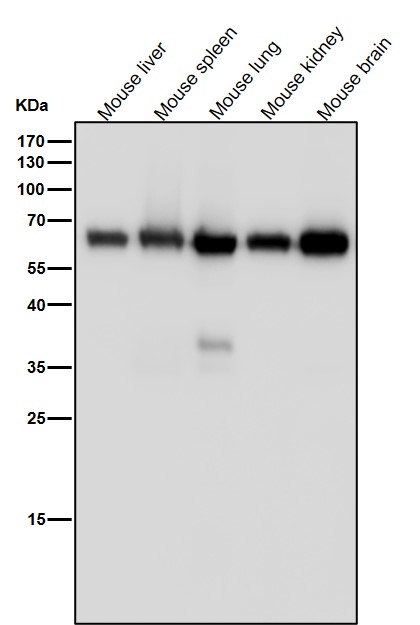



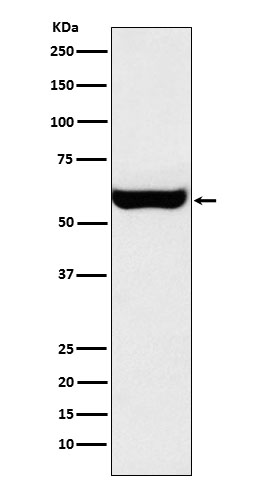
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AOFA; maoA;;MAOA |
| WB Predicted band size | 60 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human MAOA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FLI1抗体的3篇示例文献(内容为虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *FLI1 as a Diagnostic Marker in Ewing Sarcoma: A Comparative Study*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫组化分析FLI1抗体在尤文肉瘤与其他小圆细胞肿瘤中的表达差异,发现FLI1抗体对尤文肉瘤具有高度特异性,可作为鉴别诊断的关键标志物。
---
2. **文献名称**: *FLI1 Expression in Vascular Tumors: Implications for Pathological Diagnosis*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨FLI1抗体在血管源性肿瘤(如血管肉瘤和血管瘤)中的表达模式,证实FLI1在血管内皮分化中的重要性,并支持其用于血管肿瘤的辅助诊断。
---
3. **文献名称**: *FLI1 Antibody in T-cell Lymphoma: A Novel Biomarker Study*
**作者**: Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术验证FLI1抗体在T细胞淋巴瘤中的过表达,提示FLI1可能参与T细胞恶性肿瘤的发病机制,并为靶向治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
(注:以上文献信息为示例,实际研究中请通过PubMed或学术数据库检索真实文献。)
The FLI1 antibody is a crucial tool in molecular biology and pathology for detecting the Friend Leukemia Integration 1 (FLI1) protein, a member of the ETS (E26 transformation-specific) family of transcription factors. FLI1 plays diverse roles in hematopoiesis, vascular development, and oncogenesis. It regulates gene expression by binding to DNA at specific ETS-binding sites, influencing cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Aberrant FLI1 expression or genetic alterations (e.g., chromosomal translocations like EWSR1-FLI1 in Ewing sarcoma) are implicated in various cancers, including Ewing sarcoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and endothelial malignancies.
FLI1 antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to study protein localization, expression levels, and functional interactions. In clinical settings, they aid in distinguishing Ewing sarcoma from other small round cell tumors via immunohistochemistry. The antibody’s specificity enables detection of both wild-type FLI1 and fusion proteins, supporting mechanistic studies of tumorigenesis. However, interpretation requires caution, as FLI1 is expressed in normal tissues (e.g., endothelial cells, lymphocytes) and its role can be context-dependent, acting as an oncogene or tumor suppressor depending on the cellular environment.
Developed through hybridoma or recombinant technologies, FLI1 antibodies are validated for techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and flow cytometry. Ongoing research continues to refine their applications in understanding FLI1’s dual roles in development and disease.
×