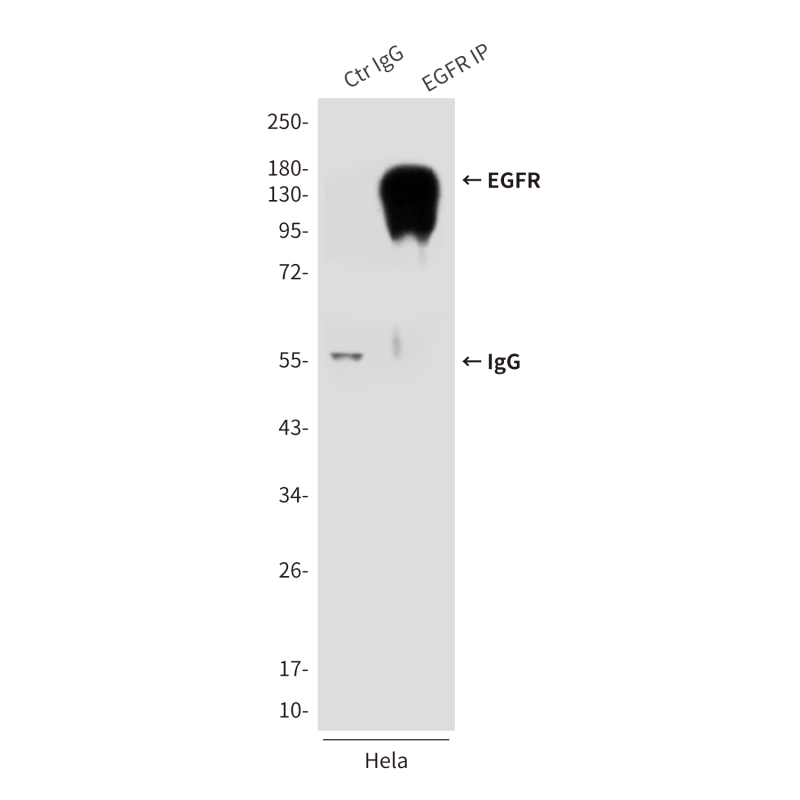
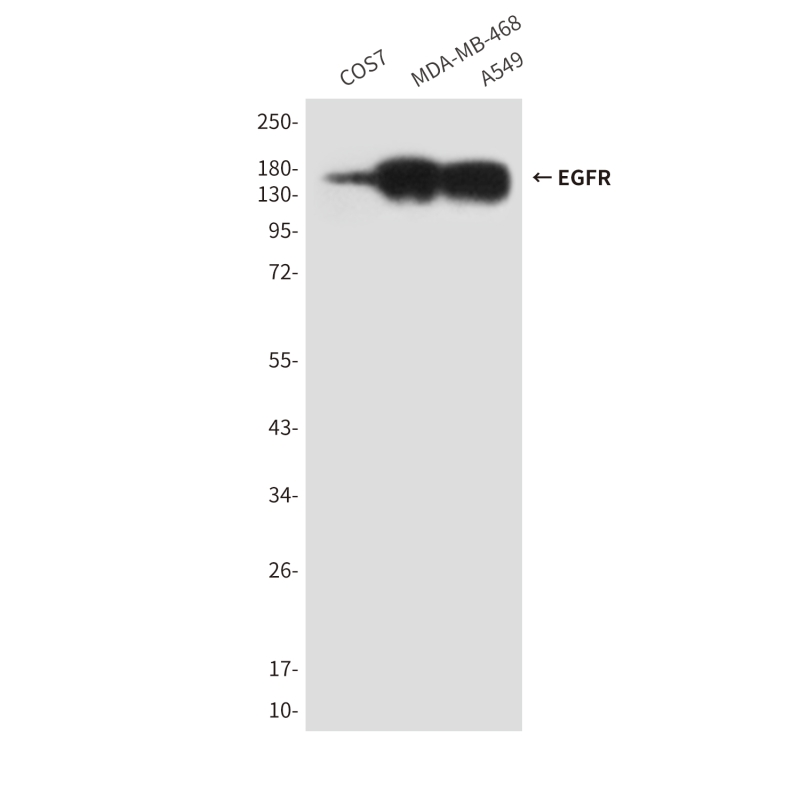
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Monkey |
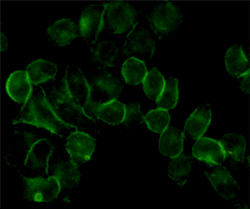
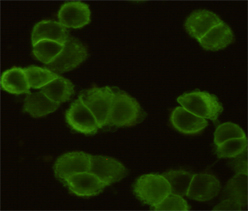
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Monkey |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Monkey |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Monkey |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Monkey |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Monkey |
| Aliases | EGFR; ERBB; ERBB1; HER1; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Proto-oncogene c-ErbB-1; Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1956 |
| clone | 8B1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 134 kDa; Observed MW: 175 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human EGFR protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于EGFR抗体的经典文献摘要示例:
1. **《Cetuximab for the treatment of colorectal cancer》**
- 作者:Van Cutsem E, et al.
- 摘要:该研究报道了西妥昔单抗(抗EGFR单抗)联合化疗在转移性结直肠癌中的疗效,证实其对KRAS野生型患者显著延长无进展生存期,成为首个针对EGFR的靶向治疗里程碑。
2. **《Panitumumab versus cetuximab in patients with chemotherapy-refractory wild-type KRAS metastatic colorectal cancer》**
- 作者:Hecht JR, et al.
- 摘要:对比帕尼单抗与西妥昔单抗在KRAS野生型结直肠癌中的效果,结果显示两者疗效相似,但帕尼单抗(全人源化抗体)的过敏反应发生率更低。
3. **《EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy》**
- 作者:Lynch TJ, et al.
- 摘要:尽管主要研究EGFR突变与小分子抑制剂的关系,但该文献为EGFR靶向治疗(包括抗体药物)的个体化应用提供了分子标志物理论基础,推动了后续抗体药物的精准开发。
4. **《Mechanisms of resistance to cetuximab and novel therapeutic regimens in metastatic colorectal cancer》**
- 作者:Wheeler DL, et al.
- 摘要:系统总结了西妥昔单抗的耐药机制,包括EGFR胞外结构域突变(如S492R)和下游信号通路异常激活,提出了联合靶向治疗策略以克服耐药。
注:实际引用时需核对文献准确性,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索最新进展。
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a transmembrane tyrosine kinase belonging to the HER family, plays a critical role in regulating cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. Overactivation of EGFR through mutations, overexpression, or ligand binding is implicated in various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), colorectal cancer, and head/neck malignancies. This led to the development of EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) as a key strategy in precision oncology.
EGFR antibodies, such as cetuximab and panitumumab, bind to the receptor’s extracellular domain, blocking ligand-induced activation and downstream signaling pathways (e.g., RAS/RAF/MAPK, PI3K/AKT). They also promote receptor internalization/degradation and mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Clinically, these agents are used in KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer and squamous cell carcinomas. However, resistance often arises due to secondary mutations (e.g., EGFR T790M), alternative pathway activation, or altered antibody-receptor interactions. Combination therapies with chemotherapy, radiation, or other targeted agents (e.g., VEGF inhibitors) are being explored to overcome resistance. Additionally, companion diagnostics for EGFR expression and mutation status guide patient selection. While generally well-tolerated, skin toxicity remains a common adverse effect. Ongoing research focuses on next-generation antibodies, bispecific formats, and improved biomarker-driven approaches to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
×