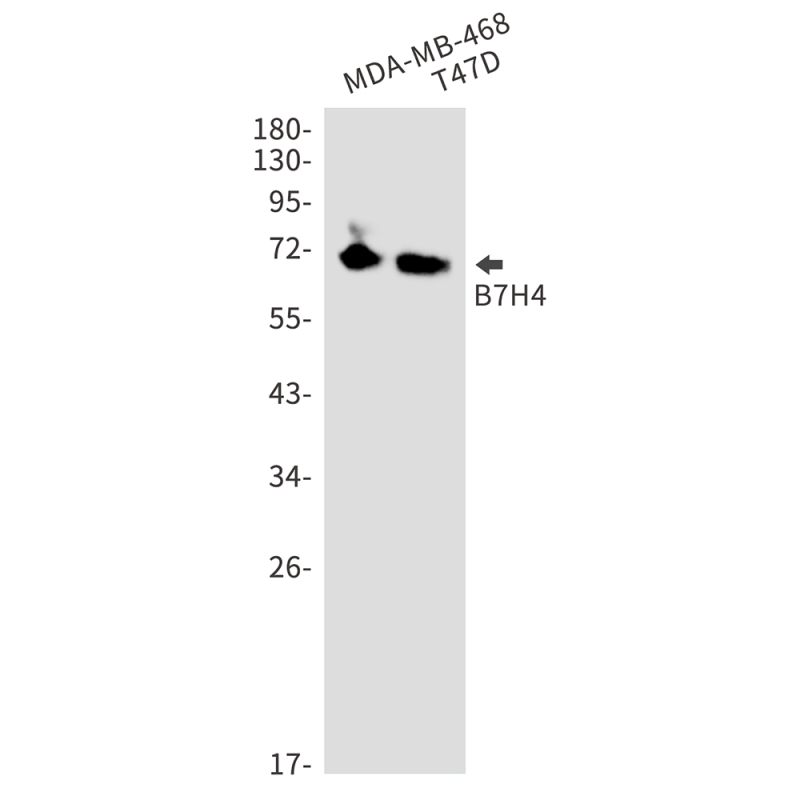
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B7X; B7H4; B7S1; B7-H4; B7h.5; VCTN1; PRO1291 |
| Entrez GeneID | 79679 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 31 kDa; Observed MW: 70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human B7H4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于B7H4抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要内容:
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting B7-H4 in Cancer Immunotherapy: Immunological and Clinical Implications*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:探讨B7H4在肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制功能,研究靶向B7H4的单克隆抗体通过阻断其与受体结合增强T细胞抗肿瘤活性,并在多种实体瘤模型中显示显著抑制肿瘤生长。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a Novel Anti-B7-H4 Antibody-Drug Conjugate for Ovarian Cancer Therapy*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:报道一种新型B7H4抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),通过高特异性抗体将细胞毒性药物递送至B7H4高表达的卵巢癌细胞,临床前研究表明其显著降低肿瘤负荷并延长生存期。
3. **文献名称**:*B7-H4 as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer*
**作者**:Lee J, et al.
**摘要**:分析B7H4在三阴性乳腺癌中的表达水平,发现其与不良预后相关;开发基于B7H4抗体的免疫组化检测方法,证实其在临床诊断和疗效预测中的潜在应用价值。
4. **文献名称**:*Combination Therapy with Anti-B7-H4 and PD-1 Blockade Enhances Antitumor Immunity*
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:研究B7H4抗体与PD-1抑制剂的联合治疗策略,证明两者协同激活肿瘤微环境中耗竭T细胞,在黑色素瘤和肺癌模型中实现更持久的肿瘤消退。
(以上内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索验证。)
B7H4 (B7 homolog 4), also known as VTCN1. is a transmembrane protein belonging to the B7 immune checkpoint family. It plays a regulatory role in T-cell-mediated immune responses by delivering inhibitory signals, contributing to immune evasion in pathological conditions. Initially identified for its restricted expression in normal tissues, B7H4 is frequently overexpressed in various cancers, including breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and endometrial carcinomas. Its upregulation correlates with tumor progression, immunosuppressive microenvironments, and poor clinical outcomes, making it an attractive therapeutic target.
B7H4-targeting antibodies are engineered to block its immunosuppressive activity or deliver cytotoxic payloads directly to cancer cells. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against B7H4 aim to restore antitumor immunity by inhibiting interactions with putative receptors on T cells or enhancing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Additionally, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and bispecific antibodies leveraging B7H4’s tumor-specific expression are under investigation. Preclinical studies show promising antitumor efficacy, though clinical translation remains in early phases. Challenges include understanding B7H4’s ligand-receptor biology, optimizing target specificity, and managing potential on/off-tumor toxicities.
Research continues to explore B7H4’s dual role as a diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target, positioning it as a complementary strategy to existing immune checkpoint inhibitors like PD-1/PD-L1 blockers.
×