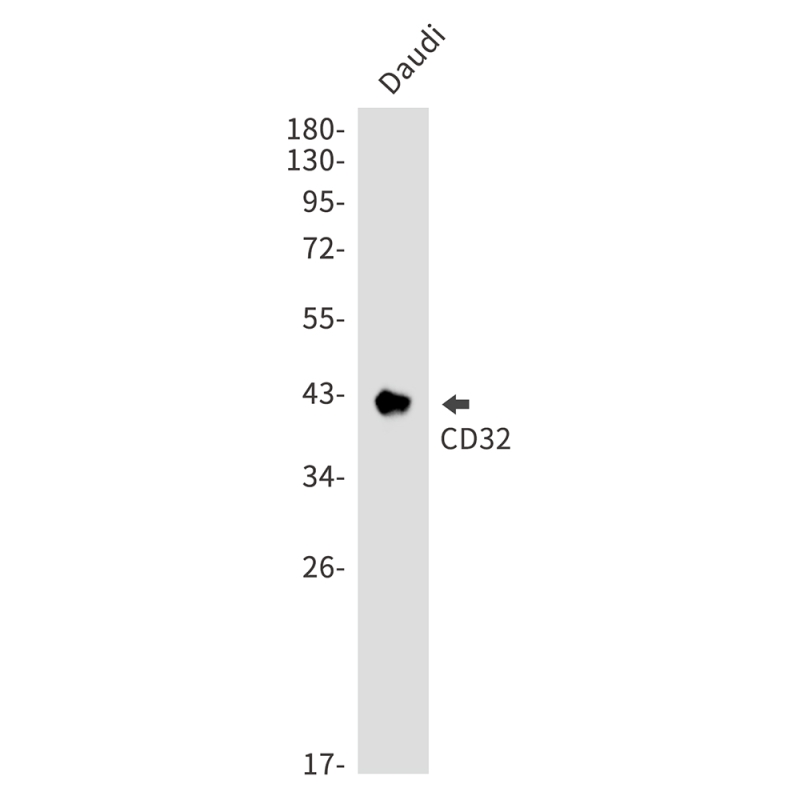
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FCGR2A; CD32; FCG2; FCGR2A1; IGFR2; Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor II-a; IgG Fc receptor II-a; CDw32; Fc-gamma RII-a; Fc-gamma-RIIa; FcRII-a; CD32 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2212 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 35 kDa; Observed MW: 35-42 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human CD32 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD32抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Human IgG Fc receptor heterogeneity: molecular aspects and clinical implications"*
**作者**:van de Winkel, J.G., Capel, P.J.
**摘要**:该综述详细阐述了CD32(FcγRII)的结构、功能及其在免疫调节中的作用,重点讨论了其在炎症和自身免疫疾病中与IgG结合的分子机制。
2. **文献名称**:*"Specificity and affinity of human Fcγ receptors and their polymorphic variants for human IgG subclasses"*
**作者**:Bruhns, P., et al.
**摘要**:通过系统实验分析CD32与其他Fcγ受体的结合特性,揭示了不同单克隆抗体对CD32亚型(如CD32A和CD32B)的选择性差异,为靶向治疗提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*"Fcγ receptors as regulators of immune responses"*
**作者**:Nimmerjahn, F., Ravetch, J.V.
**摘要**:探讨CD32B在维持免疫耐受中的作用,证明其通过抑制B细胞过度活化参与自身免疫疾病调控,为开发CD32靶向疗法奠定理论基础。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar按标题检索原文。
CD32 antibodies target CD32 (cluster of differentiation 32), a family of surface receptors known as FcγRII that bind the Fc region of immunoglobulin G (IgG). CD32 receptors are part of the immunoglobulin superfamily and play critical roles in immune regulation. They are expressed on various immune cells, including B cells, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and platelets. Three main isoforms exist in humans (CD32A, CD32B, and CD32C), each with distinct functions. CD32A (FcγRIIA) activates immune responses by transmitting activating signals through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs). In contrast, CD32B (FcγRIIB), containing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), suppresses B-cell activation and antibody production to prevent hyperimmune reactions. CD32C (FcγRIIC) has limited expression and unclear functional significance.
CD32 antibodies are widely used in research to study immune cell interactions, receptor distribution, and signaling pathways. They are employed in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional assays to investigate autoimmune diseases, infections, and cancer. For instance, CD32B-targeting antibodies are explored in therapies to modulate immune responses in conditions like lupus or lymphoma. Pathogens, such as HIV, may exploit CD32 receptors for cell entry, highlighting their relevance in infectious disease studies. Variability in CD32 isoforms and genetic polymorphisms (e.g., CD32A-H/R131) influence disease susceptibility and therapeutic responses, underscoring the importance of isoform-specific antibodies in precision research.
×