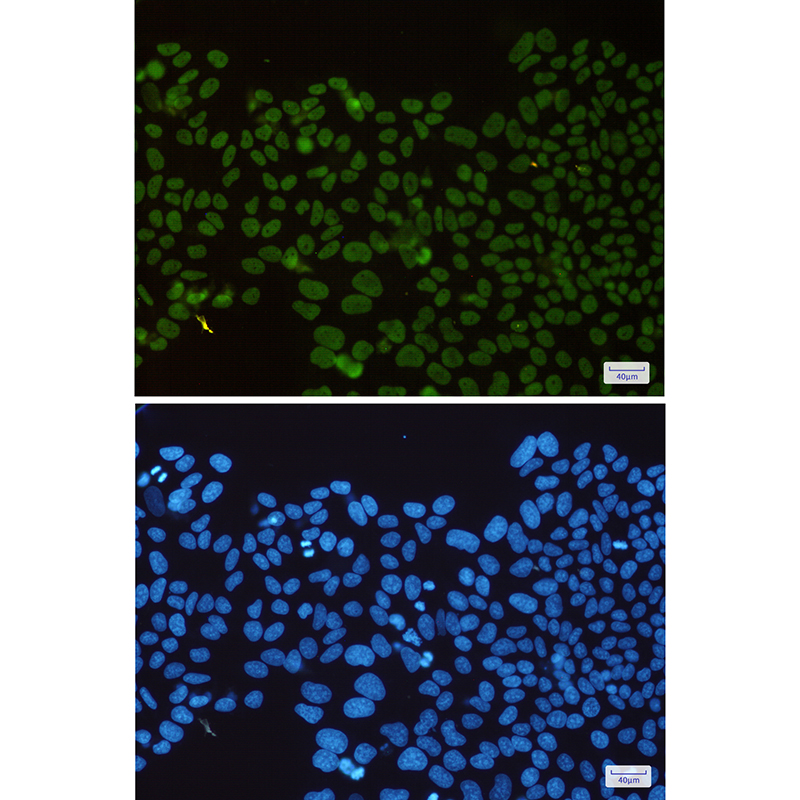
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
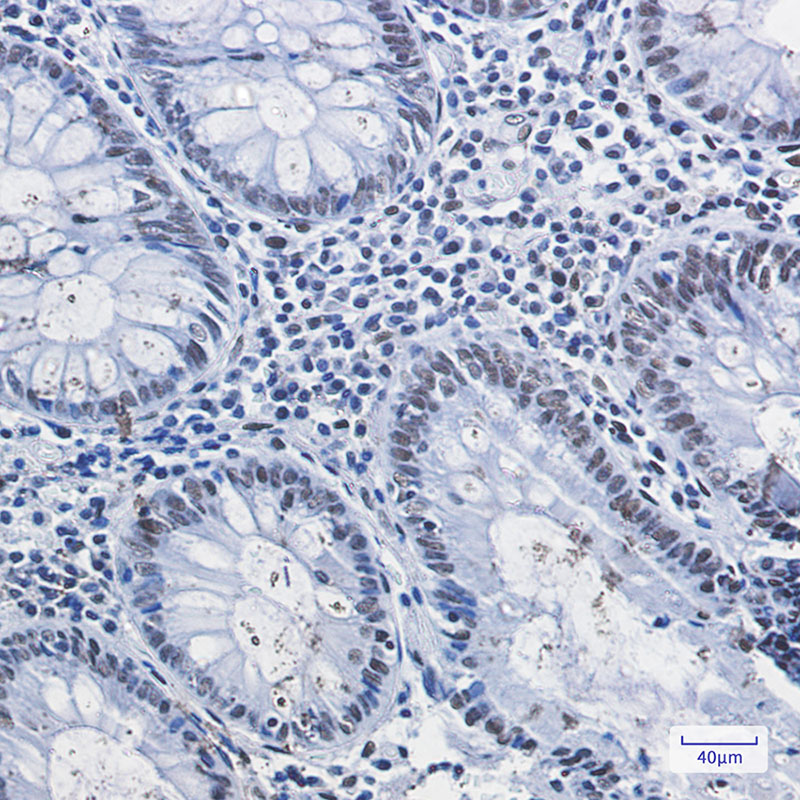
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HDAC2; Histone deacetylase 2; HD2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3066 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 55 kDa; Observed MW: 60 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human HDAC2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HDAC2抗体的3篇参考文献,简要概括作者及摘要内容:
1. **"HDAC2 regulates memory plasticity and histone acetylation"**
- **作者**: Guan JS, Haggarty SJ, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究通过HDAC2抗体分析发现,HDAC2特异性调控小鼠海马体神经元中的组蛋白乙酰化水平,抑制HDAC2可增强突触可塑性和长期记忆形成,提示其作为神经退行性疾病治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **"Roles of histone deacetylases in epigenetic regulation: emerging paradigms from studies with inhibitors"**
- **作者**: Marks PA, Dokmanovic M.
- **摘要**: 综述了HDAC家族(包括HDAC2)在癌症表观遗传调控中的作用,利用HDAC2抗体证实其在染色质重塑和基因沉默中的功能,并讨论HDAC抑制剂在肿瘤治疗中的应用机制。
3. **"HDAC2 blockade by nitric oxide and histone deacetylase inhibitors reveals a common target in Duchenne muscular dystrophy treatment"**
- **作者**: Colussi C, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究通过HDAC2抗体染色和ChIP实验,发现一氧化氮通过S-亚硝基化修饰抑制HDAC2活性,恢复肌肉细胞中抗萎缩基因的表达,为杜氏肌营养不良症提供了新的治疗策略。
4. **"Selective inhibition of HDAC2 by a small molecule reduces Aβ production and improves cognition in Alzheimer’s disease models"**
- **作者**: Gräff J, et al.
- **摘要**: 利用HDAC2特异性抗体及基因敲除技术,证明选择性抑制HDAC2可降低阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑内β-淀粉样蛋白沉积,并逆转突触功能障碍和认知损伤,提示其作为AD治疗靶点的重要性。
以上文献均涉及HDAC2抗体在机制研究或疾病模型中的应用,涵盖神经科学、癌症及遗传性疾病领域。
Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) is a member of the HDAC family, which plays a critical role in epigenetic regulation by removing acetyl groups from histone lysine residues. This activity promotes chromatin condensation, suppressing gene transcription. HDAC2 is involved in diverse cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, differentiation, apoptosis, and DNA repair. Dysregulation of HDAC2 has been linked to cancer, neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease), and cardiovascular diseases, making it a key therapeutic target.
HDAC2 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess protein levels in tissues or cultured cells. These antibodies help investigate HDAC2’s interactions with other proteins (e.g., transcription factors or chromatin remodelers) and its role in disease mechanisms. Specificity is critical, as HDAC isoforms share high sequence homology; thus, validated antibodies (monoclonal or polyclonal) with minimal cross-reactivity are preferred. Many commercial HDAC2 antibodies are raised against unique epitopes in its C-terminal region. Proper controls, such as HDAC2-knockout samples or siRNA-mediated knockdown, are recommended to confirm antibody specificity. HDAC2 inhibitors are under clinical investigation, further driving demand for reliable antibodies in preclinical research.
×