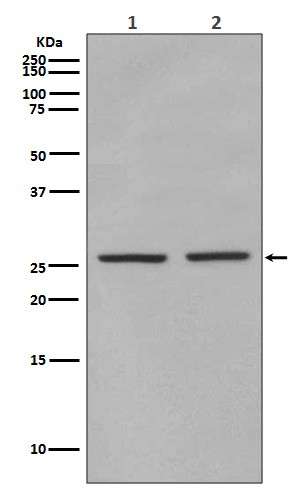
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
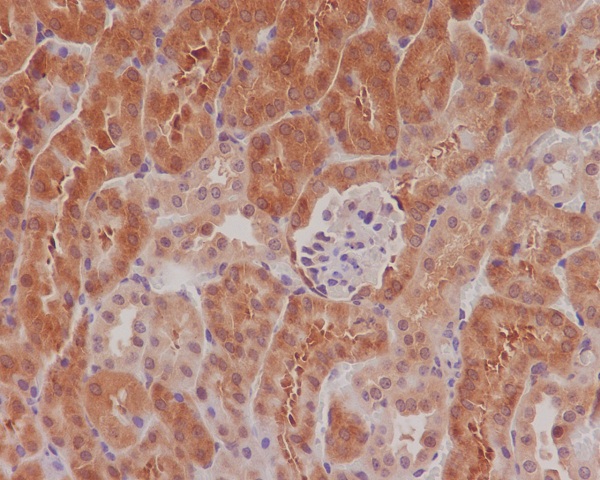
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EIF4E; EIF4EL1; EIF4F; Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; eIF-4E; eIF4E; eIF-4F 25 kDa subunit; mRNA cap-binding protein |
| Entrez GeneID | 1977 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 25 kDa; Observed MW: 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Phospho-eIF4E (S209) |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于 **Phospho-eIF4E (Ser209) 抗体**的3篇代表性文献,按研究背景与内容简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*mTOR-mediated phosphorylation of eIF4E contributes to its post-transcriptional effects on gene expression*
**作者**:Topisirovic, I. et al.
**摘要**:研究证实 mTOR 信号通路通过磷酸化 eIF4E(Ser209)调控其与 mRNA 帽结构的结合能力,影响特定致癌基因(如 cyclin D1)的翻译效率。实验中利用 Phospho-eIF4E (Ser209) 抗体验证了雷帕霉素(mTOR 抑制剂)对 eIF4E 磷酸化的抑制作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*eIF4E phosphorylation promotes tumorigenesis and is associated with prostate cancer progression*
**作者**:Furic, L. et al.
**摘要**:通过癌症细胞模型和临床样本分析,发现 eIF4E 的 Ser209 磷酸化水平与前列腺癌侵袭性呈正相关。使用 Phospho-eIF4E (Ser209) 抗体检测发现,磷酸化 eIF4E 通过增强促生存蛋白(如 Mcl-1)的翻译驱动肿瘤生长。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of eIF4E confers resistance to cellular stress and DNA-damaging agents*
**作者**:Mamane, Y. et al.
**摘要**:研究显示,DNA 损伤或氧化应激条件下,eIF4E 的 Ser209 磷酸化通过 MAPK 通路被激活,促进应激相关 mRNA 的优先翻译。利用特异性抗体阻断磷酸化 eIF4E 可显著增强细胞对化疗药物的敏感性。
---
**备注**:上述文献均聚焦于 eIF4E 磷酸化在基因表达调控、癌症进展及治疗抵抗中的机制,实验方法中均依赖 Phospho-eIF4E (Ser209) 抗体进行蛋白活性检测。如需具体期刊与年份,可进一步补充数据库检索(如 PubMed)。
Phospho-eIF4E (Ser209) antibody detects the phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) at serine residue 209. a post-translational modification critical for regulating mRNA translation. eIF4E, a key component of the eIF4F complex, binds to the 5' cap structure of mRNAs to initiate cap-dependent translation. Its activity is tightly controlled by phosphorylation, primarily mediated by the MNK (MAP kinase-interacting kinase) kinases downstream of RAS-MAPK or PI3K-AKT signaling pathways. Phosphorylation at Ser209 enhances eIF4E’s affinity for the mRNA cap and promotes the selective translation of oncogenic mRNAs involved in cell proliferation, survival, and metastasis, such as c-Myc, VEGF, and cyclin D1. Dysregulation of eIF4E phosphorylation is linked to tumorigenesis, chemoresistance, and poor prognosis in cancers like leukemia, breast cancer, and glioblastoma.
The Phospho-eIF4E (Ser209) antibody is widely used in research to study translational control mechanisms, cellular stress responses, and cancer biology. It helps assess eIF4E activation status in experimental models, including drug-treated cells or tumor samples, and validates the efficacy of therapeutic agents targeting MNK kinases or upstream signaling pathways. Specificity is ensured by using synthetic peptides corresponding to the phosphorylated Ser209 epitope for immunization. Applications span Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence, enabling insights into eIF4E’s role in diseases and its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target.
×