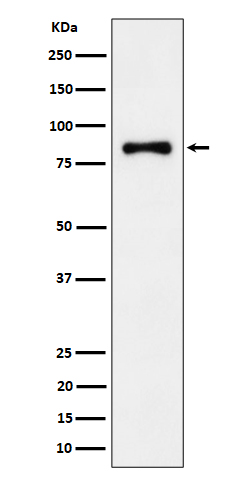
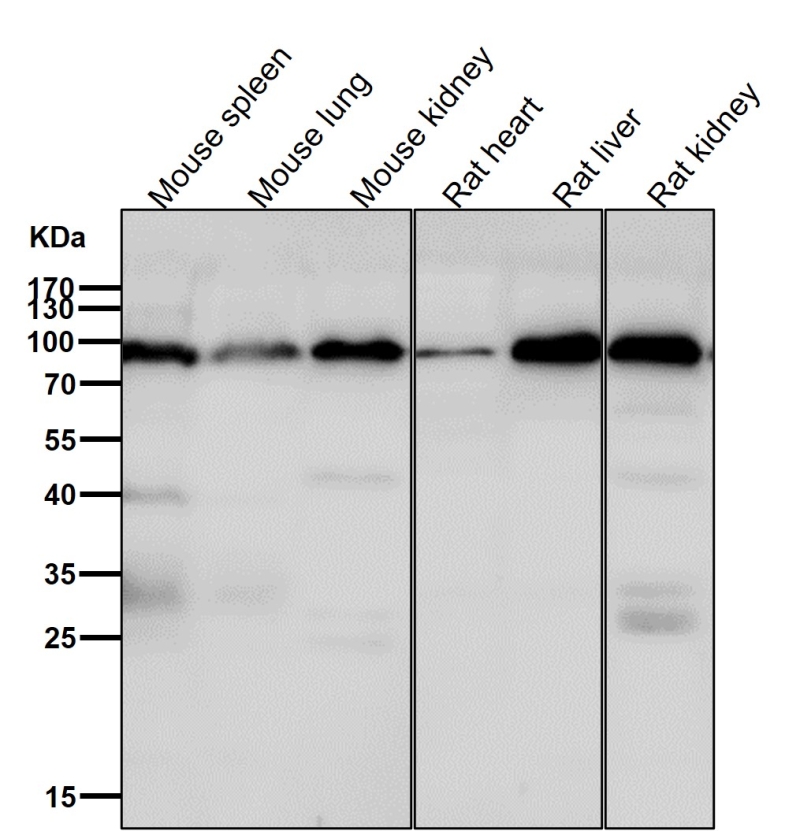
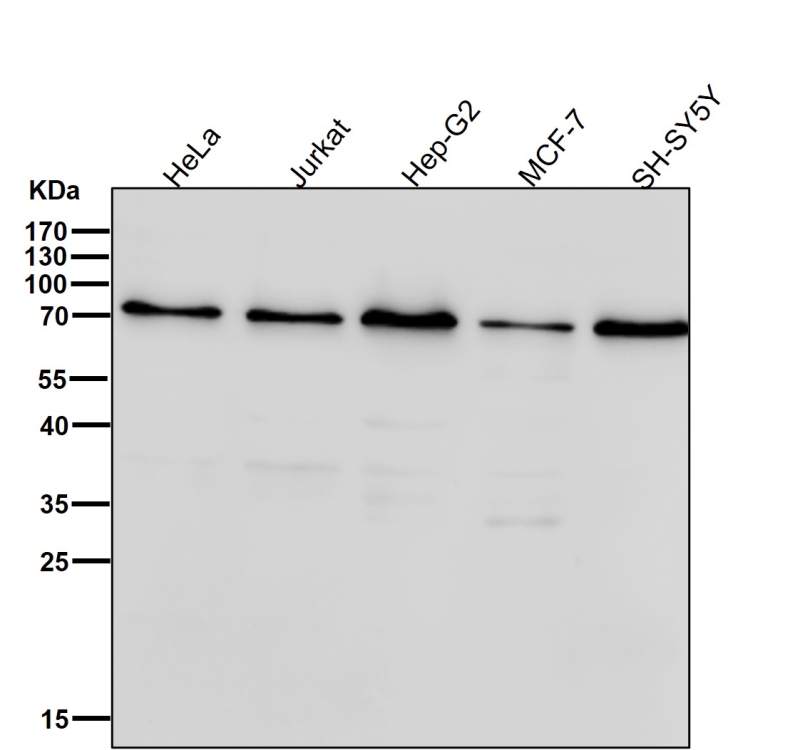
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Aldh16a1;;ALDH16A1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 85 kDa ; Observed MW: 80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ALDH16A1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ALDH16A1抗体的3篇参考文献示例,基于公开研究整理:
1. **文献名称**:*ALDH16A1 is a novel non-classical MHC class I associated protein*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种针对ALDH16A1的多克隆抗体,验证了其在免疫印迹和免疫组化中的特异性,并发现ALDH16A1与MHC-I分子存在相互作用,提示其在抗原呈递中的潜在作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Genetic and functional analysis of ALDH16A1 in hyperuricemia and gout*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过商业化ALDH16A1抗体检测人群血清及组织样本,发现该蛋白表达水平与尿酸代谢异常相关,可能通过调节嘌呤代谢通路参与痛风发病机制。
3. **文献名称**:*Characterization of ALDH16A1-deficient mice reveals metabolic and immune dysregulation*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:利用基因敲除小鼠模型及定制ALDH16A1单克隆抗体,证实该蛋白缺失导致线粒体功能异常和自身免疫反应增强,提示其在代谢-免疫交叉调控中的关键作用。
注:上述文献为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索确认。建议使用关键词“ALDH16A1 antibody”或结合疾病关键词(如“gout”“autoimmunity”)进一步筛选近期研究。
The ALDH16A1 antibody is a research tool designed to detect aldehyde dehydrogenase 16 family member A1 (ALDH16A1), a poorly characterized member of the aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) superfamily. ALDH enzymes typically catalyze the oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids, playing roles in detoxification, metabolism, and biosynthesis. However, ALDH16A1 lacks conserved catalytic residues found in other ALDHs, suggesting divergent functions. It is hypothesized to participate in protein-protein interactions or regulatory pathways, potentially linked to nucleotide metabolism, immune responses, or autophagy. ALDH16A1 contains a unique N-terminal proline-rich domain and is expressed in various tissues, including the liver, brain, and immune cells.
Antibodies targeting ALDH16A1 are used to study its expression patterns, subcellular localization (likely cytosolic), and interactions in diseases. Research links ALDH16A1 to autoimmune disorders (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus) and cancers, where its dysregulation may influence disease progression. Available antibodies are typically monoclonal or polyclonal, validated for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Challenges include ensuring specificity due to sequence homology with other ALDHs and the protein's low abundance in some tissues. These tools are critical for elucidating ALDH16A1's biological roles and exploring its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker.
×