| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
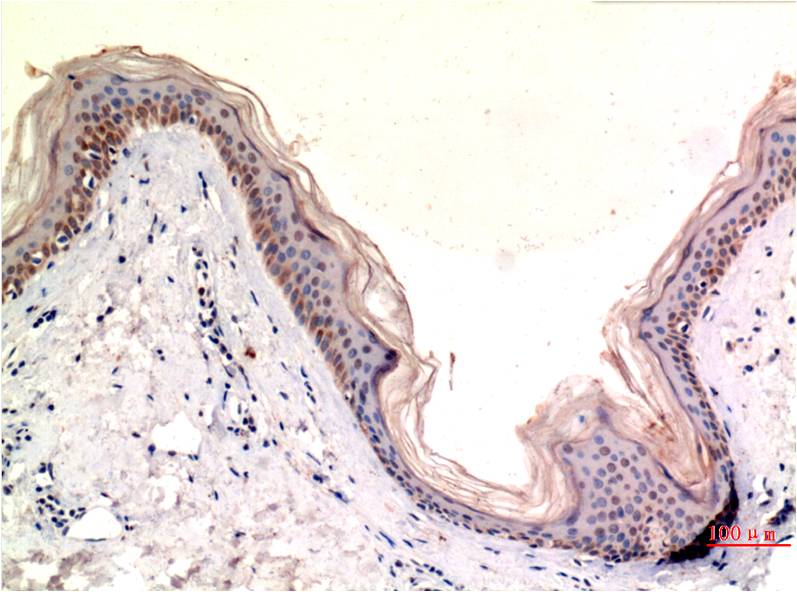
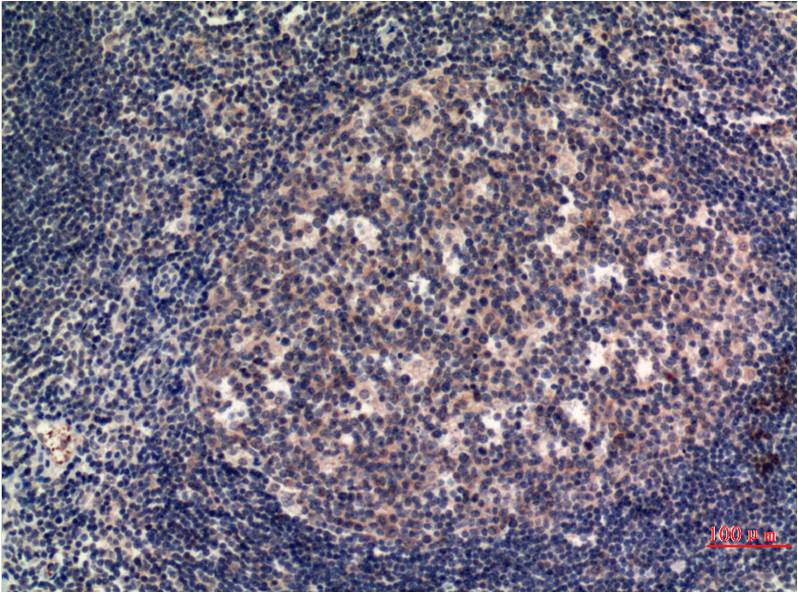
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MLKL |
| Entrez GeneID | 197259 |
| clone | 6A2 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide conjugated to KLH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MLKL抗体的3-4篇代表性文献的简要总结(文献名称、作者及摘要概括):
1. **文献名称**:*MLKL compromises plasma membrane integrity by binding to phosphatidylinositol phosphates*
**作者**:Dondelinger, Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过MLKL特异性抗体揭示了MLKL蛋白在坏死性凋亡(necroptosis)中的膜破坏机制,证明其通过结合磷脂酰肌醇磷酸导致细胞膜透化,并利用抗体验证了MLKL在细胞死亡过程中的亚细胞定位。
2. **文献名称**:*Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase*
**作者**:Sun, L. et al.
**摘要**:研究首次提出MLKL是RIP3下游的坏死性凋亡执行蛋白,通过免疫沉淀和抗体阻断实验证实MLKL的磷酸化是其激活的关键步骤,并开发了针对MLKL磷酸化位点的抗体以检测其活性形式。
3. **文献名称**:*Activation of the pseudokinase MLKL unleashes the four-helix bundle domain to induce membrane localization and necroptotic cell death*
**作者**:Hildebrand, J.M. et al.
**摘要**:利用MLKL抗体进行结构域功能研究,发现MLKL的假激酶结构域调控其四螺旋束结构域的暴露,驱动MLKL向细胞膜迁移并引发膜破裂,抗体检测证实了不同结构域在细胞死亡中的动态变化。
4. **文献名称**:*The pseudokinase MLKL mediates necroptosis via a molecular switch mechanism*
**作者**:Murphy, J.M. et al.
**摘要**:通过MLKL特异性抗体和基因敲除模型,阐明MLKL通过构象变化从“闭合”到“开放”状态触发坏死性凋亡,并验证了抗体在检测MLKL激活状态中的应用价值。
这些文献均通过MLKL抗体阐明了其在细胞死亡中的分子机制,涵盖了结构、功能及疾病相关研究。
The MLKL (Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-Like) protein is a key executor of necroptosis, a regulated form of necrotic cell death that occurs under conditions of apoptosis inhibition or specific inflammatory signaling. As a terminal component of the necroptosis pathway, MLKL is activated via phosphorylation by RIPK3 (Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 3) within the necrosome complex. This triggers MLKL's oligomerization, membrane translocation, and pore formation, leading to plasma membrane rupture and inflammatory cytokine release. MLKL antibodies are essential tools for studying necroptosis mechanisms, enabling detection of MLKL expression, phosphorylation status (e.g., at Ser358/Thr357 in humans), and subcellular localization.
Structurally, MLKL contains an N-terminal four-helix bundle (4HB) domain critical for membrane disruption and a C-terminal pseudokinase domain regulating activation. Antibodies targeting distinct epitopes (e.g., phosphorylated vs. total MLKL) help differentiate inactive and active states. Research applications include Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and flow cytometry to explore necroptosis in diseases like cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and inflammatory conditions. MLKL knockout validation and inhibitor studies also rely on specific antibodies. However, antibody specificity remains a challenge due to sequence homology across species and cross-reactivity with related kinases. Validated MLKL antibodies are crucial for elucidating pathological roles of necroptosis and developing therapeutic strategies targeting this pathway.
×