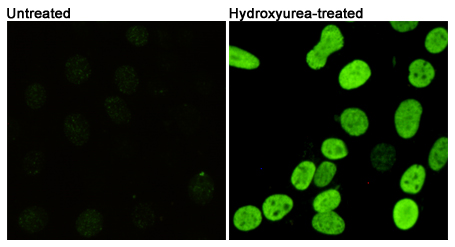
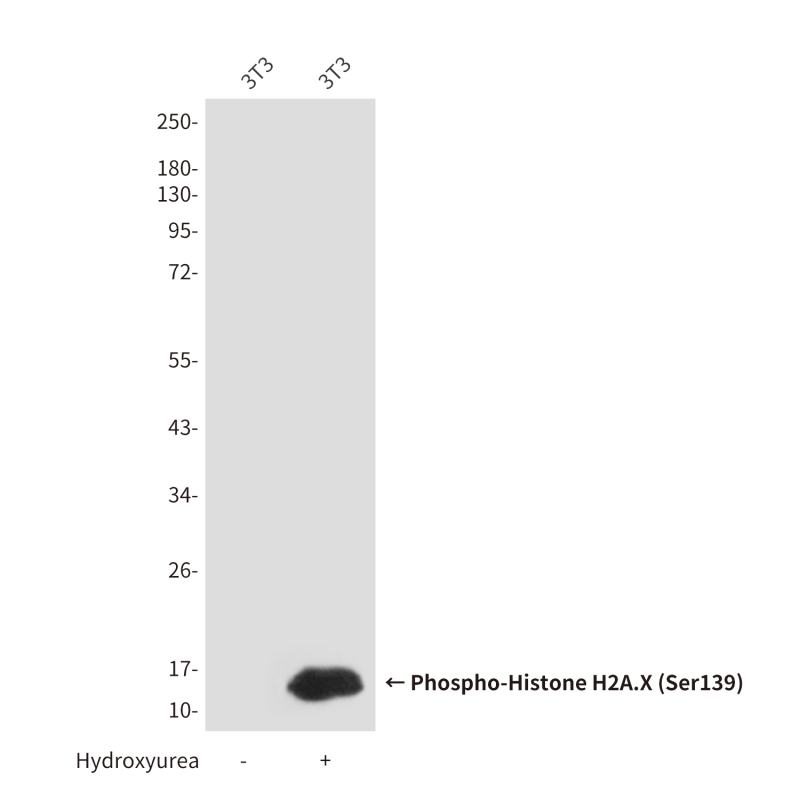
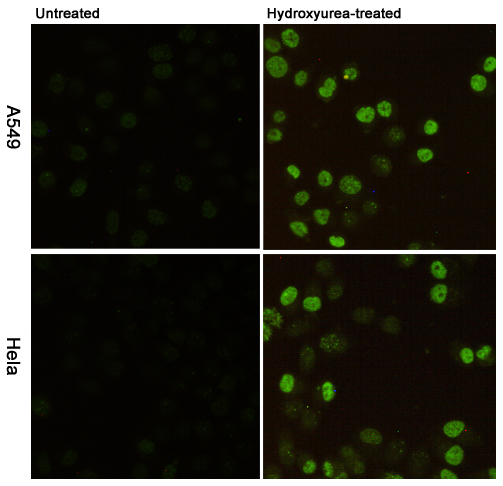
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | H2A.X; H2AFX; H2a/x; HIST5-2AX; Histone H2A.X; gamma H2A.X |
| Entrez GeneID | 3014 |
| clone | 9D4 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 15 kDa; Observed MW: 15 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser139 of human H2A.X. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **"DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139"**
- **作者**: Rogakou, E.P., Pilch, D.R., Orr, A.H., Ivanova, V.S., Bonner, W.M.
- **摘要**: 该研究首次报道了DNA双链断裂(DSBs)后组蛋白H2AX在Ser139位点的磷酸化(γ-H2AX),揭示了其在DNA损伤应答中的关键作用,并建立了γ-H2AX作为DSBs的分子标记。
2. **"γ-H2AX as a biomarker of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation in human peripheral blood lymphocytes"**
- **作者**: Sedelnikova, O.A., Rogakou, E.P., Panyutin, I.G., Bonner, W.M.
- **摘要**: 研究通过免疫荧光技术验证了γ-H2AX抗体在检测电离辐射诱导的DNA损伤中的应用,证明γ-H2AX焦点数量与辐射剂量呈正相关,支持其作为辐射暴露的生物标志物。
3. **"The role of γ-H2AX in cancer treatment"**
- **作者**: Bonner, W.M., Redon, C.E., Dickey, J.S., Nakamura, A.J., Sedelnikova, O.A., et al.
- **摘要**: 综述了γ-H2AX在癌症治疗中的重要性,强调其作为化疗和放疗后DNA损伤的动态指标,可用于评估治疗效果及预测患者预后。
4. **"Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low X-ray doses"**
- **作者**: Rothkamm, K., Löbrich, M.
- **摘要**: 利用γ-H2AX抗体检测低剂量X射线引起的DNA损伤,发现极低剂量下细胞无法有效修复DSBs,为辐射防护研究提供了关键实验依据。
Phospho-Histone H2A.X (Ser139) antibody detects the phosphorylated form of histone H2A.X at serine 139. a key biomarker of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Histone H2A.X, a variant of the H2A histone family, becomes rapidly phosphorylated at Ser139 (forming γH2A.X) in response to DNA damage, particularly DSBs induced by ionizing radiation, chemotherapeutic agents, or oxidative stress. This phosphorylation event is mediated by kinases such as ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK, which are activated as part of the DNA damage response (DDR) signaling cascade. The formation of γH2A.X foci serves as a molecular beacon, recruiting repair proteins (e.g., MDC1. 53BP1) to facilitate DNA repair and maintain genomic stability.
The Phospho-Histone H2A.X (Ser139) antibody is widely used in research to visualize and quantify DSBs, assess genomic instability, and study DDR mechanisms. Applications include immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and flow cytometry, enabling insights into cancer biology, radiation therapy, and genotoxic drug development. It is also employed in studying apoptosis, replication stress, and cellular senescence. Validating antibody specificity is critical, as non-specific signals may arise from cross-reactivity or experimental conditions. Overall, this antibody is a cornerstone tool for understanding DNA damage-related pathways and their implications in disease and therapy.
×