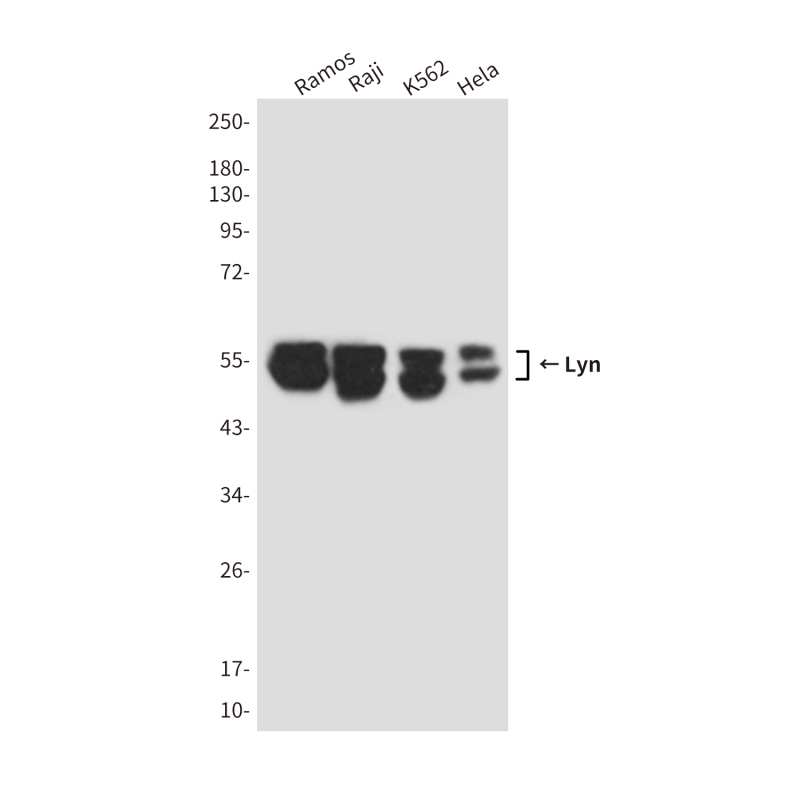
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LYN; JTK8; Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn; Lck/Yes-related novel protein tyrosine kinase; V-yes-1 Yamaguchi sarcoma viral related oncogene homolog; p53Lyn; p56Lyn |
| Entrez GeneID | 4067 |
| clone | 2D9 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 59 kDa; Observed MW: 56,53 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human Lyn protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Lyn抗体的参考文献及其摘要的简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Lyn Kinase in the Immunoreceptor Signaling and Beyond*
**作者**:Hibbs ML, Harder KW
**摘要**:该综述探讨了Lyn激酶在免疫受体(如BCR和Fc受体)信号传导中的双重作用,既作为激活介质,又通过抑制性受体调控负反馈通路。文章还讨论了Lyn在自身免疫疾病和癌症中异常表达的可能机制。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting Lyn Kinase in Cancer: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Solid Tumors*
**作者**:Gomez S, Cohen P
**摘要**:研究通过体外实验发现,Lyn在多种实体瘤(如乳腺癌、胶质母细胞瘤)中高表达,并通过激活PI3K/AKT和STAT3通路促进肿瘤存活。使用特异性Lyn抗体可抑制肿瘤生长,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Lyn-Deficient Mice Reveal a Critical Role in B Cell Tolerance and Autoantibody Production*
**作者**:Scapini P et al.
**摘要**:通过基因敲除小鼠模型,研究发现Lyn缺失会导致B细胞过度活化,引发自身抗体产生和狼疮样症状,揭示了Lyn在维持B细胞耐受性中的关键作用,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新思路。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Lyn Kinase as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia*
**作者**:Contri A et al.
**摘要**:该文献发现慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)患者中Lyn激酶活性显著升高,且与化疗耐药相关。通过抑制Lyn或使用抗体阻断其功能,可诱导CLL细胞凋亡,提示其在预后评估和靶向治疗中的应用价值。
---
以上文献涵盖Lyn在免疫调控、肿瘤治疗及自身免疫疾病中的多重作用,可根据研究方向进一步扩展。
**Background of Lyn Antibody**
Lyn is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase belonging to the Src family, primarily expressed in hematopoietic cells, including B cells, mast cells, and myeloid cells. Discovered in the early 1990s, Lyn plays a dual role in cellular signaling, regulating both activating and inhibitory pathways. It is involved in immune receptor signaling, such as B-cell receptor (BCR) and FcεRI pathways, where it modulates cell activation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Lyn phosphorylates key substrates like Syk and PI3K to propagate signals, while also recruiting phosphatases (e.g., SHIP-1) to dampen responses, maintaining immune homeostasis.
Dysregulation of Lyn is linked to pathologies. Overactivity or deficiency contributes to autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus), allergies, and cancers (e.g., chronic lymphocytic leukemia). In cancer, Lyn can promote survival and drug resistance, making it a therapeutic target.
Lyn antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, activation (via phosphorylation at specific residues like Tyr396), and interactions. They enable techniques such as Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry. Researchers also develop inhibitory antibodies or small molecules to block Lyn’s oncogenic signaling, exploring potential treatments.
Two major Lyn isoforms, LynA and LynB, arise from alternative splicing, differing in regulatory domains and function. Antibodies distinguishing these isoforms help elucidate their distinct roles. Overall, Lyn antibodies are pivotal in unraveling immune regulation mechanisms and advancing targeted therapies for Lyn-associated diseases.
×