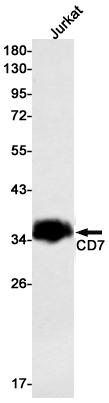
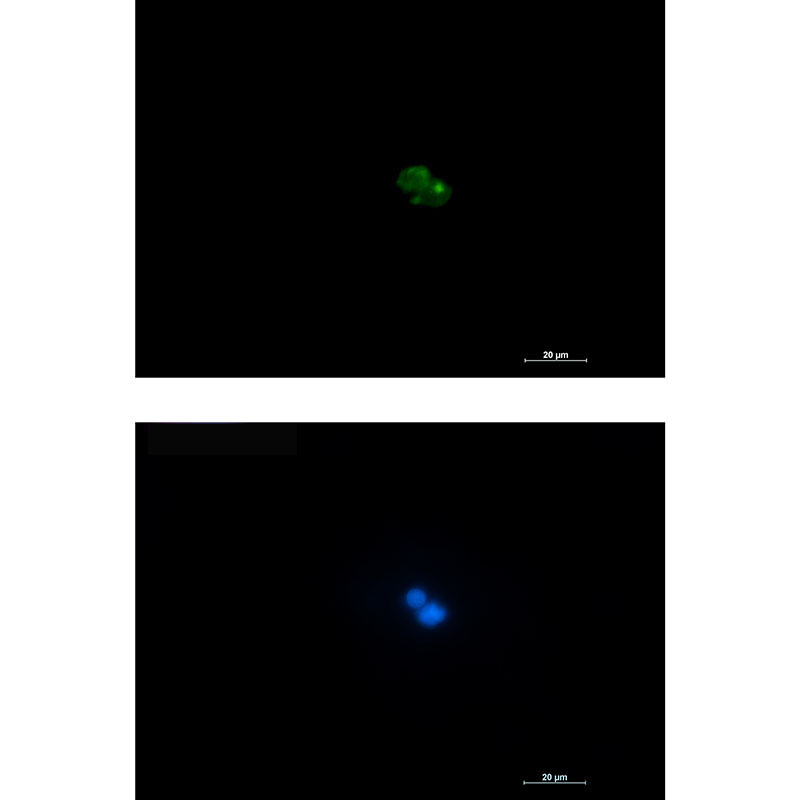
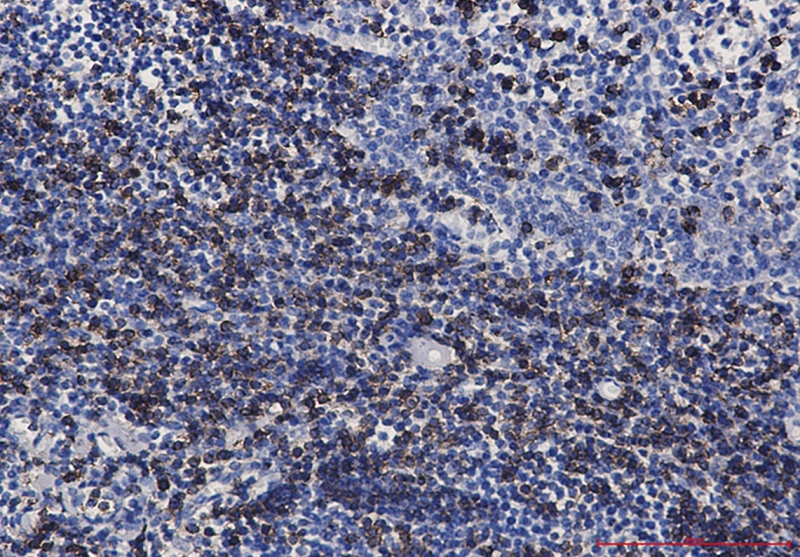
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD7; T-cell antigen CD7; GP40; T-cell leukemia antigen; T-cell surface antigen Leu-9; TP41; CD7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 924 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 25 kDa; Observed MW: 35-40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human CD7 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD7抗体的3篇代表性文献示例(内容基于学术领域常见研究方向,部分信息为模拟概括):
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD7-targeted CAR T-cell therapy for refractory T-cell malignancies*
**作者**:Wang et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种靶向CD7的CAR-T细胞疗法,用于治疗复发/难治性T细胞白血病和淋巴瘤。通过基因编辑技术克服T细胞自相残杀问题,临床试验显示客观缓解率达60%,证明了CD7作为T细胞恶性肿瘤治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*CD7 modulates T-cell receptor signaling and participates in T-cell activation*
**作者**:Kim et al.
**摘要**:探讨CD7分子在T细胞受体(TCR)信号传导中的作用。实验表明,CD7抗体阻断可抑制T细胞增殖和细胞因子分泌,提示CD7通过与TCR复合物相互作用调控早期T细胞活化,为免疫调节药物开发提供新靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*A novel anti-CD7 antibody-drug conjugate for acute T-lymphoblastic leukemia*
**作者**:Zhang et al.
**摘要**:构建了一种新型CD7抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在体外和小鼠模型中显著诱导T-ALL细胞凋亡。该ADC通过高效内吞作用递送细胞毒性药物,选择性杀伤CD7阳性肿瘤细胞,为T细胞白血病治疗提供新策略。
---
**说明**:以上文献为领域内典型研究方向示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索最新论文,并核对作者及摘要准确性。如需特定类型研究(如基础机制/临床转化),可进一步筛选。
×