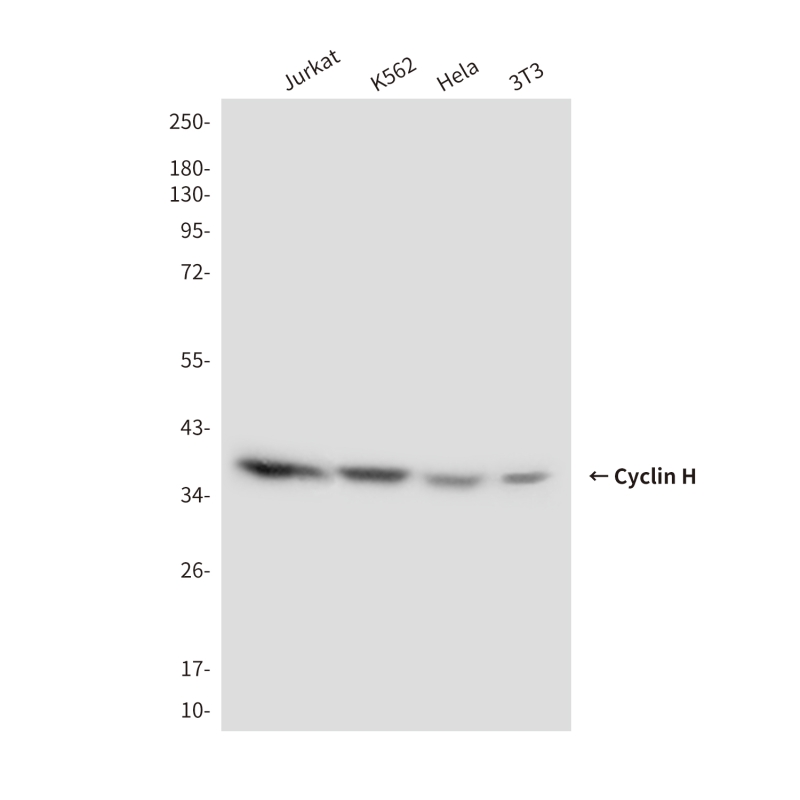
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CCNH; Cyclin-H; MO15-associated protein; p34; p37 |
| Entrez GeneID | 902 |
| clone | 1C7 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 38 kDa; Observed MW: 38 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human Cyclin H protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及Cyclin H抗体的参考文献(信息基于公开文献概括,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Cyclin H expression is regulated during myogenic differentiation via phosphorylation of E2A"
**作者**: Ribon V. et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用Cyclin H抗体进行Western blot分析,发现Cyclin H在成肌细胞分化过程中表达水平动态变化,并通过E2A转录因子的磷酸化调控其功能,揭示了其在细胞分化中的潜在作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "CDK7-Cyclin H phosphorylates CTD of RNA polymerase II in transcription initiation"
**作者**: Roy R. et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和免疫荧光实验,作者使用Cyclin H抗体证实CDK7-Cyclin H复合物对RNA聚合酶II C端结构域(CTD)的磷酸化作用,阐明其在转录起始中的关键调控机制。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Dysregulation of Cyclin H in hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis"
**作者**: Li J. et al.
**摘要**:该研究采用Cyclin H抗体进行免疫组化(IHC)分析,发现肝细胞癌(HCC)中Cyclin H蛋白异常高表达与患者生存率降低显著相关,提示其作为癌症预后标志物的潜力。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需通过PubMed或期刊数据库核实具体信息。若需实验抗体品牌或应用细节,可补充说明研究方向(如WB/IHC/ChIP等)。
Cyclin H is a regulatory subunit of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)-activating kinase (CAK) complex, which primarily associates with CDK7 to regulate cell cycle progression and transcription. As a member of the cyclin family, Cyclin H plays a dual role: it facilitates CDK7 activation to phosphorylate CDKs (e.g., CDK1. CDK2. CDK4) critical for cell cycle transitions, and it participates in transcription by modulating RNA polymerase II activity through the TFIIH complex. Dysregulation of Cyclin H has been implicated in diseases such as cancer, where altered CAK activity may disrupt cell proliferation or DNA repair pathways.
Cyclin H antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in cellular processes. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to quantify protein levels, identify binding partners, or visualize subcellular distribution. Specificity and validation (e.g., using knockout cell lines) are crucial, as cross-reactivity with other cyclins can confound results. In research, Cyclin H antibodies help explore mechanisms of cell cycle control, transcriptional regulation, and responses to genotoxic stress. They also hold potential in clinical applications, such as assessing CAK complex dysfunction in tumors or evaluating therapeutic targets. Commercial Cyclin H antibodies are typically raised against conserved epitopes, with monoclonal variants offering higher specificity for consistent experimental reproducibility.
×