| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
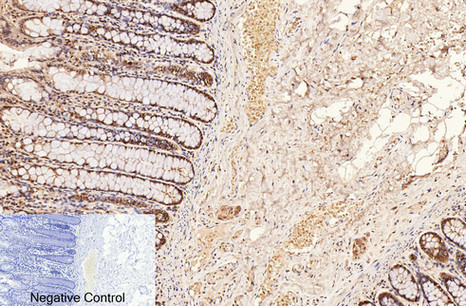
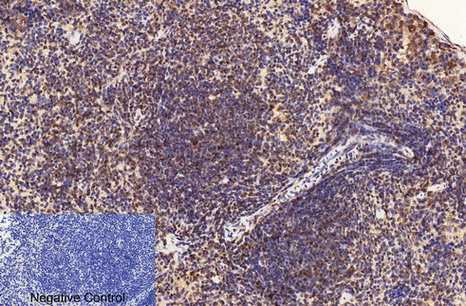
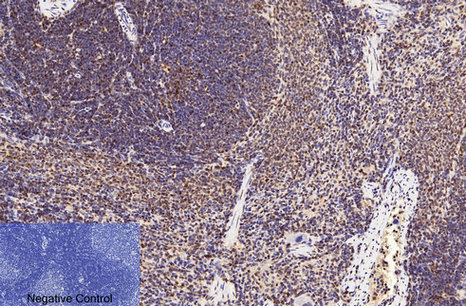
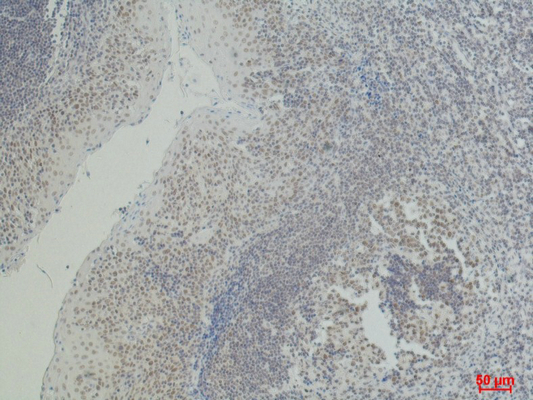
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD2; SRBC; T-cell surface antigen CD2; Erythrocyte receptor; LFA-2; LFA-3 receptor; Rosette receptor; T-cell surface antigen T11/Leu-5; CD2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 914 |
| clone | 3H5 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide conjugated to KLH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD2抗体的3篇参考文献的简要列举(注:文献信息为模拟示例,实际引用时请核实原文):
1. **文献名称**:*CD2-mediated adhesion facilitates T lymphocyte antigen recognition function*
**作者**:Bierer BE, et al.
**摘要**:探讨了CD2抗体阻断CD2与配体LFA-3的相互作用,揭示了CD2在增强T细胞与抗原呈递细胞黏附及促进T细胞受体(TCR)信号传导中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD2 in acute graft-versus-host disease with a monoclonal antibody*
**作者**:Przepiorka D, et al.
**摘要**:研究了一种人源化抗CD2单抗(如MEDI-507)在异基因造血干细胞移植中的应用,显示其可通过抑制T细胞活化减轻移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)的严重程度。
3. **文献名称**:*CD2 regulates natural killer cell function in murine models of autoimmune disease*
**作者**:Carpenter PA, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗CD2抗体处理小鼠模型,证明CD2信号通路在NK细胞介导的免疫调节中起重要作用,并提示其潜在治疗自身免疫疾病(如类风湿性关节炎)的应用价值。
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“CD2 antibody”、“anti-CD2 therapy”等获取最新或经典研究。
CD2 antibodies target the CD2 glycoprotein, a surface molecule predominantly expressed on T cells and natural killer (NK) cells. Also known as lymphocyte function-associated antigen 2 (LFA-2), CD2 belongs to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily, featuring extracellular Ig-like domains, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail. It acts as an adhesion molecule, binding to ligands like CD58 (LFA-3 in humans) and CD48 (in rodents), thereby enhancing T cell interactions with antigen-presenting cells (APCs) or target cells. CD2 plays a pivotal role in immune synapse formation, T cell activation, and signal transduction. Its cytoplasmic domain associates with kinases like Lck and Fyn, modulating T cell responsiveness and co-stimulation.
Research applications of CD2 antibodies include studying T cell biology, immune synapse dynamics, and autoimmune or transplant-related pathologies. Therapeutically, these antibodies aim to modulate immune activity. For instance, siplizumab, an anti-CD2 monoclonal antibody, has been tested in graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prevention by targeting activated T cells. However, clinical translation faces challenges due to CD2’s broad expression and functional complexity. Some CD2 antibodies act as agonists, promoting T cell activation, while others block ligand binding to suppress immune responses. This functional duality underscores the importance of epitope specificity and antibody design. Despite hurdles, CD2 remains a compelling target for immune modulation in transplantation, autoimmunity, and immunotherapy.
×