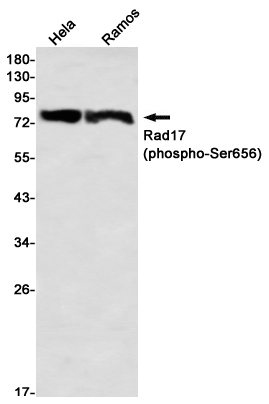
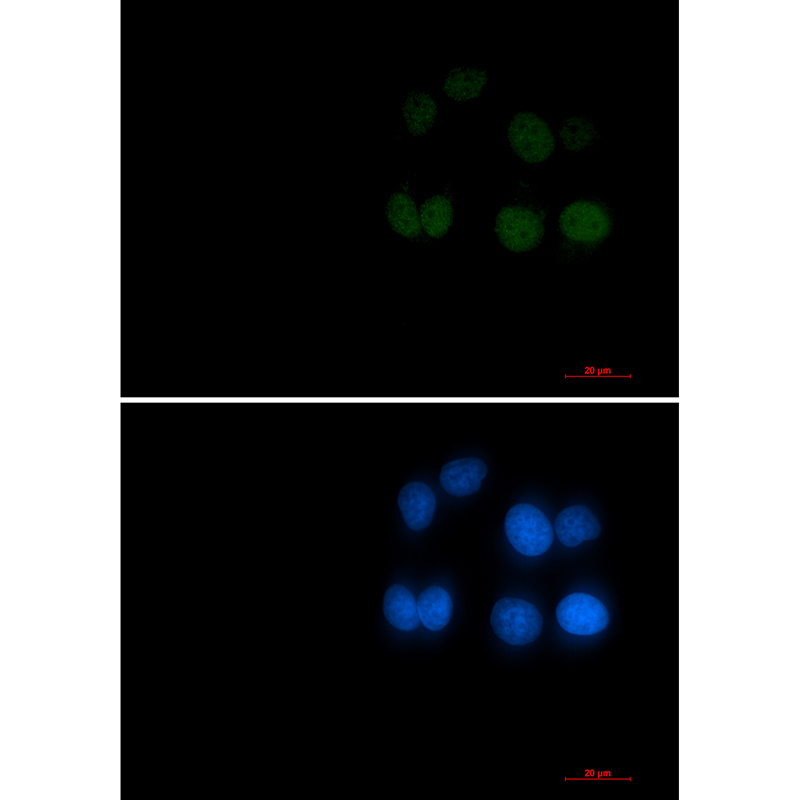
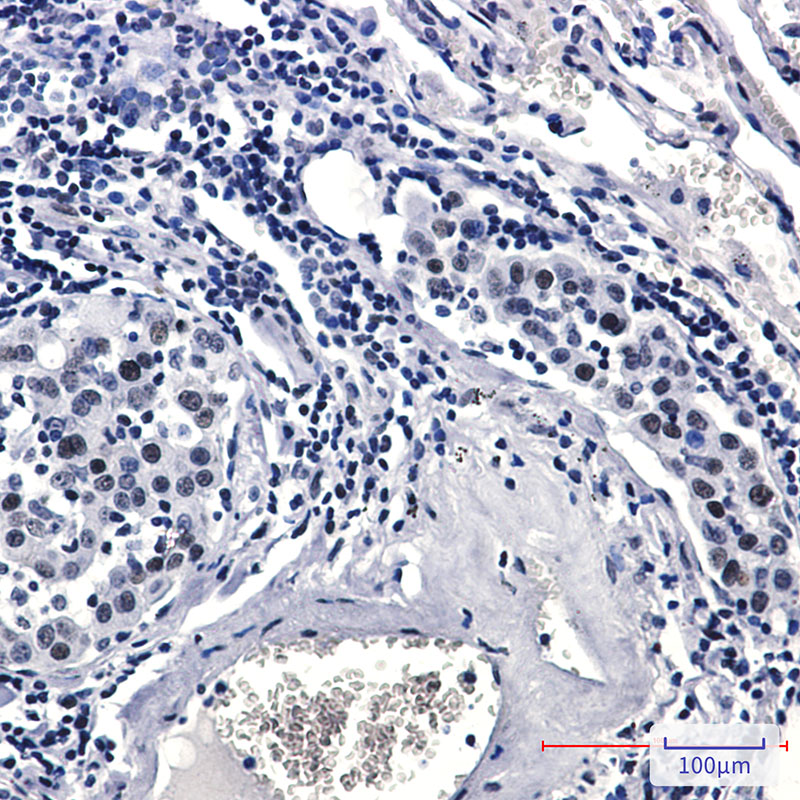
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RAD17; R24L; Cell cycle checkpoint protein RAD17; hRad17; RF-C/activator 1 homolog |
| Entrez GeneID | 5884 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 77 kDa; Observed MW: 80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser656 of human Rad17 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **"Phosphorylation of Rad17 by ATR is required for checkpoint activation"**
- **作者**: Zhao H, Piwnica-Worms H
- **摘要**: 研究发现Rad17在Ser656位点的磷酸化由ATR激酶介导,是DNA损伤后激活细胞周期检查点的关键步骤,确保基因组稳定性。
2. **"Distinct roles of Rad17 and Chk1 phosphorylation in DNA damage checkpoint control"**
- **作者**: Post S, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过Phospho-Rad17 (Ser656)抗体验证,Rad17的磷酸化在DNA复制压力中特异性激活ATR-Chk1信号通路,区别于其他检查点蛋白的调控机制。
3. **"Rad17 phosphorylation is required for claspin recruitment and ATR signaling activation"**
- **作者**: Bao S, et al.
- **摘要**: 实验利用Phospho-Rad17 (Ser656)抗体证实,Rad17的磷酸化促进Claspin蛋白向损伤位点募集,从而激活下游ATR信号并阻滞细胞周期进程。
4. **"DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of Rad17 regulates its interaction with the 9-1-1 complex"**
- **作者**: Wang X, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究通过磷酸化特异性抗体分析,表明Ser656磷酸化调控Rad17与9-1-1复合体的结合,影响DNA损伤修复效率及检查点功能。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用需核实具体论文内容及数据库。)
The Phospho-Rad17 (Ser656) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect Rad17 protein phosphorylated at serine residue 656. a post-translational modification critical for its role in DNA damage response and cell cycle regulation. Rad17. a key component of the Rad9-Rad1-Hus1 (9-1-1) complex-related family, functions as a checkpoint clamp loader. It facilitates the recruitment of DNA repair and signaling proteins to sites of genomic lesions, particularly during replication stress or ionizing radiation-induced damage. Phosphorylation of Rad17 at Ser656 is mediated by ATM/ATR kinases in response to DNA damage, marking its activation and promoting checkpoint signaling to halt cell cycle progression until repairs are completed.
This antibody is widely utilized in research to study the molecular mechanisms of DNA damage checkpoints, replication stress, and genomic stability. It helps assess Rad17 activation status in experimental models, including cancer cells, where dysregulated DNA repair pathways contribute to tumorigenesis or therapeutic resistance. Detection of phosphorylated Rad17 (Ser656) via Western blot, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry provides insights into cellular responses to genotoxic agents, such as chemotherapy or radiation. Its specificity for the phosphorylated form makes it valuable for distinguishing active Rad17 from its inactive state, aiding in the exploration of checkpoint adaptation, apoptosis, and cancer biology. Proper validation using phosphorylation-deficient mutants or kinase inhibitors is recommended to confirm signal specificity.
×