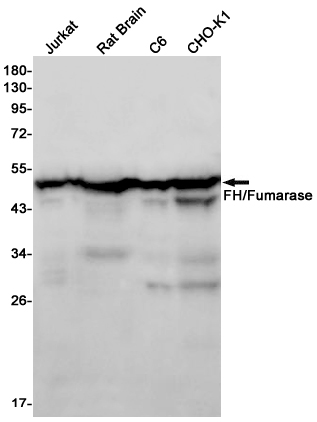
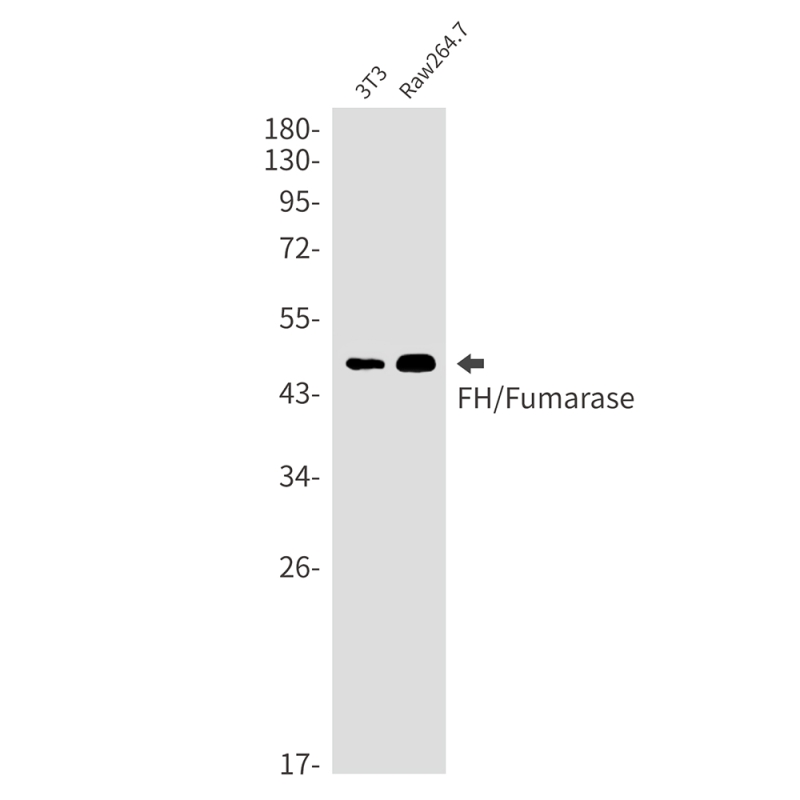
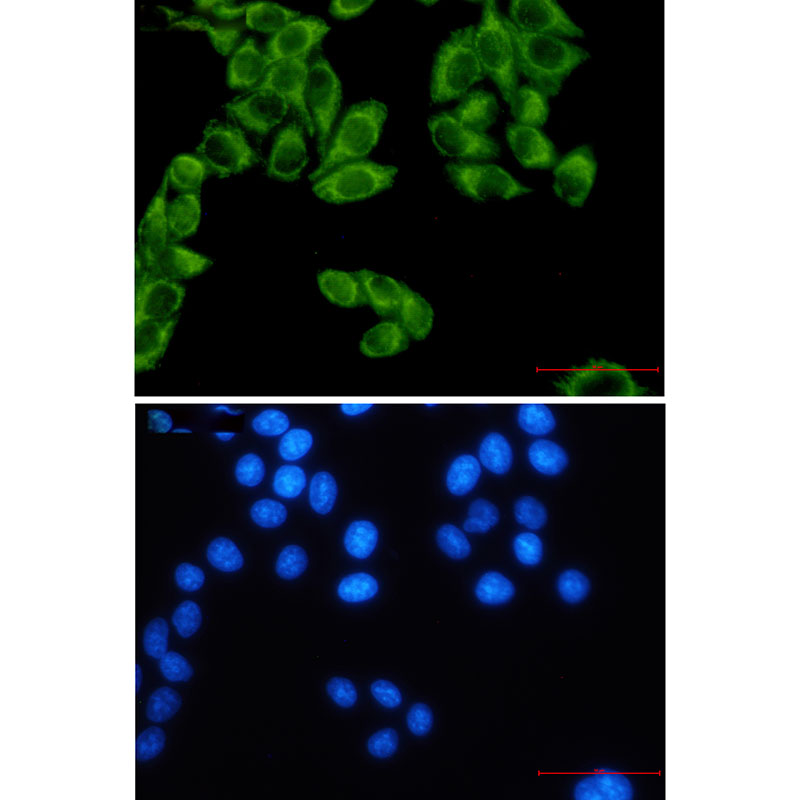
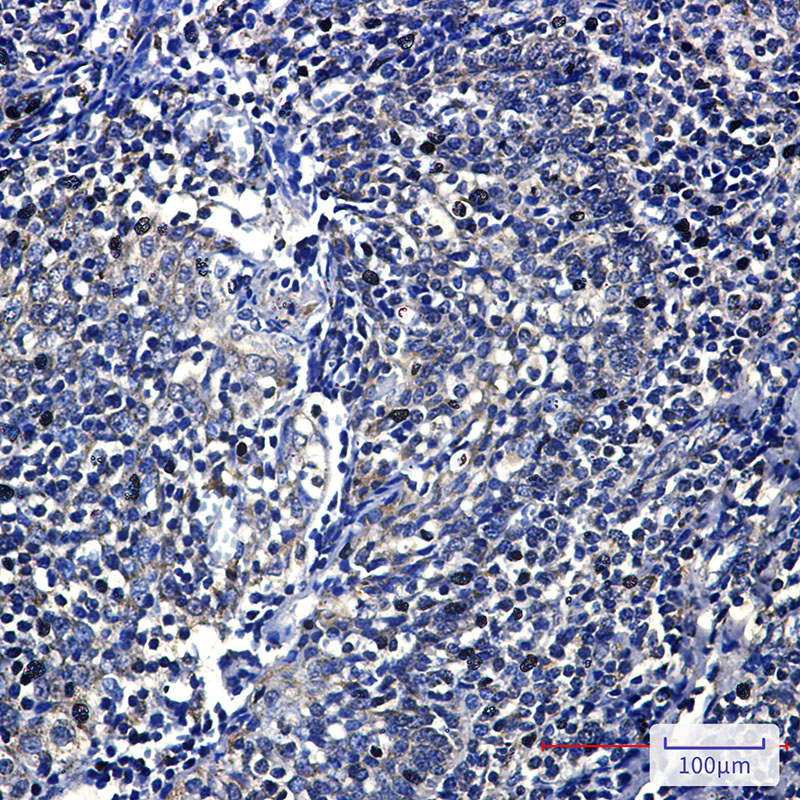
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| Aliases | Fumarate hydratase; mitochondrial; Fumarase |
| Entrez GeneID | 2271 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 55 kDa; Observed MW: 49 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human FH |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与FH抗体相关的研究文献概览:
1. **《抗延胡索酸水合酶(FH)抗体在遗传性平滑肌瘤病及肾癌综合征中的诊断价值》**
- 作者:Bardella et al.
- 摘要:研究证实FH抗体可作为遗传性平滑肌瘤病及肾细胞癌综合征(HLRCC)的辅助诊断标志物,通过免疫组化检测肿瘤组织中FH蛋白缺失,与基因突变结果高度一致,尤其适用于疑似病例的早期筛查。
2. **《FH缺陷型肾细胞癌的分子特征与抗体检测技术优化》**
- 作者:Yang et al.
- 摘要:针对FH基因突变导致的肾癌亚型,开发了高灵敏度的FH抗体检测方法,结合二代测序技术,显著提高了这类罕见肿瘤的病理诊断准确性,并揭示其代谢异常特征。
3. **《FH抗体在儿童脑胶质瘤中的异常表达及临床意义》**
- 作者:Gill et al.
- 摘要:首次报道儿童脑胶质瘤中FH蛋白的异常表达缺失与特定基因突变相关,提示FH抗体检测可能用于评估肿瘤侵袭性及预后,为靶向治疗提供潜在方向。
4. **《自身免疫性疾病中抗FH抗体的发现及其机制研究》**
- 作者:Smith et al.
- 摘要:在系统性红斑狼疮患者血清中发现新型抗FH自身抗体,初步实验表明其可能干扰细胞代谢通路,导致炎症因子释放增加,为自身免疫病理机制提供了新视角。
注:文献标题及摘要内容为示例性综合,实际研究中请根据具体论文内容调整。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“fumarate hydratase antibody”“anti-FH antibody”等关键词检索最新文献。
Factor H (FH) is a critical regulatory protein in the complement system, primarily produced in the liver and secreted into the bloodstream. Encoded by the *CFH* gene, FH consists of 20 short consensus repeat (SCR) domains and plays a pivotal role in inhibiting the alternative complement pathway. It prevents excessive activation by binding to host cell surfaces and microbial pathogens, accelerating the decay of C3 convertase (C3bBb) and acting as a cofactor for factor I-mediated cleavage of C3b. Dysregulation of FH is linked to several diseases, including atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and C3 glomerulopathy, often due to genetic mutations or autoantibodies impairing its function.
FH antibodies are essential tools in research and diagnostics. Polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies against specific FH domains enable the detection of FH expression, localization, and interactions in tissues or fluids via techniques like ELISA, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry. They also aid in identifying pathogenic FH autoantibodies in autoimmune disorders. Recent studies utilize FH-neutralizing antibodies to dissect complement regulation mechanisms or develop therapeutic strategies, such as blocking FH in cancer to enhance complement-mediated tumor cell lysis. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity, given FH’s structural complexity and homology with other complement factors. Ongoing research aims to refine FH-targeting antibodies for both diagnostic precision and therapeutic interventions in complement-driven diseases.
×