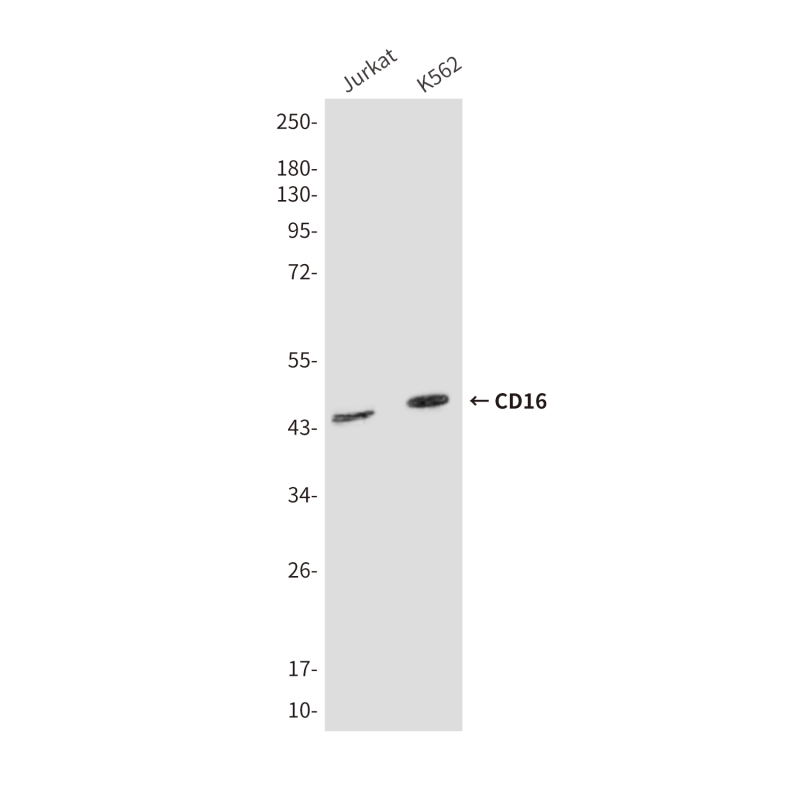
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
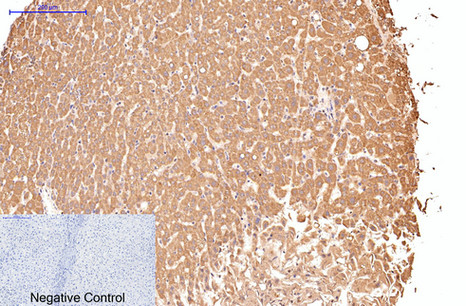
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IGFR3; CD16; CD16a; IMD20 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2214 |
| clone | 7E4 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 29 kDa; Observed MW: 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide of CD16 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD16抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
1. **标题**:*Fc receptor engineering of antibodies for enhanced cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**:Jeffrey V. Ravetch 等
**摘要**:该研究探讨了通过改造抗体Fc段结构,增强其与CD16A(FcγRIIIA)的结合能力,从而提升抗体依赖性细胞介导的细胞毒性(ADCC),为癌症免疫治疗提供新策略。
2. **标题**:*CD16 polymorphism and NK cell-mediated ADCC activity impact therapeutic efficacy of anti-CD20 antibodies*
**作者**:Monica M.等
**摘要**:文章分析了CD16(FcγRIIIA)基因多态性(如V158F突变)对NK细胞功能的影响,揭示了不同基因型患者对抗CD20抗体(如利妥昔单抗)治疗反应的差异。
3. **标题**:*A CD16/CD30 bispecific antibody triggers NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against Hodgkin lymphoma*
**作者**:Christian Kellner 等
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种双特异性抗体,同时靶向NK细胞表面的CD16和霍奇金淋巴瘤细胞表面的CD30.显著增强了NK细胞对肿瘤的特异性杀伤效果。
CD16 antibodies target the CD16 antigen, a low-affinity Fc gamma receptor III (FcγRIII) expressed primarily on natural killer (NK) cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and a subset of T cells. CD16 exists as two isoforms: CD16a (FcγRIIIA), a transmembrane protein critical for antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), and CD16b (FcγRIIIB), a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored receptor on neutrophils. These receptors bind the Fc portion of IgG antibodies, bridging innate and adaptive immunity by mediating immune cell activation, phagocytosis, and cytokine release.
CD16 antibodies are widely used in research and clinical applications. In diagnostics, they help identify and isolate NK cells via flow cytometry. Therapeutically, they are explored to modulate immune responses, either by enhancing ADCC in cancer immunotherapy (e.g., rituximab) or suppressing inflammation in autoimmune diseases. Anti-CD16 monoclonal antibodies, such as 3G8 and B73.1. are common tools for functional studies. Recent advances include bispecific antibodies engaging CD16 to redirect NK cells against tumors. However, CD16 polymorphisms (e.g., FcγRIIIa-V158F) influence clinical outcomes, driving personalized therapeutic strategies. Challenges remain in optimizing CD16-targeted therapies to balance efficacy with immune-related adverse effects. Ongoing research focuses on engineering high-affinity CD16 antibodies and understanding their regulatory roles in disease pathogenesis.
×