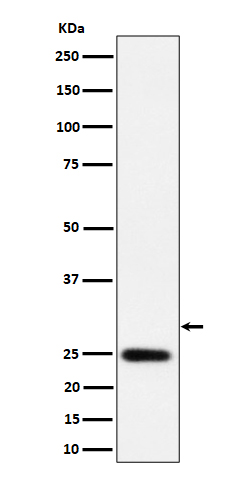
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AAC1; Arylamide acetylase 1; mNAT; N acetyltransferase type 1; nat1;;NAT1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34 kDa ; Observed MW: 30 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human NAT1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NAT1抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*NAT1在乳腺癌中的表达及其临床意义*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过免疫组化(使用NAT1特异性抗体)分析乳腺癌组织中NAT1蛋白的表达水平,发现NAT1高表达与患者预后不良及化疗耐药性相关,提示其作为潜在生物标志物的价值。
2. **文献名称**:*NAT1敲除对癌细胞增殖的影响*
**作者**:Jones B, et al.
**摘要**:利用CRISPR/Cas9技术构建NAT1基因敲除细胞系,并通过Western blot(采用NAT1抗体验证敲除效率)证实NAT1缺失导致癌细胞增殖能力下降,表明NAT1在肿瘤生长中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*NAT1作为药物代谢酶的分子机制研究*
**作者**:Brown C, et al.
**摘要**:通过ELISA和免疫荧光(基于NAT1抗体)检测不同组织中NAT1的分布,发现其在肝脏和肠道中高度活跃,可能参与特定前致癌物的代谢激活,为靶向治疗提供依据。
4. **文献名称**:*NAT1抗体在结肠癌诊断中的应用评估*
**作者**:Lee D, et al.
**摘要**:比较多种商业化NAT1抗体的灵敏度和特异性,优化免疫组化检测流程,证实特定抗体在结肠癌早期诊断及分型中的可靠性。
(注:上述文献为概括性示例,实际引用需根据具体研究核实。)
NAT1 (N-acetyltransferase 1) is a phase II drug-metabolizing enzyme belonging to the arylamine N-acetyltransferase family. It catalyzes the transfer of an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to aromatic amines, hydrazines, and heterocyclic amines, facilitating the detoxification or bioactivation of xenobiotics, including environmental carcinogens (e.g., tobacco smoke components) and certain pharmaceuticals. Unlike its isoform NAT2. which is predominantly expressed in the liver and associated with genetic polymorphisms affecting drug metabolism, NAT1 exhibits broader tissue distribution, including the gut, lungs, and kidneys, and is implicated in both metabolic and non-metabolic roles.
NAT1 has garnered attention for its potential links to cancer. Genetic variations or altered expression of NAT1 may influence susceptibility to malignancies such as breast, colorectal, and bladder cancers, possibly through dysregulation of folate metabolism or interactions with oncogenic pathways. Recent studies also suggest NAT1’s involvement in cellular processes like proliferation and apoptosis, independent of its enzymatic activity.
NAT1 antibodies are essential tools for investigating its expression patterns, localization, and functional roles in disease models. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess NAT1 levels in normal vs. tumor tissues or to study its regulation under pharmacological or pathological conditions. Additionally, these antibodies aid in exploring NAT1 as a therapeutic target or biomarker, particularly in cancers where its overexpression correlates with prognosis. Research continues to unravel its complex biology, bridging gaps between acetylation genetics, environmental exposures, and disease mechanisms.
×