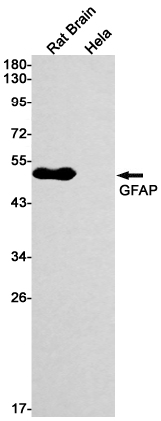
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GFAP; FLJ45472; cb345; ALXDRD |
| Entrez GeneID | 2670 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 50 kDa; Observed MW: 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human GFAP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于GFAP抗体的参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969–2000)*
**作者**: Eng LF, Ghirnikar RS, Lee YL
**摘要**: 这篇综述总结了GFAP作为星形胶质细胞特异性标志物的发现、结构和功能,重点讨论了GFAP抗体在中枢神经系统损伤、肿瘤诊断(如胶质瘤)和神经退行性疾病研究中的应用。
2. **文献名称**: *Astrocytic intermediate filaments: Lessons from GFAP and vimentin knock-out mice*
**作者**: Pekny M, et al.
**摘要**: 通过基因敲除小鼠模型,研究GFAP和波形蛋白在星形胶质细胞中的作用,发现GFAP抗体在检测星形胶质细胞活化和中枢神经系统损伤修复机制中的关键性。
3. **文献名称**: *GFAP in health and disease*
**作者**: Middeldorp J, Hol EM
**摘要**: 探讨GFAP在不同神经系统疾病(如阿尔茨海默病、亚历山大病)中的表达变化,强调GFAP抗体在病理学诊断、细胞特异性标记及疾病机制研究中的重要性。
4. **文献名称**: *GFAP as a biomarker for traumatic brain injury*
**作者**: Yang Z, et al.
**摘要**: 研究创伤性脑损伤(TBI)患者血液和脑脊液中GFAP水平的动态变化,利用GFAP抗体开发高灵敏度检测方法,证明其作为临床生物标志物的潜力。
---
以上文献均聚焦于GFAP抗体的应用场景(如疾病诊断、细胞标记、机制研究)及其在基础与临床研究中的价值。
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is an intermediate filament protein predominantly expressed in astrocytes, a type of glial cell in the central nervous system (CNS). It plays a structural role in maintaining astrocyte integrity, supporting blood-brain barrier function, and regulating synaptic activity. GFAP antibodies are immunological tools designed to detect and visualize this protein, enabling researchers and clinicians to study astrocyte biology and pathology.
In research, GFAP antibodies are widely used in techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and flow cytometry to identify astrocytes in tissue samples, track their activation during CNS injury, inflammation, or neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s), and investigate gliomas. Elevated GFAP levels in cerebrospinal fluid or serum are increasingly recognized as biomarkers for conditions like traumatic brain injury, stroke, or multiple sclerosis.
Clinically, GFAP autoantibodies are associated with autoimmune disorders such as autoimmune GFAP astrocytopathy, a rare inflammatory disease causing meningoencephalitis, myelitis, or optic neuropathy. Detection of these autoantibodies aids in diagnosis and informs immunotherapy strategies.
Overall, GFAP antibodies serve as critical reagents in both neuroscience research and diagnostic pathology, bridging insights into astrocyte dysfunction and CNS disease mechanisms. Their utility continues to expand with advances in neuroimmunology and biomarker discovery.
×