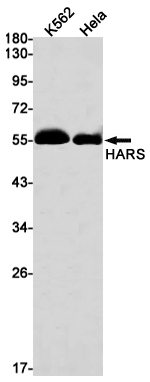
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HRS; CMT2W; USH3B |
| Entrez GeneID | 3035 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 57 kDa; Observed MW: 57 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human HARS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HARS(组氨酰-tRNA合成酶)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要总结:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to histidyl-tRNA synthetase in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy*
**作者**:Targoff IN, et al.
**摘要概述**:该研究首次报道了抗HARS抗体(抗-Jo-1抗体)与特发性炎症性肌病(如多发性肌炎/皮肌炎)的关联。研究发现,患者血清中的抗HARS抗体与间质性肺病、关节炎和“机械手”症状显著相关,提示其作为诊断标志物及疾病分型的价值。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-synthetase syndrome: a closer look at the heterogeneous clinical spectrum of anti-Jo-1 autoantibodies*
**作者**:Cavagna L, et al.
**摘要概述**:本文系统分析了抗HARS抗体(抗-Jo-1)在抗合成酶综合征(ASS)中的临床表现异质性。研究指出,该抗体不仅与肌肉炎症相关,还与肺部受累(如间质性肺炎)高度相关,强调了早期检测抗体对预后评估的重要性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Myositis-specific autoantibodies: biomarkers for idiopathic inflammatory myopathies*
**作者**:Satoh M, et al.
**摘要概述**:综述总结了HARS抗体在内的多种肌炎特异性自身抗体的临床意义。抗HARS抗体被归类为抗合成酶抗体的核心类型,其存在提示患者可能对抗免疫抑制剂治疗敏感,但肺部并发症风险较高。
---
(注:若需具体文献年份或期刊信息,可补充关键词进一步检索。)
**Background of HARS Antibodies**
HARS (histidyl-tRNA synthetase) antibodies are autoantibodies targeting histidyl-tRNA synthetase, an enzyme critical for charging tRNA with histidine during protein synthesis. These antibodies are primarily associated with antisynthetase syndrome (ASS), a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by interstitial lung disease (ILD), myositis, arthritis, and skin manifestations like mechanic’s hands. HARS antibodies, specifically anti-Jo-1 (the most common antisynthetase antibody), are detected in 15–30% of ASS patients, while non-Jo-1 antisynthetase antibodies (including anti-PL-7. PL-12. and others) are less frequent.
The presence of HARS antibodies aids in diagnosing ASS and predicts clinical phenotypes. For example, anti-Jo-1 is strongly linked to myositis and ILD comorbidity, whereas other antisynthetase antibodies may correlate with predominant lung involvement. Their formation is thought to arise from molecular mimicry, environmental triggers (e.g., viral infections), or genetic susceptibility (e.g., HLA-DRβ1 alleles). Detection methods include ELISA, immunoprecipitation, or line immunoassays.
Research highlights their role in disease monitoring, as antibody levels may fluctuate with disease activity. Despite therapeutic advances, ASS remains challenging to manage, emphasizing the importance of early antibody identification for tailored treatment and improved outcomes.
×