| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ACAT; acat1; MAT; RATACAL; THIL;;ACAT1 |
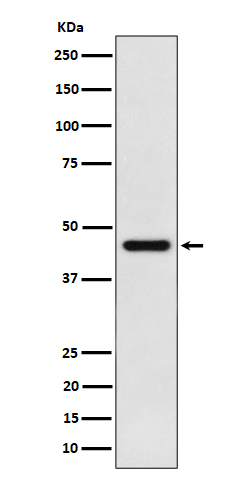
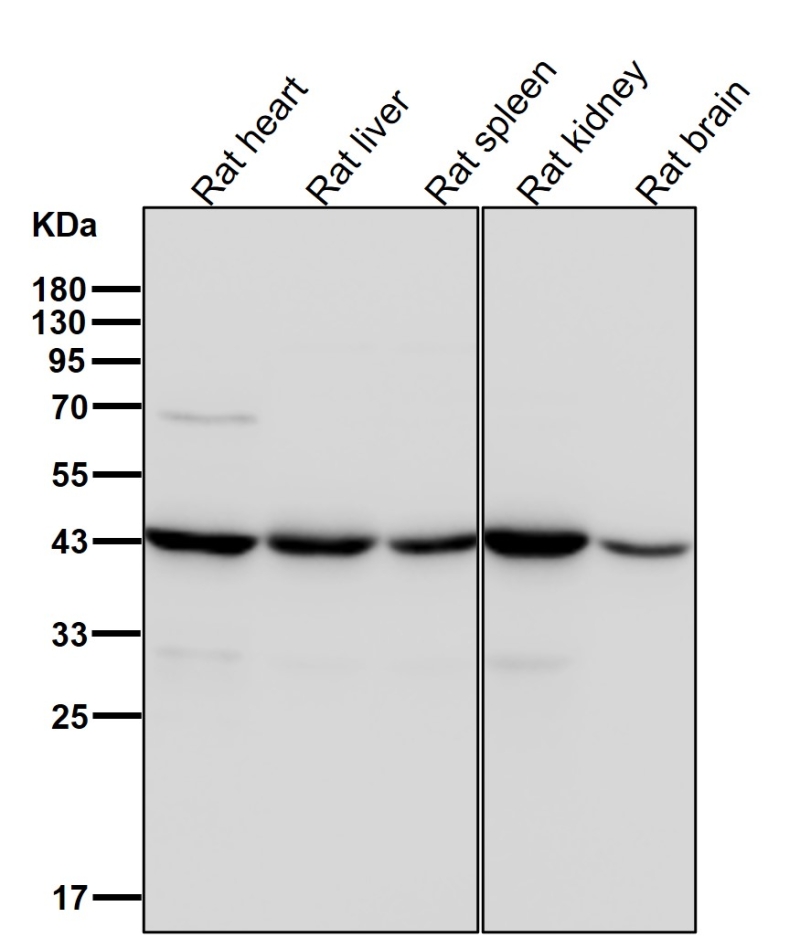
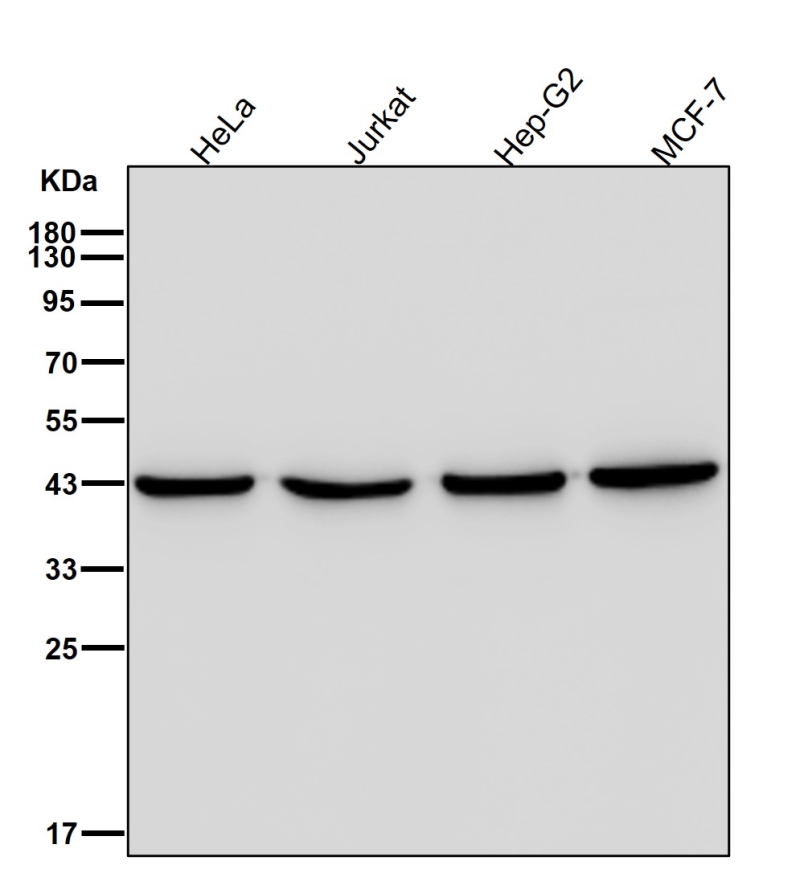
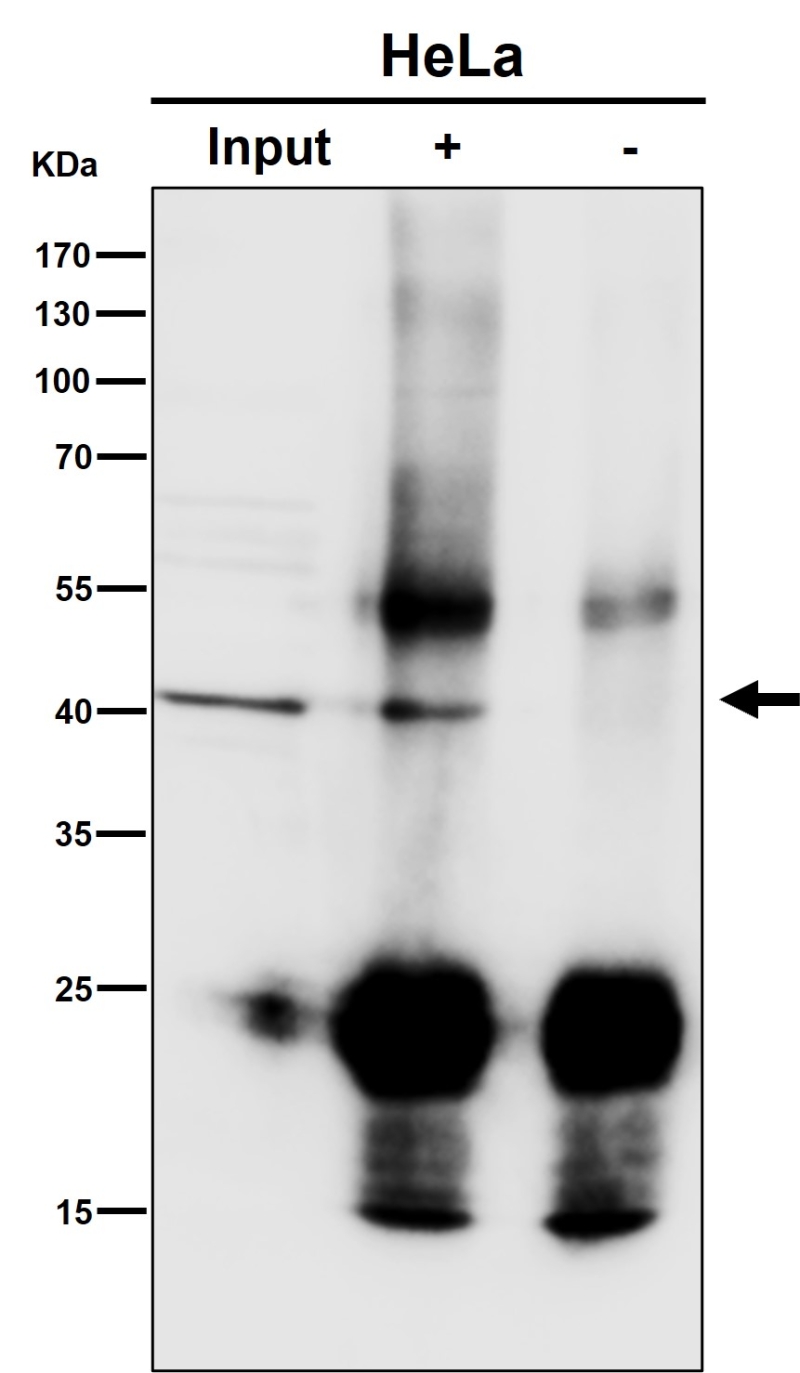
| WB Predicted band size | 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ACAT1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ACAT1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究整理,建议通过学术数据库核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Molecular cloning and functional expression of human acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase cDNA in mammalian cells*
**作者**: Chang TY, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次克隆了人源ACAT1基因,并利用哺乳动物细胞表达系统验证其酶活性。研究中开发的ACAT1抗体被用于蛋白质定位和表达水平检测,证实ACAT1在内质网中的分布及其在胆固醇酯化中的核心作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Tissue-specific expression of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) isoforms*
**作者**: Ikemoto M, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组织化学和Western blot技术,结合ACAT1特异性抗体,揭示了ACAT1在小鼠肝脏、巨噬细胞等组织中的高表达模式,并对比了其与ACAT2的亚细胞定位差异,为研究不同组织胆固醇代谢机制提供依据。
---
3. **文献名称**: *ACAT1 deficiency in mice increases amyloid beta deposition in Alzheimer's disease models*
**作者**: Hutter-Paier B, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用ACAT1基因敲除小鼠模型及特异性抗体检测,发现ACAT1缺失会加剧β-淀粉样蛋白沉积,提示其在阿尔茨海默病病理中的潜在调控作用,抗体被用于验证脑组织中ACAT1蛋白水平的改变。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用时请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台核对原文信息及可用性。
ACAT1 (Acetyl-CoA Acetyltransferase 1), also known as sterol O-acyltransferase 1. is an enzyme encoded by the *SOAT1* gene. It plays a critical role in cellular cholesterol metabolism by catalyzing the esterification of cholesterol into cholesteryl esters, which are stored in lipid droplets. This process is essential for maintaining cholesterol homeostasis, as excess free cholesterol can be toxic to cells. ACAT1 is primarily localized in the endoplasmic reticulum and is highly expressed in tissues involved in lipid metabolism, such as the liver, adrenal glands, and macrophages.
ACAT1-specific antibodies are widely used in research to study the enzyme's expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate ACAT1's role in diseases linked to dysregulated cholesterol metabolism, including atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. For example, ACAT1 inhibition has been explored as a therapeutic strategy to reduce cholesteryl ester accumulation in atherosclerotic plaques.
Commercial ACAT1 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes of the human or mouse protein, with validation in knockout models to ensure specificity. Researchers rely on these tools to dissect ACAT1's regulatory mechanisms, its interaction with lipid droplets, and its potential as a biomarker or drug target. However, variability in antibody performance across applications and species necessitates careful validation for experimental consistency.
×