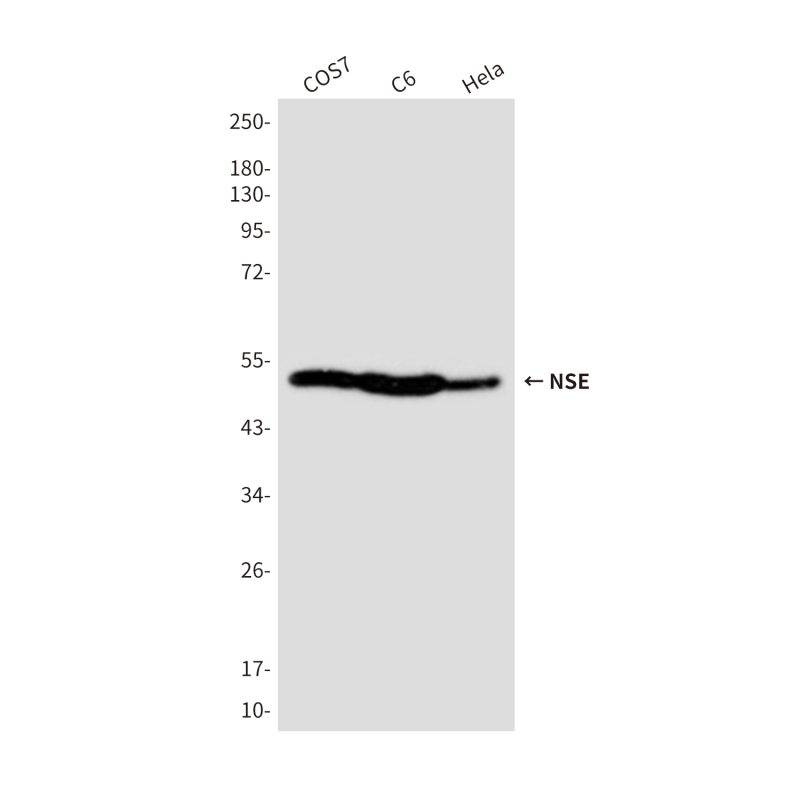
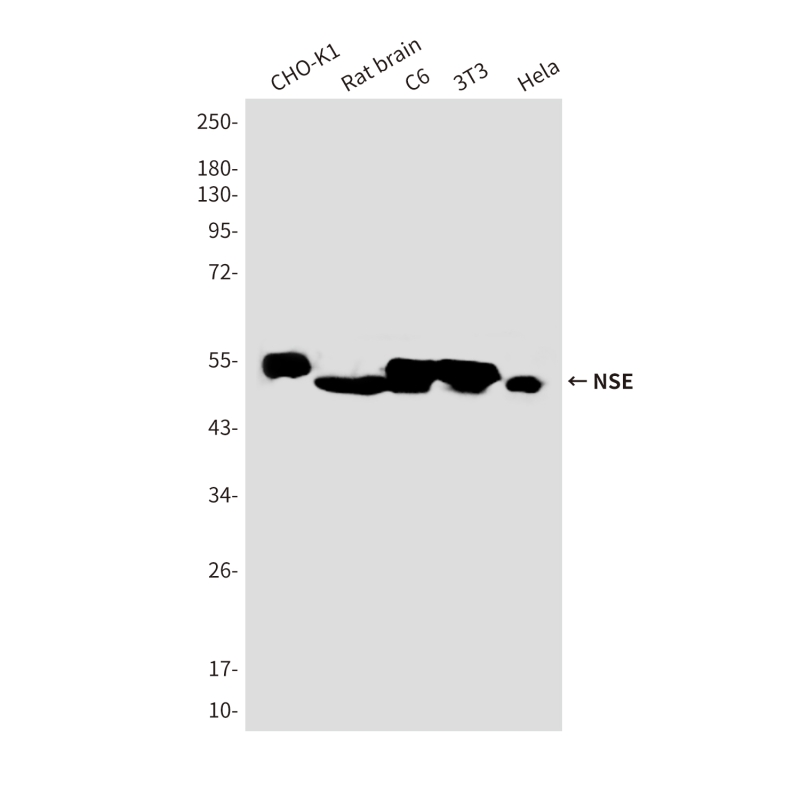
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
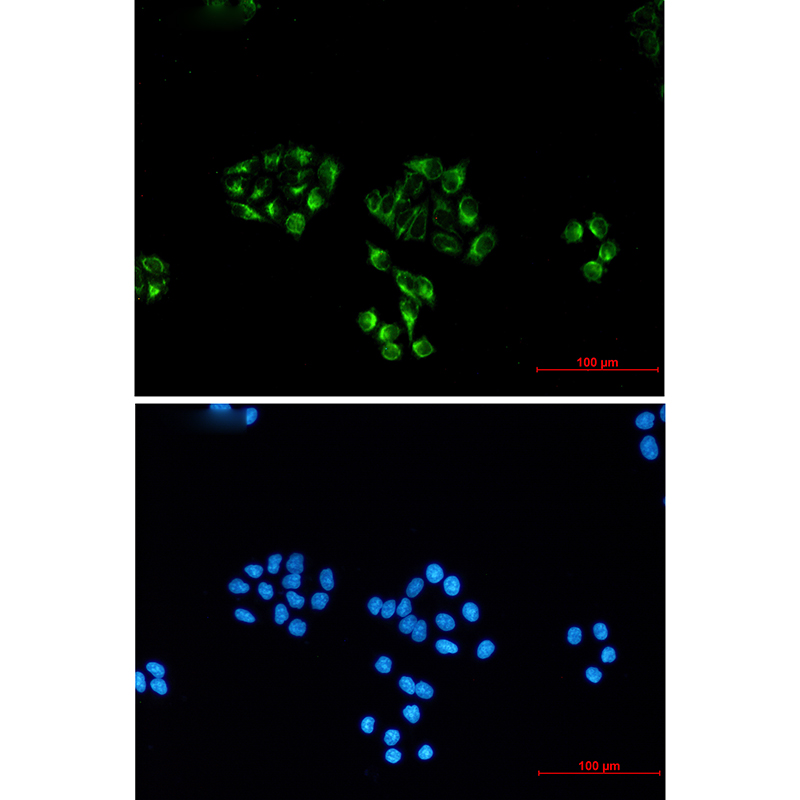
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
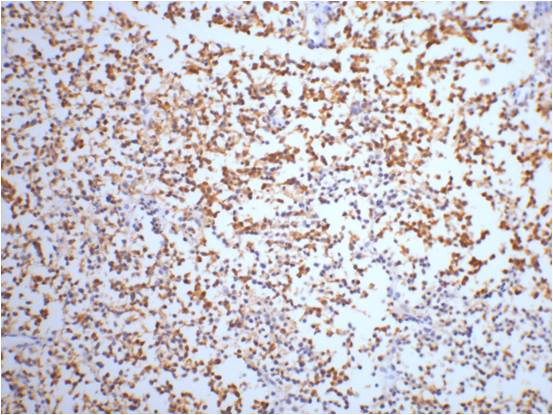
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ENO2; Gamma-enolase; 2-phospho-D-glycerate hydro-lyase; Enolase 2; Neural enolase; Neuron-specific enolase; NSE |
| Entrez GeneID | 2026 |
| clone | 7D8 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 47 kDa; Observed MW: 47 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide of NSE |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NSE抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Development and clinical application of a monoclonal antibody-based immunoassay for neuron-specific enolase*
**作者**: Ishiguro Y. 等
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种新型单克隆抗体,用于高灵敏度检测血清中的NSE水平,并验证其在神经母细胞瘤和小细胞肺癌患者中的诊断价值,结果显示与疾病分期及预后相关。
2. **文献名称**: *Neuron-specific enolase as a biomarker: a comparative study of antibody-based detection methods in lung cancer*
**作者**: Johnson R.W. 等
**摘要**: 比较了不同抗体(多克隆 vs. 单克隆)在ELISA和免疫组化中对NSE的检测效能,发现单克隆抗体在肺癌组织样本中具有更高的特异性,减少了交叉反应。
3. **文献名称**: *Prognostic significance of serum neuron-specific enolase in traumatic brain injury: correlation with antibody-based assay standardization*
**作者**: Müller C. 等
**摘要**: 研究探讨了NSE抗体检测标准化对创伤性脑损伤患者预后评估的影响,强调标准化流程可提高结果一致性,并证实血清NSE水平与神经损伤严重程度正相关。
---
这些文献涵盖了NSE抗体的技术开发、检测方法优化及临床应用场景,可作为相关研究的参考。如需具体期刊信息或DOI,可进一步补充检索关键词。
Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) antibodies are immunological tools targeting NSE, a glycolytic enzyme predominantly expressed in neurons, neuroendocrine cells, and tumors of neural origin. NSE, also known as enolase 2 (ENO2), is one of three enolase isoenzymes (α, β, γ), with the γ-isoform being neuron-specific. It plays a critical role in energy metabolism by catalyzing the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate.
NSE gained clinical significance as a biomarker due to its release into bodily fluids upon neuronal or neuroendocrine cell damage. Elevated serum NSE levels are associated with neurological injuries (e.g., stroke, traumatic brain injury) and neuroendocrine tumors, particularly small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and neuroblastoma. Antibodies against NSE enable its detection in diagnostic assays, including immunohistochemistry (IHC), ELISA, and Western blotting, aiding in tumor classification and disease monitoring.
In research, NSE antibodies are widely used to identify neuronal populations, study neurodegenerative diseases, and investigate neuroendocrine system dynamics. However, their specificity requires careful validation due to potential cross-reactivity with other enolase isoforms in non-neural tissues. Despite limitations like false positives from hemolysis in serum tests, NSE remains a valuable diagnostic and research target, with antibodies serving as essential reagents in both clinical and experimental neurobiology contexts.
×