| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
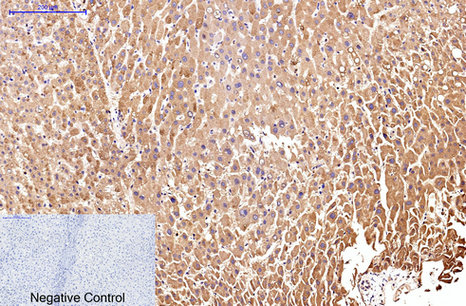
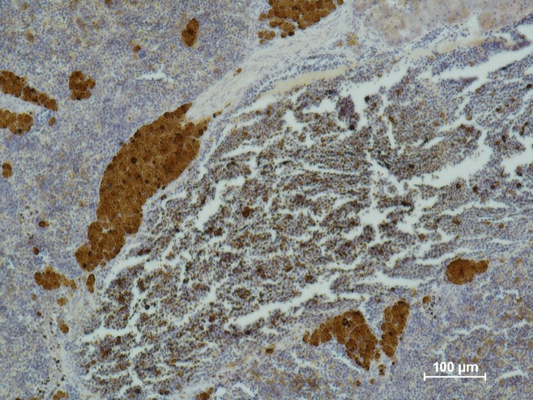
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL2RA; Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha; IL-2 receptor subunit alpha; IL-2-RA; IL-2R subunit alpha; IL2-RA; TAC antigen; p55; CD25 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3559 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide of CD25 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IL-2受体α(CD25)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要列举:
1. **"The interleukin-2 receptor: a target for monoclonal antibody treatment of human T-cell lymphotrophic virus I-induced adult T-cell leukemia"**
- **作者**: Waldmann, T.A. 等
- **摘要**: 该研究探讨了抗IL-2Rα单克隆抗体在成人T细胞白血病(ATL)治疗中的应用,证明其可通过靶向CD25抑制白血病细胞增殖,为免疫治疗提供理论依据。
2. **"Basiliximab (Simulect) in renal transplantation: A review of its use as induction therapy in adults"**
- **作者**: Nashan, B. 等
- **摘要**: 评估巴利昔单抗(抗CD25抗体)作为肾移植诱导疗法的效果,显示其显著降低急性排斥反应发生率,且安全性良好。
3. **"Daclizumab: Development, clinical trials, and practical aspects of humanized antibodies"**
- **作者**: Junghans, R.P. 等
- **摘要**: 分析达利珠单抗的人源化设计及其在多发性硬化症中的临床试验,揭示其通过阻断IL-2信号通路抑制过度激活的T细胞,但也讨论其因副作用退市的原因。
4. **"Targeting regulatory T cells by addressing tumor necrosis factor and its receptors in autoimmune disease and cancer"**(补充文献,涉及CD25机制)
- **作者**: Chen, X. 等
- **摘要**: 研究抗CD25抗体通过耗竭调节性T细胞(Treg)增强抗肿瘤免疫反应的机制,为癌症联合治疗提供新思路。
注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对最新研究。
The IL-2 receptor alpha chain (IL-2Rα, CD25) is a key component of the high-affinity interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor complex, which also includes IL-2Rβ (CD122) and the common gamma chain (γc, CD132). IL-2Rα is primarily expressed on activated T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), and certain leukemic cells. While it lacks intrinsic signaling capacity, IL-2Rα enhances IL-2 binding affinity, enabling critical immune functions such as T cell proliferation, differentiation, and immune tolerance mediated by Tregs.
Dysregulation of IL-2Rα is implicated in autoimmune diseases, organ transplant rejection, and cancers. In autoimmunity, excessive T cell activation via IL-2 signaling drives inflammation, whereas in T cell malignancies like adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL), CD25 overexpression promotes pathological cell survival. Therapeutic antibodies targeting IL-2Rα, such as basiliximab and daclizumab, exploit this specificity. These agents block IL-2/IL-2Rα interaction, suppressing T cell activation. Basiliximab remains widely used to prevent acute organ rejection, while daclizumab (withdrawn due to safety concerns) previously treated multiple sclerosis.
Beyond immunosuppression, anti-CD25 antibodies serve diagnostic roles. Elevated CD25 levels in serum or on cell surfaces are biomarkers for diseases like ATLL or autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS). Emerging applications include antibody-drug conjugates and engineered CAR-T cells targeting CD25+ malignancies. However, challenges persist in balancing efficacy with off-target effects, particularly on Tregs, which are essential for maintaining immune homeostasis. Ongoing research aims to refine targeting strategies to improve therapeutic precision.
×