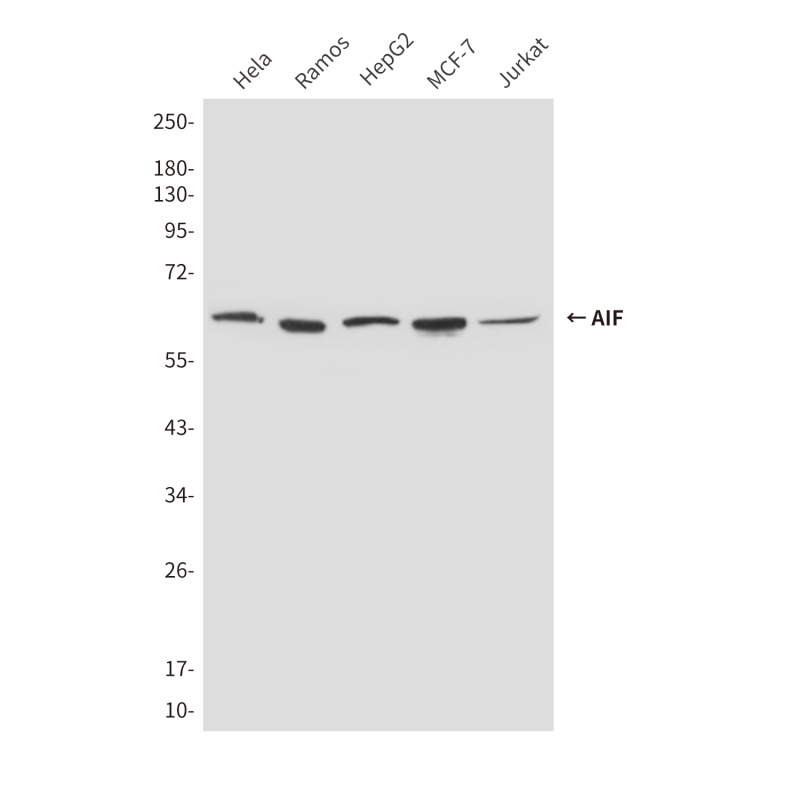
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
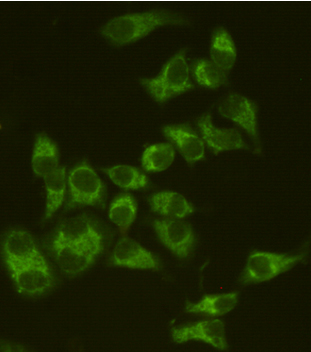
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AIFM1; AIF; PDCD8; Apoptosis-inducing factor 1; mitochondrial; Programmed cell death protein 8 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9131 |
| clone | 8H1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 67 kDa; Observed MW: 67 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human AIF protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于AIF(Apoptosis-Inducing Factor)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Molecular Characterization of Mitochondrial Apoptosis-Inducing Factor*
**作者**:Susin, S. A., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次克隆并鉴定了AIF蛋白,揭示了其在细胞凋亡中的关键作用。通过使用AIF特异性抗体,发现AIF在凋亡过程中从线粒体转位至细胞核,引发染色质凝集和DNA片段化,独立于caspase途径。
2. **文献名称**:*AIF Deficiency Compromises Oxidative Phosphorylation*
**作者**:Klein, J. A., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用AIF抗体分析基因敲除小鼠模型,发现AIF缺失导致线粒体呼吸链功能异常,引发神经退行性病变。结果表明AIF不仅是凋亡因子,还对维持线粒体能量代谢至关重要。
3. **文献名称**:*AIF-mediated Caspase-independent Apoptosis in Myocardial Ischemia*
**作者**:Cheung, E. C., et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化和Western blotting使用AIF抗体,该研究证实心肌缺血再灌注损伤中,AIF从线粒体释放至细胞核,触发caspase非依赖性细胞死亡,为心脏保护策略提供了新靶点。
4. **文献名称**:*AIF in Neurodegeneration: Translocation and Therapeutic Implications*
**作者**:Yu, S. W., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用AIF抗体检测其在帕金森病模型中的表达,发现AIF在神经元兴奋性中毒后易位至细胞核,促进DNA损伤和细胞死亡,提示抑制AIF通路可能具有神经保护潜力。
以上文献均聚焦于AIF的功能机制及抗体在其研究中的应用,涵盖凋亡、代谢和疾病模型等领域。
Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) is a mitochondrial flavoprotein with dual roles in cellular homeostasis. Initially identified for its involvement in caspase-independent apoptosis, AIF translocates to the nucleus under stress conditions, triggering chromatin condensation and DNA fragmentation. Beyond apoptosis, AIF plays a crucial role in maintaining mitochondrial structure, regulating oxidative phosphorylation, and protecting against oxidative stress through its redox activity.
AIF antibodies are essential tools for studying its subcellular localization, expression patterns, and pathological mechanisms. Research has linked AIF dysfunction to various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Parkinson's and Alzheimer's), ischemic injuries, and cancer. Autoantibodies against AIF have been detected in autoimmune conditions, suggesting its potential as a diagnostic biomarker.
In experimental settings, AIF antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Recent studies explore AIF's therapeutic potential, targeting its mitochondrial release or nuclear translocation to modulate cell death pathways. However, challenges remain in distinguishing its pro-survival versus pro-death functions, highlighting the need for context-specific antibody applications in both basic research and clinical investigations.
×