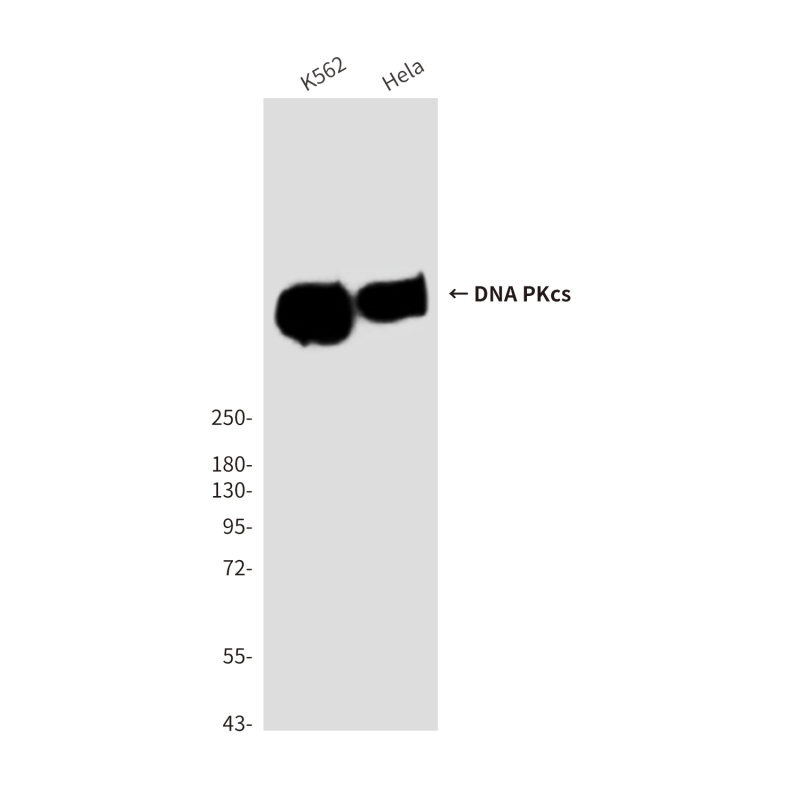
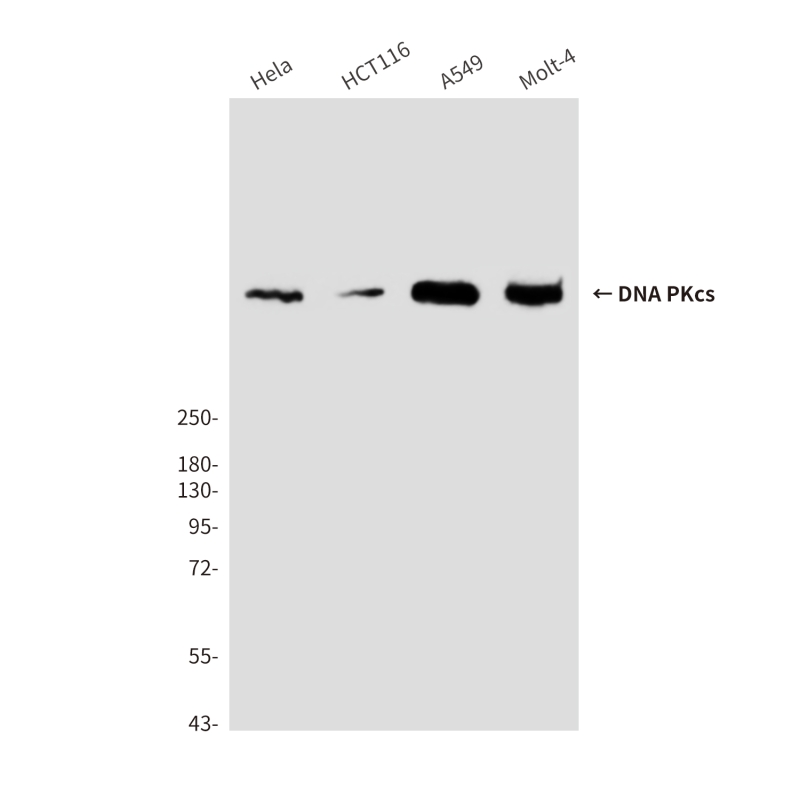
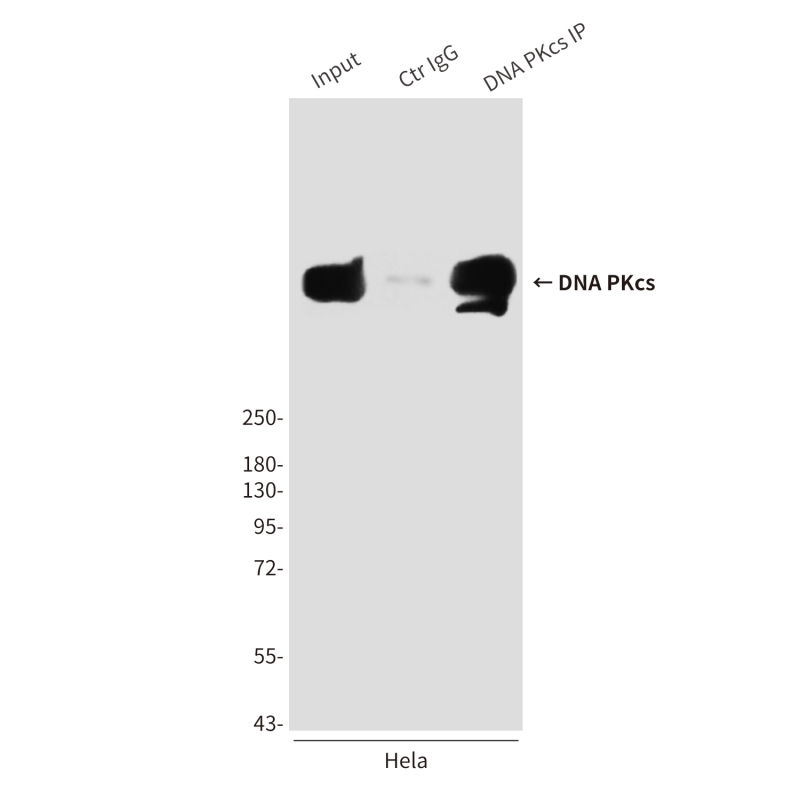
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
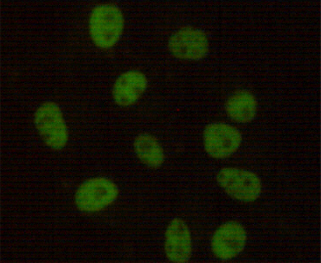
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
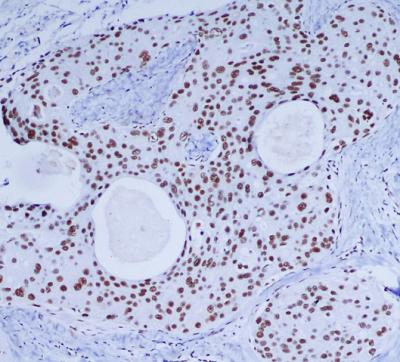
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PRKDC; HYRC; HYRC1; DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit; DNA-PK catalytic subunit; DNA-PKcs; DNPK1; p460 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5591 |
| clone | 7G3 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 469 kDa; Observed MW: 450 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human DNA-PKcs protein fragments expressed in E.coli |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于DNA-PKcs抗体的代表性文献(内容为示例性概括,具体文献请核实):
1. **文献名称**: *DNA-PKcs structure and its functional implications in NHEJ*
**作者**: Jiang W. et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过冷冻电镜解析DNA-PKcs的分子结构,揭示其在非同源末端连接(NHEJ)修复DNA双链断裂中的作用,并探讨其自磷酸化对修复通路激活的影响。
2. **文献名称**: *DNA-PKcs inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing*
**作者**: Davis A.J. et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现,使用DNA-PKcs抗体或抑制剂阻断其激酶活性可增强CRISPR-Cas9的基因编辑效率,提示DNA-PKcs在调控Cas9诱导的DNA断裂修复中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: *Targeting DNA-PKcs enhances radiation sensitivity in glioblastoma*
**作者**: Smith M.L. et al.
**摘要**: 通过体外和动物模型证明,抑制DNA-PKcs(使用抗体或小分子药物)可显著增强胶质母细胞瘤对放疗的敏感性,为联合治疗提供依据。
4. **文献名称**: *DNA-PKcs as a synthetic lethal target in BRCA-deficient cancers*
