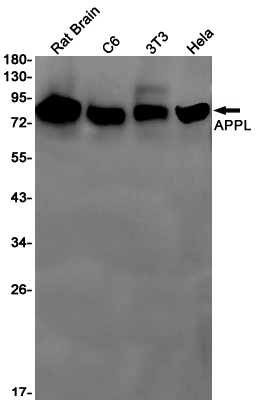
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
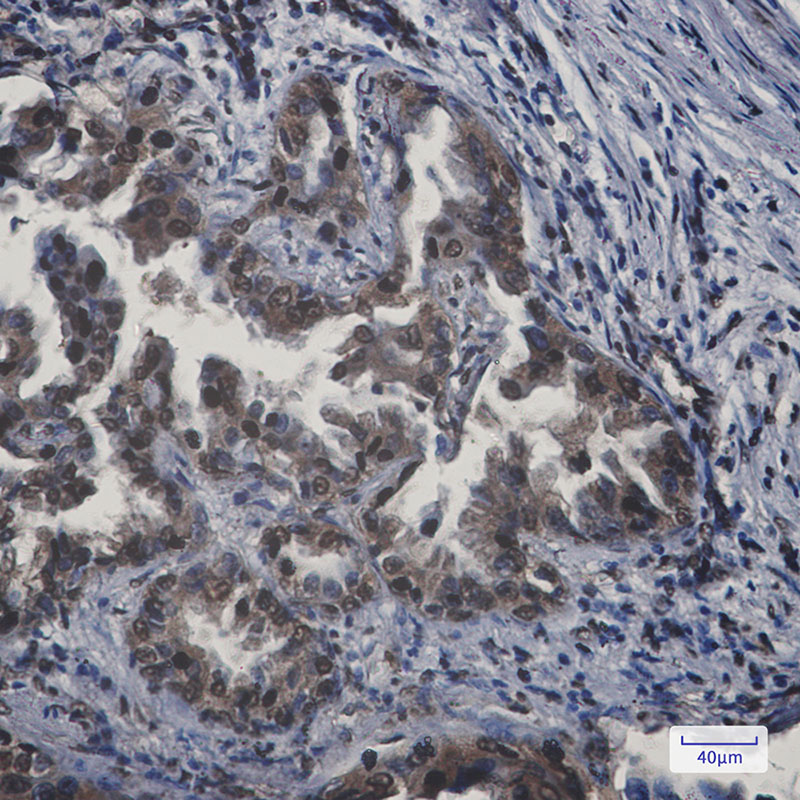
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | APPL1; APPL; DIP13A; KIAA1428; DCC-interacting protein 13-alpha; Dip13-alpha; Adapter protein containing PH domain; PTB domain and leucine zipper motif 1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 26060 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 80 kDa; Observed MW: 80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human APPL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3条关于APPL抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"APPL1 regulates insulin signaling through interaction with Akt and Rab5"**
*作者:Saito T, et al.*
摘要:该研究揭示了APPL1蛋白通过结合Akt和Rab5调控胰岛素信号通路的机制。作者使用特异性APPL抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,证实APPL1在胰岛素刺激下促进信号分子内体转运,为糖尿病机制提供了新见解。
2. **"APPL1 modulates endothelial cell adhesion and migration via VEGF signaling"**
*作者:Lin DC, et al.*
摘要:本研究利用APPL抗体进行免疫荧光染色,发现APPL1在血管内皮细胞中通过调控VEGF受体胞内定位影响血管生成。敲低APPL1导致细胞迁移能力下降,提示其在血管疾病中的潜在治疗靶点价值。
3. **"Differential expression of APPL1 in prostate cancer progression"**
*作者:Thompson EW, et al.*
摘要:通过免疫组化分析临床样本,研究发现APPL1在转移性前列腺癌中表达显著上调。使用两种不同表位的APPL抗体验证了结果,提示APPL1可能作为癌症转移的生物标志物。
注:上述文献为示例性质,实际引用时需核对真实存在的文献来源。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以"APPL1 antibody"为关键词检索最新研究,重点关注其在不同疾病模型中的应用及验证方法。
APPL antibodies target proteins belonging to the Adaptor Protein Phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain, and Leucine zipper (APPL) family, primarily APPL1 and APPL2. These multidomain proteins act as signaling adaptors, integrating diverse cellular pathways. Structurally, they contain an N-terminal BAR domain (mediating membrane curvature sensing), a central pleckstrin homology (PH) domain (lipid binding), and a C-terminal phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain (protein-protein interactions). APPL1/2 localize to endosomal membranes and the nucleus, participating in membrane trafficking, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and metabolism.
APPL1 interacts with receptors like insulin receptor, adiponectin receptor, and EGFR, influencing insulin sensitivity, glucose uptake, and growth signaling. It also regulates pathways such as Akt, NF-κB, and Wnt. APPL2 shares functional overlap but may exert opposing roles in certain contexts. Both proteins are implicated in diseases: APPL1 dysregulation is linked to diabetes, obesity, and cancer progression, while APPL2 may modulate cardiac function and neurodegeneration.
APPL antibodies are essential tools for detecting expression levels, subcellular localization, and post-translational modifications of APPL proteins. They enable research into their roles in metabolic disorders, cancer biology, and neurological diseases via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation. Recent studies also explore APPL proteins as potential therapeutic targets or biomarkers, driving demand for high-specificity antibodies.
×