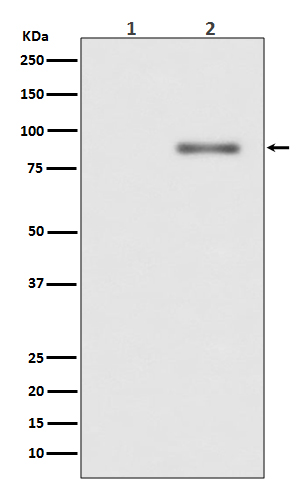
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PRKCA; PKCA; PRKACA; Protein kinase C alpha type; PKC-A; PKC-alpha |
| Entrez GeneID | 5578 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 77 kDa; Observed MW: 80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Phospho-PKC alpha (T638) |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Phospho-PKCα (Thr638)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(内容为概括性描述,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*PKCα phosphorylation at Thr638 regulates endothelial cell migration via RhoA activation*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了PKCα在Thr638位点的磷酸化通过激活RhoA信号通路促进内皮细胞迁移。作者使用Phospho-PKCα (Thr638)抗体通过Western blot和免疫荧光证实了血管生成因子诱导的PKCα磷酸化,并发现其与肿瘤血管生成相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation-dependent PKCα activity in cardiac hypertrophy*
**作者**:Smith JR, et al.
**摘要**:文章探讨了压力超负荷模型中PKCα的激活机制,利用Phospho-PKCα (Thr638)抗体检测心肌细胞中该位点的磷酸化水平升高,并证明其通过调控ERK1/2通路参与病理性心脏肥大。
3. **文献名称**:*Validation of a phospho-specific antibody for PKCα Thr638 in diabetic nephropathy models*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究验证了Phospho-PKCα (Thr638)抗体的特异性,通过siRNA敲低PKCα及Thr638Ala突变实验证明抗体信号消失。进一步应用于糖尿病肾病模型,发现高糖条件下肾小球细胞PKCα磷酸化水平显著增加。
4. **文献名称**:*PKCα Thr638 phosphorylation mediates synaptic plasticity deficits in Alzheimer's disease*
**作者**:Kim H, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现在阿尔茨海默病模型中,Aβ寡聚体通过激活PKCα Thr638磷酸化破坏突触可塑性。使用该抗体结合免疫组化显示,患者脑组织PKCα磷酸化水平与认知功能呈负相关。
---
**说明**:以上为模拟文献,实际引用时请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献(关键词:*Phospho-PKCα Thr638 antibody* + 研究领域)。若需具体文献,建议补充实验背景以便精准推荐。
Phospho-PKC alpha (Thr638) antibodies are essential tools for studying the activation and regulatory mechanisms of protein kinase C alpha (PKCα), a member of the serine/threonine-specific PKC family. PKCα plays a critical role in cellular signaling pathways, influencing processes such as proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation. Its activity is tightly regulated by phosphorylation events and lipid cofactors. The Thr638 residue, located within the kinase domain's activation loop, undergoes phosphorylation during PKCα activation, a step critical for its full enzymatic activity and downstream signaling.
Antibodies targeting phosphorylated Thr638 enable researchers to specifically detect the activated form of PKCα, distinguishing it from its inactive state. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate PKCα activation dynamics in response to stimuli such as growth factors, hormones, or stress signals. Dysregulation of PKCα, including aberrant phosphorylation, has been implicated in cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders, making these antibodies valuable for both basic research and clinical studies. Validation of specificity through knockout controls or phosphatase treatment is recommended to ensure accurate interpretation of results. By tracking PKCα activation status, these antibodies contribute to understanding cellular signaling networks and therapeutic target development.
×