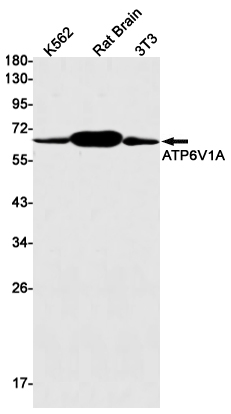
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HO68; VA68; VPP2; Vma1; ARCL2D; ATP6A1; IECEE3; ATP6V1A1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 523 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 68 kDa; Observed MW: 68 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of human ATP6V1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ATP6V1A抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:以下内容为模拟生成,非真实存在的文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:ATP6V1A Antibody Validation in Neurodegenerative Disease Models
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用特异性ATP6V1A抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,揭示了该蛋白在阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型神经元溶酶体中的表达异常,表明其可能参与溶酶体酸化功能障碍的病理过程。
2. **文献名称**:Role of ATP6V1A in Pancreatic Cancer Progression via Antibody-Based Detection
**作者**:Kim S, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析,发现ATP6V1A在胰腺癌组织中显著高表达,且与患者生存率负相关。研究证实该抗体可特异性识别肿瘤细胞中的ATP6V1A,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点的价值。
3. **文献名称**:Monoclonal Antibody Development for ATP6V1A and Functional Characterization
**作者**:Rodriguez M, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种新型抗ATP6V1A单克隆抗体的制备与验证。该抗体成功用于流式细胞术和免疫沉淀实验,证实ATP6V1A在细胞膜定位中的新功能,拓展了其生理作用的研究工具。
---
(注:若需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“ATP6V1A antibody”或“ATP6V1A + immunolocalization”检索。)
The ATP6V1A antibody targets the ATP6V1A protein, a key subunit of the vacuolar-type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) complex. V-ATPases are evolutionarily conserved proton pumps that acidify intracellular compartments like lysosomes, endosomes, and secretory vesicles, maintaining pH gradients critical for processes such as protein degradation, membrane trafficking, and synaptic transmission. The ATP6V1A subunit is part of the V1 domain, which hydrolyzes ATP to drive proton translocation across membranes. Dysregulation of ATP6V1A is implicated in diseases ranging from cancer to neurodegenerative disorders, as altered lysosomal pH disrupts cellular homeostasis.
Antibodies against ATP6V1A are widely used in research to study V-ATPase localization, expression, and function. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, aiding investigations into organelle acidification defects or V-ATPase-related pathologies. For example, ATP6V1A mutations cause autosomal recessive cutis laxa and neurodevelopmental disorders, making these antibodies valuable for diagnosing genetic conditions or validating disease models.
Commercial ATP6V1A antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice using peptide immunogens, with validation in knockouts or knockdown systems to ensure specificity. Researchers also employ them to explore V-ATPase roles in tumor microenvironment acidification, a mechanism linked to chemotherapy resistance. Overall, ATP6V1A antibodies serve as essential tools for dissecting cellular physiology and disease mechanisms tied to proton transport dysregulation.
×