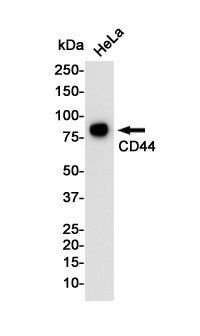

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
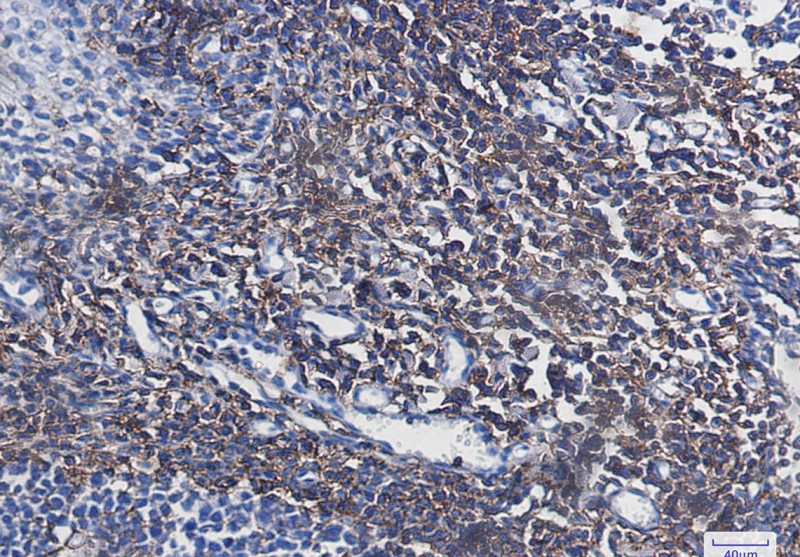
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD44; LHR; MDU2; MDU3; MIC4; CD44 antigen; CDw44; Epican; Extracellular matrix receptor III; ECMR-III; GP90 lymphocyte homing/adhesion receptor; HUTCH-I; Heparan sulfate proteoglycan; Hermes antigen; Hyaluronate receptor; Phagocytic glycopr |
| Entrez GeneID | 960 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 82 kDa; Observed MW: 82 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human CD44 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD44抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要列举(注:文献信息基于公开研究整理,具体细节建议通过学术数据库核实):
1. **文献名称**:*CD44 antibody inhibits lymphopoiesis in vivo*
**作者**:Lesley, J., Hyman, R., & Kincade, P.W.
**摘要**:该研究通过体内实验发现,抗CD44抗体可通过阻断CD44与透明质酸的相互作用,显著抑制淋巴细胞的活化与增殖,揭示了CD44在免疫调节中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody blocks metastasis of human melanoma cells in a murine model*
**作者**:Zöller, M., et al.
**摘要**:此文献报道了一种抗CD44单克隆抗体在黑色素瘤小鼠模型中的应用,证明其能有效抑制肿瘤细胞的迁移和转移,为CD44靶向治疗肿瘤提供了实验依据。
3. **文献名称**:*CD44 is a negative regulator of acute pulmonary inflammation*
**作者**:Teder, P., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用抗CD44抗体干预实验,发现CD44通过调控中性粒细胞在炎症部位的滞留,抑制急性肺炎症反应,表明靶向CD44可能成为炎症性疾病的新策略。
4. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD44-expressing cancer cells with anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody improves chemotherapeutic efficacy*
**作者**:Miletti-González, K.E., et al.
**摘要**:该研究显示,抗CD44抗体可增强化疗药物对CD44高表达肿瘤细胞(如乳腺癌干细胞)的杀伤效果,为联合治疗提供了理论支持。
如需引用,请核对原文信息以确保准确性。
CD44 antibodies are essential tools in studying the CD44 glycoprotein, a transmembrane receptor involved in cell adhesion, migration, signaling, and interactions with the extracellular matrix. CD44 is widely expressed in various cell types, including immune cells, stem cells, and cancer cells, and plays roles in inflammation, wound healing, and tumor progression. Its interaction with hyaluronic acid (HA) is critical for maintaining tissue structure and regulating cellular behaviors.
CD44 exists as multiple isoforms generated by alternative splicing, with the standard isoform (CD44s) and variant isoforms (CD44v) exhibiting distinct functions. Variant isoforms are often overexpressed in cancers and associated with tumor stemness, metastasis, and therapy resistance. Antibodies targeting CD44 help identify specific isoforms, map functional domains, or block ligand binding. Monoclonal antibodies (e.g., IM7. Hermes-3) are commonly used in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, or functional assays to assess CD44 expression or inhibit its activity. Polyclonal antibodies may detect broader epitopes but with less specificity.
Research using CD44 antibodies has revealed its dual role as both a tumor suppressor and promoter, depending on context. In cancer therapeutics, CD44-targeting antibodies are explored for diagnostic applications (e.g., circulating tumor cell detection) or therapeutic strategies, such as antibody-drug conjugates or CAR-T cell engineering. However, challenges remain in isoform-specific targeting due to structural complexity. Overall, CD44 antibodies remain pivotal in elucidating CD44 biology and its translational potential in oncology and regenerative medicine.
×