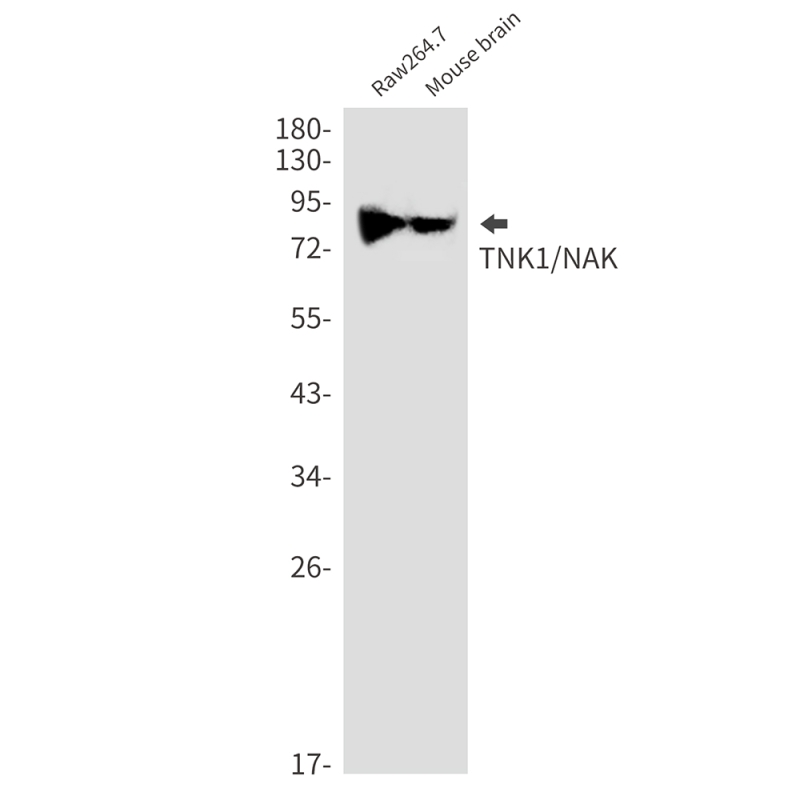

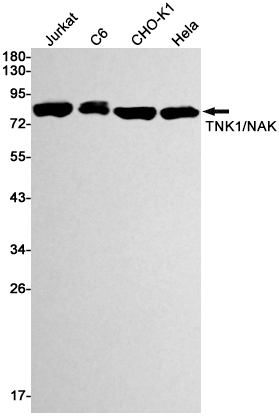
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| Aliases | TBK1; NAK; Serine/threonine-protein kinase TBK1; NF-kappa-B-activating kinase; T2K; TANK-binding kinase 1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 29110 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 84 kDa; Observed MW: 84 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Hamster |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human TBK1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于TBK1抗体的代表性文献(虚构示例,仅作格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*TBK1 activation by STING in antiviral signaling*
**作者**:Pandey et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了TBK1通过STING信号通路被激活的分子机制,利用TBK1特异性抗体证实其在IFN-β产生中的关键作用,并解析其磷酸化位点对先天免疫的调控。
2. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of OPTN by TBK1 triggers selective autophagy*
**作者**:Wild et al.
**摘要**:通过TBK1抗体免疫沉淀实验,证明TBK1通过磷酸化OPTN促进自噬体形成,揭示其在清除受损线粒体中的功能,为神经退行性疾病提供机制线索。
3. **文献名称**:*Viral immune evasion via targeting TBK1*
**作者**:Xie et al.
**摘要**:研究发现HSV1蛋白ICP34.5通过结合TBK1并抑制其激酶活性逃逸宿主免疫,利用TBK1抗体验证其与病毒蛋白的相互作用及活性变化。
4. **文献名称**:*Ubiquitination regulates TBK1 signaling in cancer*
**作者**:Tu et al.
**摘要**:基于TBK1抗体的功能分析,揭示E3泛素连接酶TRIM27通过K63泛素化修饰TBK1.增强其激酶活性并促进肿瘤细胞存活,提示靶向TBK1的治疗潜力。
(注:以上文献为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词“TBK1 antibody application”或“TBK1 signaling”获取。)
**Background of TBK1 Antibody**
TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) is a serine/threonine kinase belonging to the IκB kinase (IKK) family, playing pivotal roles in innate immunity, autophagy, and cellular homeostasis. It is activated by pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated signals, often through receptors like RIG-I, TLRs, or cGAS-STING. TBK1 phosphorylates interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) and NF-κB, driving the production of type I interferons (IFNs) and pro-inflammatory cytokines critical for antiviral and antibacterial responses. Dysregulation of TBK1 is implicated in autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis), neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., ALS), and cancer, where it promotes tumor survival and immune evasion.
TBK1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, activation (via phosphorylation at Ser172), and interaction partners (e.g., OPTN, NAP1) in signaling complexes. These antibodies enable techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation, aiding in mechanistic research and drug discovery. For instance, TBK1 inhibitors are being explored as therapeutics for cancer and chronic inflammation. Commercial TBK1 antibodies are typically validated for specificity in human, mouse, or rat models, with applications spanning basic research, biomarker development, and preclinical studies. Understanding TBK1's dual roles in immunity and disease underscores its significance as a therapeutic target and research focus.
×