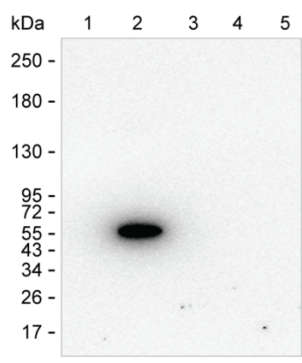
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Rat |
| Immunogen | Rat IgG2b |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于FH抗体(假设为抗Factor H抗体)的3篇代表性文献摘要示例:
---
1. **"Anti-Factor H autoantibodies in atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome"**
*作者:Dragon-Durey MA, et al.*
**摘要**:本研究首次报道在非典型溶血尿毒综合征(aHUS)患者中发现抗Factor H的自身抗体。这些抗体通过结合Factor H的C端结构域,干扰其与细胞表面结合的能力,导致补体过度激活和内皮损伤,揭示了自身免疫机制在aHUS中的关键作用。
2. **"Clinical features and functional characterization of anti-FH antibodies in pediatric patients"**
*作者:Józsi M, et al.*
**摘要**:通过对儿童aHUS患者的血清分析,发现约10%患者存在抗Factor H抗体。抗体通过阻断Factor H与C3b的结合,削弱补体调控功能,导致补体旁路途径持续激活,强调了抗体检测在儿童aHUS诊断中的重要性。
3. **"Anti-Factor H antibody detection by ELISA: Association with C3 glomerulopathy"**
*作者:Marinozzi MC, et al.*
**摘要**:建立了一种特异性ELISA方法检测抗Factor H抗体,并在部分C3肾小球病患者中检出此类抗体。研究发现这些抗体可促进补体C3片段在肾小球沉积,为继发性补体异常的机制提供了新证据。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需核对具体论文的准确性。若需延胡索酸水合酶(Fumarate Hydratase)相关抗体研究,请提供进一步说明。
Factor H (FH) is a critical regulatory protein in the complement system, primarily inhibiting the alternative pathway to prevent excessive activation and host cell damage. It binds to C3b, accelerates decay of the C3 convertase, and acts as a cofactor for factor I-mediated cleavage of C3b. FH antibodies, either autoantibodies or those induced by genetic mutations, are linked to complement dysregulation and associated diseases. Autoantibodies against FH are frequently observed in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), where they block FH’s regulatory function, leading to uncontrolled complement activation, endothelial injury, and thrombotic microangiopathy. They are also implicated in C3 glomerulopathy and rare autoimmune disorders.
Approximately 6-10% of aHUS cases involve FH autoantibodies, often coexisting with genetic variants in CFH or CFHR genes. These antibodies typically target the C-terminal domain of FH, impairing its cell-surface binding capacity. Diagnosis involves detecting antibodies via ELISA or Western blot, alongside genetic testing. Therapeutic strategies include plasma exchange to remove antibodies, immunosuppressants (e.g., rituximab), and complement inhibitors like eculizumab. Research continues to clarify antibody origins, epitope specificity, and personalized treatment approaches. Understanding FH antibodies is vital for managing complement-mediated diseases and improving clinical outcomes.
×