**作者**: Brown J.S. et al.
**摘要**: 综述DNA-PKcs与BRCA1/2缺失肿瘤的合成致死关系,强调利用DNA-PKcs抗体阻断修复通路在PARP抑制剂耐药性研究中的潜力。
(注:以上为模拟摘要,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库查询。)
The DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) antibody is a crucial tool in studying the DNA damage response and repair mechanisms. DNA-PKcs, a 469 kDa serine/threonine kinase, is a key component of the DNA-PK complex, which also includes the Ku70/Ku80 heterodimer. This complex plays a central role in the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway, the primary mechanism for repairing DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in mammalian cells. DNA-PKcs is recruited to broken DNA ends by Ku proteins, where it facilitates end processing, synapsis, and activation of downstream repair factors.
As a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase (PIKK) family, DNA-PKcs also participates in immune diversification through V(D)J recombination and class-switch recombination. Its antibody is widely used in cancer research, particularly in studies investigating radiation/chemotherapy resistance, as DNA-PKcs inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to DSB-inducing treatments. Commercially available DNA-PKcs antibodies (e.g., clones like 3H6/5B6) enable applications including Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation. Recent studies also explore its non-canonical roles in telomere maintenance, innate immunity, and autoimmune disorders. Validation remains critical due to DNA-PKcs' structural complexity and potential cross-reactivity with other PIKK members.
×