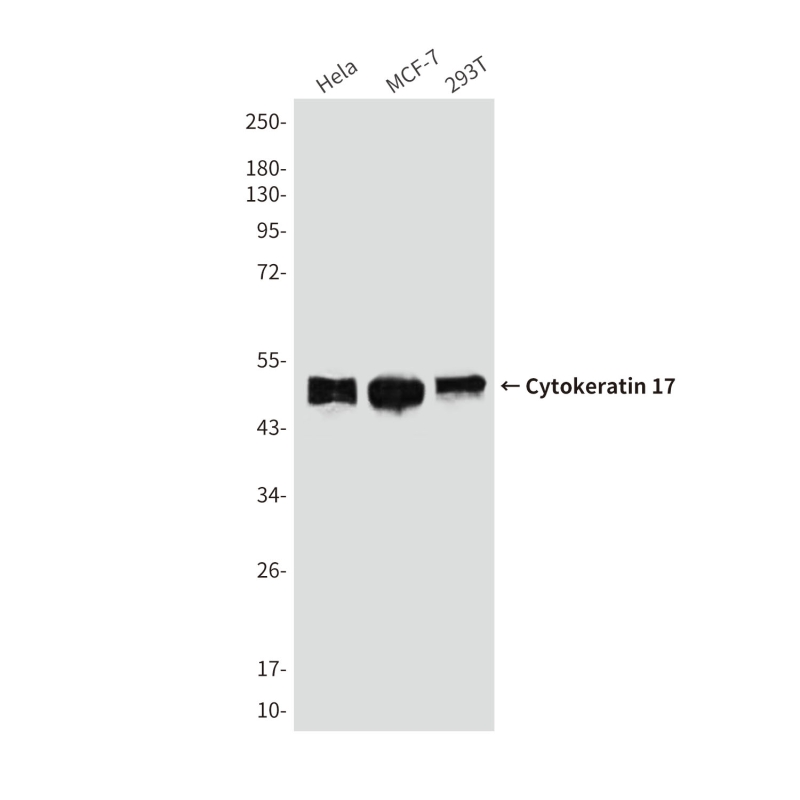
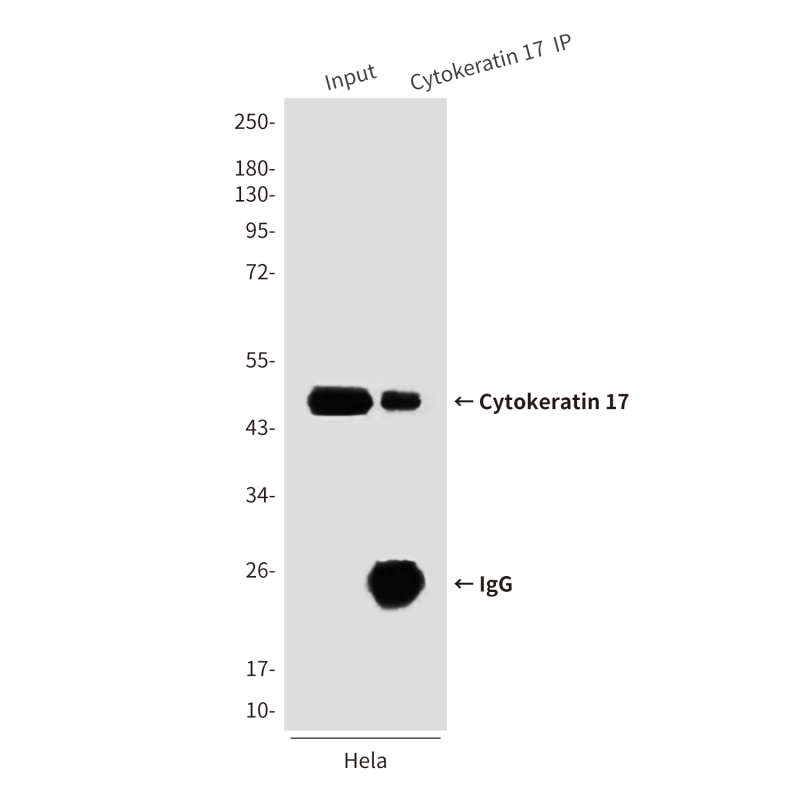
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
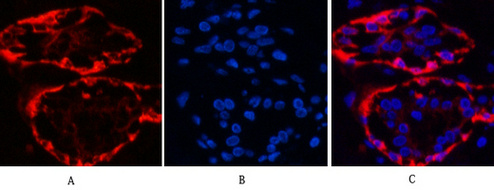
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
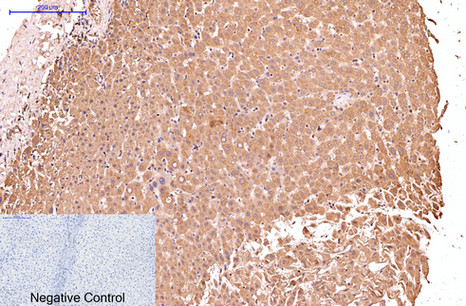
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Keratin; type I cytoskeletal 17; Cytokeratin-17; CK-17; Keratin-17; K17 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3872 |
| clone | 9D7 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 48 kDa; Observed MW: 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide of CK17 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Cytokeratin 17(CK17)抗体的参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Cytokeratin 17 as a Diagnostic Biomarker in Basal-like Breast Cancer*
**作者**: Nagatsuka H et al.
**摘要**: 该研究证实CK17抗体在基底样乳腺癌组织中高表达,可作为区分三阴性乳腺癌与其他亚型的特异性标志物,提出其在病理诊断中的潜在应用价值。
---
2. **文献名称**: *CK17 Immunoreactivity in Cervical Squamous Neoplasia*
**作者**: Smedts F et al.
**摘要**: 通过CK17抗体免疫组化分析,发现CK17在宫颈高度鳞状上皮内病变(HSIL)及鳞癌中显著表达,提示其可作为宫颈癌前病变的早期诊断指标。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Cytokeratin 17 Regulates Skin Stem Cell Differentiation*
**作者**: Hobbs RP et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用CK17抗体敲除模型,揭示CK17通过调控Wnt/β-catenin通路影响皮肤干细胞分化,为治疗表皮发育异常疾病提供新机制。
---
如需具体DOI或发表年份,可进一步补充检索!
Cytokeratin 17 (CK17) is a type I intermediate filament protein encoded by the *KRT17* gene, part of the cytokeratin family crucial for maintaining epithelial cell structure and integrity. It pairs with type II cytokeratins (e.g., CK5) to form a cytoskeletal network, providing mechanical stability and resilience to epithelial tissues. CK17 is primarily expressed in basal and stratified epithelial cells, notably in skin appendages (hair follicles, sweat glands), mammary ducts, cervical epithelium, and certain glandular tissues. Its expression is dynamically regulated during development, wound healing, and pathological conditions.
Notably, CK17 is absent in normal stratified squamous epithelia but is upregulated in hyperproliferative or neoplastic contexts. It serves as a biomarker in diagnostic pathology, particularly for distinguishing epithelial tumors. Overexpression is observed in aggressive carcinomas (e.g., triple-negative breast cancer, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, cervical squamous cell carcinoma) and correlates with poor prognosis. CK17 antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry to identify tumor subtypes, such as basal-like breast cancers or squamous cell carcinomas, aiding differential diagnosis. Additionally, CK17's role in cancer progression—linked to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), invasion, and therapy resistance—makes it a research focus for targeted therapies. Its expression in precancerous lesions (e.g., cervical intraepithelial neoplasia) further highlights its potential in early cancer detection.
×