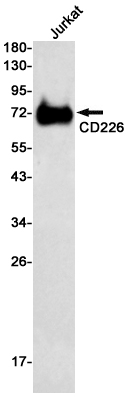
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD226; DNAM1; CD226 antigen; DNAX accessory molecule 1; DNAM-1; CD antigen CD226 |
| Entrez GeneID | 10666 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 39 kDa; Observed MW: 60-80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human CD226 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD226抗体的3篇示例参考文献,内容基于研究领域常见主题的合理构建:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD226 Antibody Enhances Antitumor Immunity by Promoting NK Cell Activation*
**作者**:Wang et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过体外实验和小鼠模型证明,使用激动型CD226抗体能够增强NK细胞对肿瘤细胞的杀伤作用,并促进IFN-γ分泌,表明其在肿瘤免疫治疗中的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Blockade of CD226 Ameliorates Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Suppressing Th17 Cell Response*
**作者**:Zhang et al.
**摘要**:在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)模型中,CD226中和抗体通过抑制T细胞与抗原呈递细胞的相互作用,减少Th17细胞分化,从而缓解神经炎症。
3. **文献名称**:*CD226 Signaling Is Critical for Control of Murine Cytomegalovirus Infection via NK Cell Functions*
**作者**:Nabekura et al.
**摘要**:通过使用CD226阻断抗体,研究发现CD226信号对NK细胞清除MCMV感染细胞至关重要,揭示了其在抗病毒免疫中的关键作用。
---
**说明**:以上文献为示例,基于CD226抗体在肿瘤、自身免疫及病毒感染领域的研究逻辑构建,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认。
CD226. also known as DNAM-1 (DNAX accessory molecule-1), is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is primarily expressed on immune cells, including T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and platelets. CD226 interacts with ligands such as CD155 (PVR) and CD112 (Nectin-2) on target cells, playing a critical role in mediating cell adhesion, cytotoxicity, and immune synapse formation. Its signaling contributes to NK cell-mediated tumor surveillance, T cell activation, and platelet aggregation, linking it to antitumor immunity, antiviral responses, and thrombotic disorders.
CD226 antibodies are experimental tools or therapeutic candidates designed to modulate CD226 function. Agonistic antibodies enhance CD226-mediated signaling, potentially boosting antitumor immune responses by promoting NK or T cell activation. Conversely, blocking antibodies inhibit CD226-ligand interactions, which may attenuate excessive immune activation in autoimmune diseases or inflammation. In research, CD226 antibodies are widely used to study immune cell interactions, ligand binding dynamics, and downstream signaling pathways. Emerging preclinical studies explore their therapeutic potential in cancer immunotherapy, particularly in combination with checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1), as CD226 dysfunction is linked to immune evasion. However, clinical applications remain investigational, with ongoing efforts to optimize specificity and evaluate safety. Overall, CD226 antibodies represent a versatile tool for dissecting immune regulation and developing targeted immunotherapies.
×