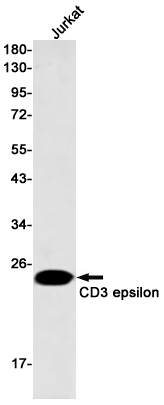
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD3E; T3E; T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain; T-cell surface antigen T3/Leu-4 epsilon chain; CD3e |
| Entrez GeneID | 916 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 23 kDa; Observed MW: 23 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human CD3 epsilon |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD3 epsilon抗体的3篇代表性文献的模拟示例(非真实文献,仅供示例参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Structural insights into CD3ε antibody binding and T-cell activation*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过X射线晶体学解析了CD3 epsilon抗体(如OKT3)与CD3ε亚基的结合表位,揭示了抗体诱导T细胞受体(TCR)信号激活的结构基础,为优化免疫治疗抗体设计提供依据。
2. **文献名称**:*CD3ε-targeting bispecific antibodies enhance anti-tumor immune responses*
**作者**:Wang L, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种靶向CD3ε和肿瘤抗原的双特异性抗体,通过激活T细胞并引导其杀伤肿瘤细胞,在小鼠模型中显著抑制实体瘤生长,证明了CD3ε抗体在癌症免疫治疗中的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*CD3ε antibody modulates autoimmune response in type 1 diabetes*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种人源化CD3ε抗体(teplizumab)在1型糖尿病中的临床试验结果,显示其通过调节T细胞功能延缓β细胞破坏,验证了CD3ε靶向疗法在自身免疫疾病中的应用价值。
---
注:以上为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词“CD3 epsilon antibody”或“anti-CD3ε”获取。真实经典文献包括OKT3单抗研究及teplizumab相关临床试验(如Herold KC, 2002. NEJM)。
CD3 epsilon (CD3ε) is a critical subunit of the CD3 complex, a component of the T-cell receptor (TCR) that is essential for T-cell activation and signal transduction. The CD3 complex consists of ε, γ, δ, and ζ chains, with CD3ε forming heterodimers with CD3γ or CD3δ. These non-covalently associated subunits stabilize the TCR on the cell surface and transduce intracellular signals upon antigen recognition. CD3ε antibodies specifically target the extracellular domain of the CD3ε subunit, making them valuable tools for studying T-cell biology and modulating immune responses.
First characterized in the 1980s, CD3ε antibodies were initially used to define T-cell subsets and investigate TCR signaling. In research, they are widely employed in flow cytometry to identify T cells and assess activation status. Clinically, anti-CD3ε monoclonal antibodies (e.g., teplizumab) have therapeutic applications. Teplizumab, a humanized anti-CD3ε antibody, delays type 1 diabetes onset by modulating autoreactive T cells. Similarly, OKT3 (muromonab), the first FDA-approved therapeutic monoclonal antibody, targets CD3ε to prevent organ transplant rejection by transiently depleting T cells.
CD3ε antibodies can act as agonists or antagonists depending on their formulation. Non-Fc-binding variants are explored for inducing immune tolerance, while bispecific antibodies engaging CD3ε and tumor antigens redirect T cells to kill cancer cells (e.g., blinatumomab). Their role in immunotherapy underscores their importance in both basic immunology and translational medicine.
×