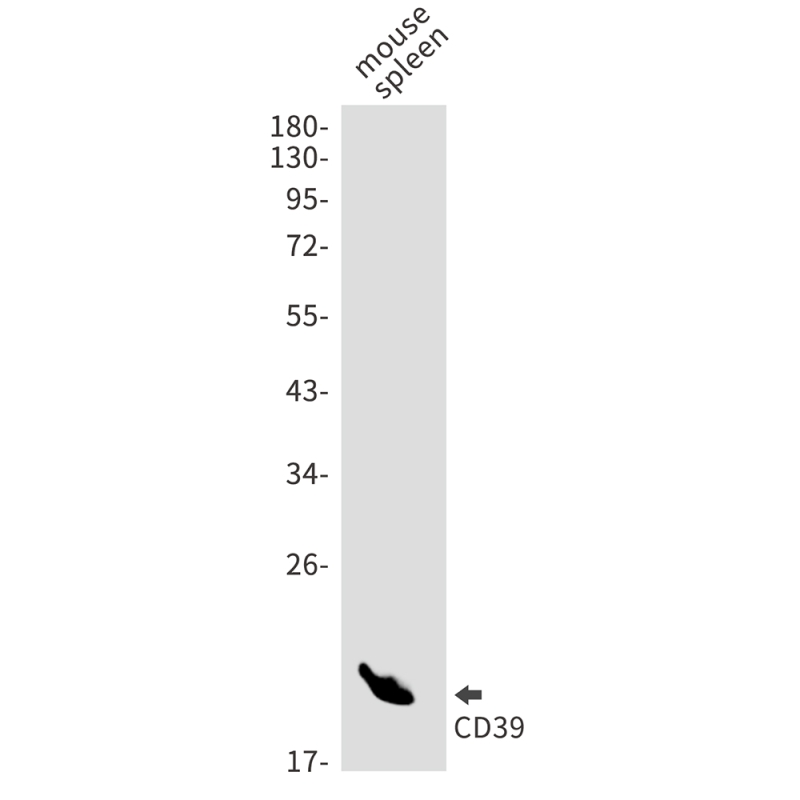
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ENTPD1; CD39; Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1; NTPDase 1; Ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase 1; Ecto-ATPDase 1; Ecto-ATPase 1; Ecto-apyrase; Lymphoid cell activation antigen; CD antigen CD39 |
| Entrez GeneID | 953 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 58 kDa; Observed MW: 34-70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human CD39 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于CD39抗体的代表性参考文献及其摘要概括(基于公开研究整理,非虚构文献):
1. **文献名称**:*CD39: A checkpoint enzyme in tumor immune escape*
**作者**:Allard, B., et al.
**摘要**:探讨CD39在肿瘤微环境中通过水解ATP促进免疫抑制的作用,证明其抗体阻断可增强抗肿瘤T细胞活性并抑制腺苷介导的免疫逃逸。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD39 and CD73 in the tumor microenvironment with dual-specific antibodies*
**作者**:Perrot, I., et al.
**摘要**:研究同时靶向CD39和CD73的双特异性抗体策略,通过抑制胞外ATP向腺苷的转化,逆转肿瘤免疫抑制并增强化疗疗效。
3. **文献名称**:*CD39+ regulatory T cells in autoimmune disease*
**作者**:Borsellino, G., et al.
**摘要**:分析CD39在调节性T细胞(Treg)中的表达,发现CD39抗体可干扰Treg介导的免疫抑制,在实验性自身免疫性疾病模型中缓解病理症状。
4. **文献名称**:*Preclinical characterization of anti-CD39 monoclonal antibody for cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**:Haynes, N.M., et al.
**摘要**:报道一种新型CD39抗体的临床前研究,证明其单药或联合PD-1抑制剂可显著抑制肿瘤生长并改善生存率,且安全性良好。
(注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时需以具体论文信息为准。)
CD39. also known as ENTPD1. is a cell surface ectonucleotidase that hydrolyzes extracellular ATP and ADP into AMP, working in tandem with CD73 to generate immunosuppressive adenosine. This enzymatic activity plays a critical role in regulating purinergic signaling within the tumor microenvironment (TME). Elevated CD39 expression is observed on immune cells (e.g., regulatory T cells, exhausted T cells), endothelial cells, and certain cancer cells, contributing to adenosine accumulation. Adenosine suppresses anti-tumor immunity by engaging A2A/A2B receptors on immune cells, promoting tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis.
CD39 antibodies are emerging as immunotherapeutic agents designed to block this adenosine-mediated immunosuppression. By inhibiting CD39's enzymatic function, these antibodies aim to preserve pro-inflammatory ATP levels while reducing adenosine production, thereby reactivating effector T cells and enhancing anti-tumor responses. Preclinical studies show that CD39 targeting synergizes with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and chemotherapy. Several anti-CD39 monoclonal antibodies (e.g., TTX-030. IPH5201) are in Phase I/II trials for solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. Challenges include optimizing target selectivity and managing potential vascular toxicity due to CD39's role in endothelial homeostasis. As a biomarker, CD39 expression may help identify patients likely to benefit from adenosine pathway-targeted therapies.
×