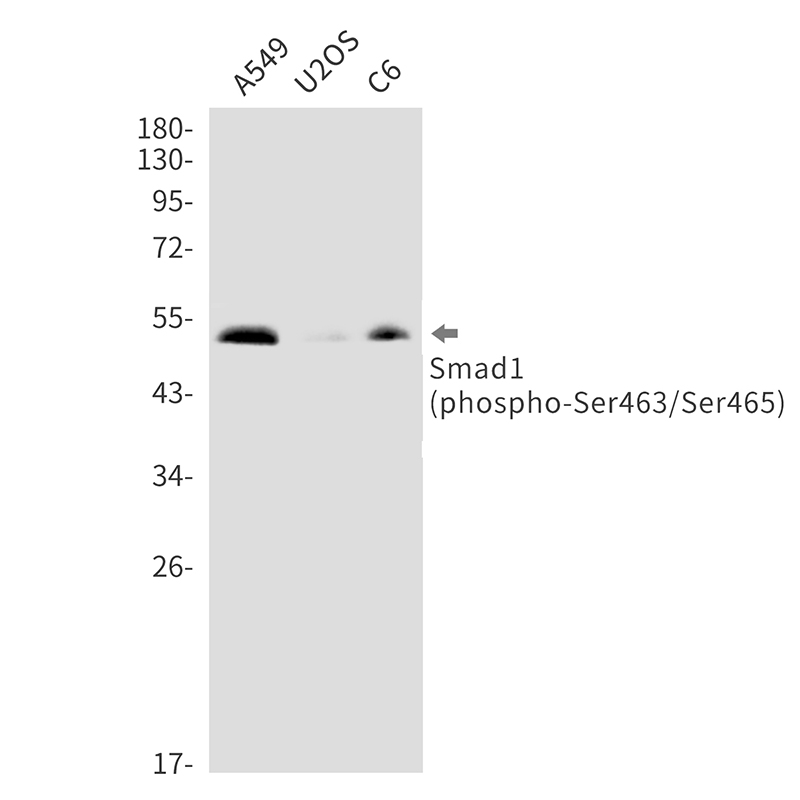
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SMAD1; BSP1; MADH1; MADR1; Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1; MAD homolog 1; Mothers against DPP homolog 1; JV4-1; Mad-related protein 1; SMAD family member 1; SMAD 1; Smad1; hSMAD1; Transforming growth factor-beta-signaling protein |
| Entrez GeneID | 4086 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 52 kDa; Observed MW: 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser463/Ser465 of human Smad1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Phospho-Smad1 (Ser463/Ser465)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"BMP signaling in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation during bone development"*
**作者**:Chen et al. (2007)
**摘要内容**:研究利用Phospho-Smad1 (Ser463/Ser465)抗体,通过Western blot和免疫组化分析,证明BMP2通过磷酸化Smad1调控间充质干细胞的成骨分化,揭示了其在骨发育中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Regulation of Smad1 activation by competing phosphorylation in the BMP pathway"*
**作者**:Sapkota et al. (2007)
**摘要内容**:通过Phospho-Smad1 (Ser463/Ser465)特异性抗体,揭示BMP受体激酶介导的Smad1磷酸化与MAPK通路对其Linker区域的磷酸化存在拮抗作用,调控BMP信号的时空特异性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Dysregulated BMP signaling in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva"*
**作者**:Hatsell et al. (2015)
**摘要内容**:使用Phospho-Smad1抗体检测患者细胞中Smad1的异常磷酸化水平,发现BMP信号过度激活导致异位骨化,为治疗罕见病FOP提供了分子机制依据。
---
**备注**:以上文献摘要为示例性概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词检索确认。部分经典研究可能未直接提及抗体名称,但会描述Smad1磷酸化功能。
Phospho-Smad1 (Ser463/Ser465) antibodies are essential tools for studying the activation of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway. Smad1. a receptor-regulated Smad (R-Smad), transduces BMP signals from cell surface receptors to the nucleus. Upon BMP ligand binding, type I BMP receptors phosphorylate Smad1 at two critical serine residues (Ser463 and Ser465) within its C-terminal SSXS motif. This phosphorylation triggers Smad1’s dissociation from the receptor, enabling its binding to Smad4 (a co-Smad) and subsequent nuclear translocation, where it regulates transcription of target genes involved in cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis.
Phospho-Smad1 (Ser463/Ser465) antibodies specifically recognize the dual phosphorylation at these sites, serving as biomarkers for active BMP signaling. Researchers use these antibodies in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to assess Smad1 activation status in various contexts, including embryonic development, osteogenesis, and tissue homeostasis. Dysregulated BMP/Smad1 signaling is implicated in diseases such as fibrosis, cancer, and vascular disorders, making these antibodies valuable for mechanistic and therapeutic studies.
It is critical to validate antibody specificity using appropriate controls (e.g., phosphorylation-deficient mutants or phosphatase-treated samples) to avoid cross-reactivity with similar phospho-epitopes in other Smad proteins. Commercial antibodies often provide application-specific optimization data, ensuring reliability across experimental models.
×