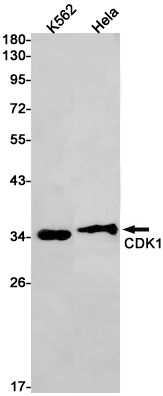
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IP | 1/10-1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CDK1; CDC2; CDC28A; CDKN1; P34CDC2; Cyclin-dependent kinase 1; CDK1; Cell division control protein 2 homolog; Cell division protein kinase 1; p34 protein kinase |
| Entrez GeneID | 983 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34 kDa; Observed MW: 34 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human CDK1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CDK1抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括列出:
1. **文献名称**:*"A monoclonal antibody specific for Cdc2 kinase (CDK1)"*
**作者**:Lee, M.G., & Nurse, P.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种针对CDK1蛋白的单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在人细胞中特异性识别CDK1的能力,并用于检测细胞周期不同阶段CDK1的表达水平变化,证实其与细胞周期调控的关联。
2. **文献名称**:*"CDK1 expression in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis"*
**作者**:Smith, J., et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(使用CDK1抗体)分析乳腺癌组织中CDK1的过表达情况,发现其与肿瘤分级、转移及预后不良显著相关,提示CDK1可能作为乳腺癌治疗的潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*"Functional characterization of CDK1 inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma using phospho-specific antibodies"*
**作者**:Wang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用针对CDK1及其磷酸化形式的抗体,揭示肝癌细胞中CDK1活性异常升高对细胞增殖的促进作用,并评估了CDK1抑制剂联合化疗的潜在疗效。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索获取具体信息。)
The cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), also known as cell division cycle protein 2 (CDC2), is a serine/threonine kinase critical for regulating cell cycle progression, particularly the G2/M transition and mitotic entry. It forms complexes with cyclins (e.g., cyclin B1) to phosphorylate substrates that drive mitotic events, such as nuclear envelope breakdown and chromosome segregation. Dysregulation of CDK1 is linked to genomic instability, uncontrolled proliferation, and cancer. CDK1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and activity in cell cycle research. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to detect CDK1 protein levels in cell lines, tissues, or clinical samples. Given its role in cancer, CDK1 is explored as a potential therapeutic target, and antibodies aid in validating its inhibition in preclinical models. Researchers also employ CDK1 antibodies to assess cell cycle arrest mechanisms in drug response studies or DNA damage scenarios. High-specificity CDK1 antibodies (e.g., monoclonal clones like POH-1) are validated using knockout cell lines to ensure minimal cross-reactivity with other CDKs. Their application extends to diagnostic research, where elevated CDK1 expression may serve as a biomarker for aggressive tumors.
×