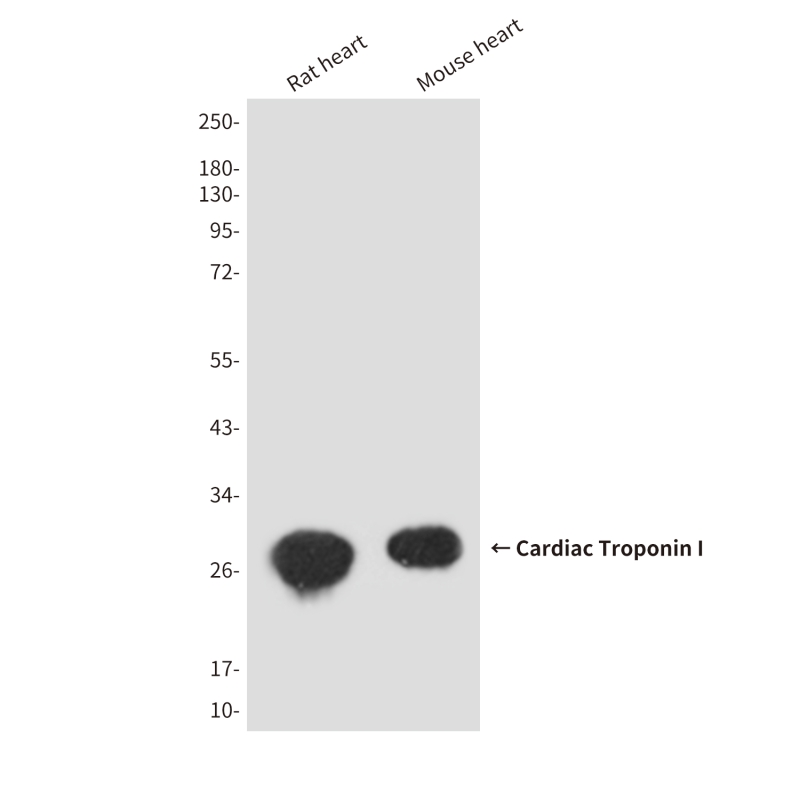
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
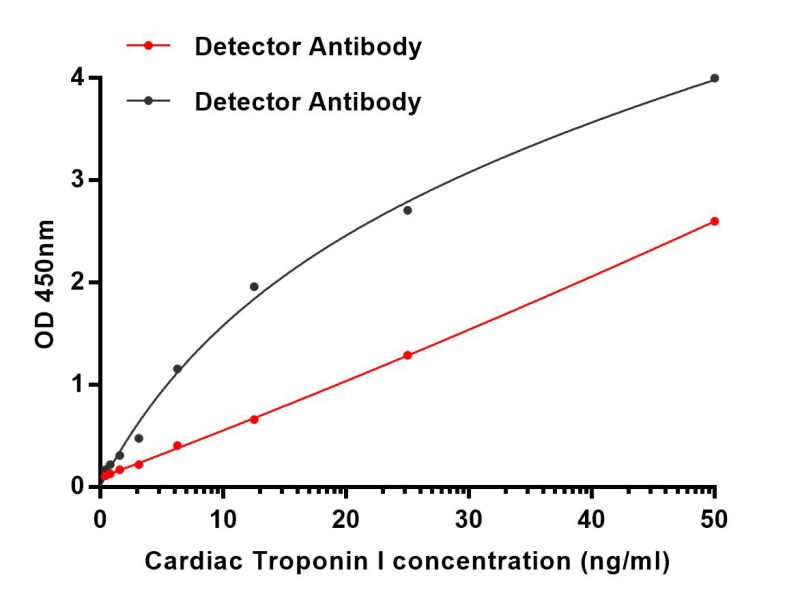
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TNNI3; TNNC1; Troponin I; cardiac muscle; Cardiac troponin I |
| Entrez GeneID | 7137 |
| clone | 1G7 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 24 kDa; Observed MW: 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptides corresponding to the sequence of human Cardiac Troponin I. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于Cardiac Troponin I(cTnI)抗体的经典文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Cardiac Troponin I: A Marker with High Specificity for Cardiac Injury"*
**作者**: Apple FS, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究系统评估了cTnI抗体在心肌损伤诊断中的特异性,验证其作为急性心肌梗死的敏感生物标志物,并探讨了其在临床检测中的标准化方法。
2. **文献名称**: *"Development of Monoclonal Antibodies for an Ultrasensitive Cardiac Troponin I Assay"*
**作者**: Bodor GS, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了高亲和力的单克隆cTnI抗体,显著提升了检测灵敏度(可达0.01 ng/mL),推动了高敏cTnI(hs-cTnI)检测技术在早期心肌缺血诊断中的应用。
3. **文献名称**: *"Point-of-Care Testing of Cardiac Troponin I in Acute Coronary Syndromes"*
**作者**: Collinson PO, et al.
**摘要**: 该文献验证了基于cTnI抗体的床旁检测(POCT)设备在急诊场景下的可行性,证明其与传统实验室检测结果高度一致,缩短了急性冠脉综合征的诊断时间。
4. **文献名称**: *"Epitope Mapping of Cardiac Troponin I Antibodies for Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis"*
**作者**: Wu AHB, et al.
**摘要**: 通过表位定位技术分析了不同cTnI抗体的结合特性,揭示了抗体选择对检测结果的影响,为优化免疫分析法提供了理论依据。
---
**备注**:以上文献为领域内代表性研究,实际引用时需核对期刊名称、年份及具体卷期(例如Clin Chem、Circulation等期刊常见相关主题)。
Cardiac troponin I (cTnI) is a regulatory protein exclusively expressed in cardiomyocytes, playing a critical role in muscle contraction by inhibiting actin-myosin interactions. Due to its cardiac specificity, cTnI has become the gold-standard biomarker for diagnosing myocardial infarction (MI) and assessing cardiac injury. Antibodies targeting cTnI are essential components of immunoassays used to detect and quantify this protein in blood samples.
The development of cTnI-specific antibodies requires careful selection to ensure high specificity, as troponin I exists in three isoforms (cardiac, slow skeletal, and fast skeletal) with significant structural homology. Early polyclonal antibodies faced cross-reactivity challenges, but advancements in monoclonal antibody (mAb) technology enabled the production of highly selective clones. These antibodies typically target stable epitopes in the central region of cTnI (residues 30–110), avoiding degradation-prone areas at the N- and C-termini.
Clinically, cTnI assays rely on paired antibodies in sandwich ELISA or chemiluminescence platforms. High-sensitivity (hs-cTnI) assays, utilizing optimized antibody pairs, can detect picogram-level concentrations, improving early MI diagnosis. However, challenges persist, including interference from heterophilic antibodies, cTnI degradation products, or autoantibodies. Recent efforts focus on engineering recombinant antibodies or using phage display libraries to enhance affinity and stability.
Research also explores point-of-care testing (POCT) and multiplex platforms, driving demand for robust cTnI antibodies. Ongoing studies investigate post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation, oxidation) and their impact on antibody binding, aiming to refine diagnostic accuracy in diverse patient populations.
×