| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HARS; HisRS; histidine translase; HRS; USH3B;;Histidine tRNA ligase |
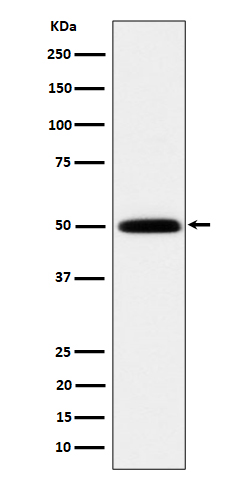
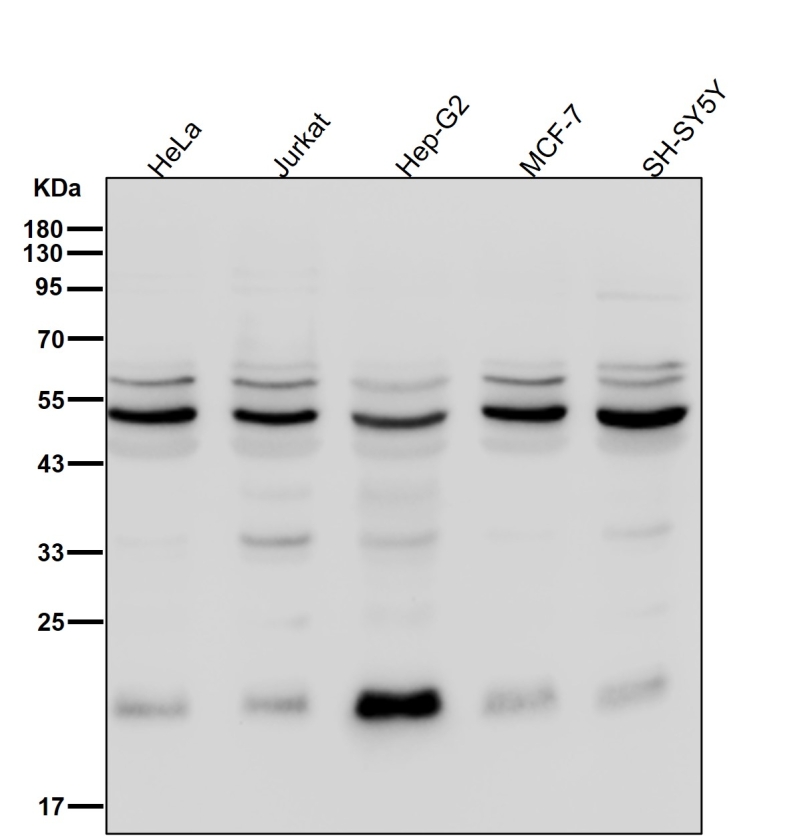
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 57 kDa ; Observed MW: 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Histidine tRNA ligase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HARS抗体(抗组氨酰-tRNA合成酶抗体)的3篇代表性文献的简要总结:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Clinical and Genetic Features of Patients With Anti-Histidyl-tRNA Synthetase (Anti-Jo1) Antibodies*
**作者**: Cavazzana I, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究分析了抗Jo-1抗体(HARS抗体最常见的亚型)阳性患者的临床特征,发现其与抗合成酶综合征(如肌炎、间质性肺病、关节炎)显著相关,并探讨了不同抗体亚型对预后的影响。
2. **文献名称**: *Myositis-specific autoantibodies: their clinical and pathogenic significance in disease expression*
**作者**: Targoff IN, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究系统描述了肌炎特异性抗体(包括HARS抗体)的诊断价值,指出HARS抗体是抗合成酶综合征的核心标志物,与急性间质性肺病和较差的治疗反应相关。
3. **文献名称**: *Anti-synthetase syndrome in the context of anti-Jo1 and anti-HA antibodies: a case series and literature review*
**作者**: Meyer A, et al.
**摘要**: 通过病例分析与文献回顾,该研究强调了HARS抗体阳性患者(尤其是抗Jo-1和抗HA亚型)的异质性临床表现,并建议早期筛查以预防肺部并发症进展。
---
**备注**:HARS抗体属于抗氨基酰-tRNA合成酶抗体家族,主要与抗合成酶综合征相关,其研究多聚焦于临床表型、诊断标志及并发症管理。如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或学术数据库检索上述作者及关键词获取全文。
**Background of HARS Antibodies**
HARS (histidyl-tRNA synthetase) antibodies are autoantibodies targeting histidyl-tRNA synthetase, an enzyme critical for protein synthesis. This enzyme catalyzes the attachment of histidine to its cognate tRNA during translation, a process essential for accurate mRNA decoding. HARS is one of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (ARS), a family of enzymes frequently implicated in autoimmune disorders.
HARS antibodies are most notably associated with antisynthetase syndrome (ASS), a rare autoimmune condition characterized by interstitial lung disease, myositis, arthritis, and mechanic’s hands. Among ARS antibodies, anti-HARS (also called anti-Jo-1) is the most common and well-studied subtype, detected in ~20–30% of ASS cases. Their presence aids in diagnosis, prognosis, and stratification of patients, as they often correlate with specific clinical features, such as severe lung involvement.
The exact mechanism triggering autoimmunity against HARS remains unclear, though molecular mimicry, viral infections, or genetic predisposition (e.g., HLA-DR3 haplotype) may contribute. These antibodies are thought to perpetuate inflammation by forming immune complexes or directly disrupting enzymatic function, leading to cellular stress and tissue damage.
Research continues to explore their pathogenic role and utility as biomarkers, with recent studies highlighting associations with treatment response and disease progression. Understanding HARS antibodies enhances insights into autoimmune pathophysiology and personalized therapeutic approaches.
×