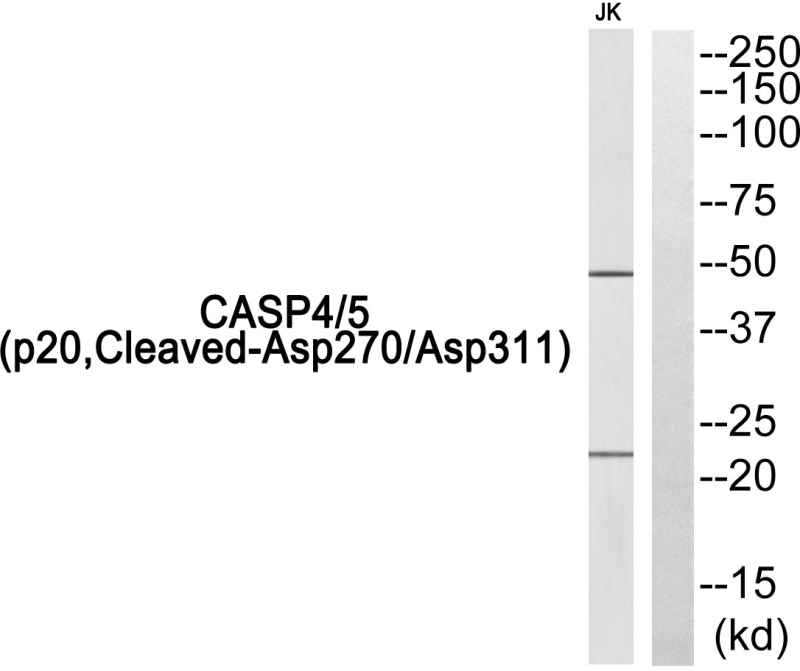
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TX; Mih1; ICH-2; Mih1/TX; ICEREL-II; ICE(rel)II |
| Entrez GeneID | 837/838 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 43 kDa; Observed MW: 47,22 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human Caspase 4/5. AA range:221-270 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及Cleaved-Caspase 4/5 p20抗体使用的参考文献,按研究背景与核心结论整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Caspase-11 activates interleukin-1 via cleavage of the pyroptotic protein gasdermin D*
**作者**:Kayagaki N. et al.
**摘要**:本研究证明,在革兰氏阴性菌感染或LPS刺激下,Caspase-11(小鼠同源为人类Caspase-4/5)通过切割gasdermin D诱导细胞焦亡,并激活IL-1β。Western blot使用Cleaved-Caspase-4/5 p20抗体证实其活化,为败血症模型中的炎症机制提供依据。
---
2. **文献名称***:*Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11*
**作者**:Shi J. et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示非经典炎症小体通过Caspase-4/5识别胞内LPS,导致p20片段的生成。通过特异性抗体检测p20.证实其在巨噬细胞响应沙门氏菌感染时的激活,并触发细胞焦亡及IL-1β释放,揭示了病原体免疫应答的新通路。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Human caspase-4 mediates noncanonical inflammasome activation against gram-negative bacterial pathogens*
**作者**:Casson C.N. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用Cleaved-Caspase-4 p20抗体,证明人源Caspase-4在识别志贺氏菌等病原体时被激活,切割下游底物并诱导细胞死亡。该抗体在感染模型中特异性标记活化的Caspase-4.为宿主防御机制研究提供关键工具。
---
**备注**:上述研究均通过Western blot或免疫荧光使用p20抗体,验证Caspase-4/5在感染或炎症中的活化状态,并关联其病理生理学功能(如焦亡、细胞因子释放)。若需具体实验细节,建议查阅原文方法学部分。
Cleaved-Caspase-4/5 p20 antibodies are immunological tools designed to detect the activated forms of Caspase-4 and Caspase-5. two inflammatory caspases involved in innate immunity and pyroptosis. Caspase-4 and Caspase-5 (functionally analogous to Caspase-11 in mice) are cytosolic sensors that recognize intracellular lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Gram-negative bacteria, triggering non-canonical inflammasome activation. Upon LPS binding, these caspases undergo oligomerization and autoproteolytic cleavage, generating active subunits including the p20 fragment. The p20 subunit, a conserved catalytic domain, is critical for their enzymatic activity in cleaving gasdermin D (GSDMD) to induce pyroptosis and promote IL-1β/IL-18 maturation.
Antibodies targeting the cleaved p20 subunit specifically recognize the processed, active forms of Caspase-4/5. avoiding cross-reactivity with their inactive pro-forms. These antibodies are widely used in immunoblotting, immunofluorescence, and flow cytometry to study inflammasome activation, host-pathogen interactions, and inflammatory cell death in conditions like sepsis, infections, or autoimmune diseases. Their specificity makes them valuable for distinguishing between basal and pathogen-induced caspase activation, aiding research on inflammatory signaling pathways and therapeutic targeting. Validation often includes knockout controls to confirm signal specificity, as Caspase-4/5 share high homology.
×