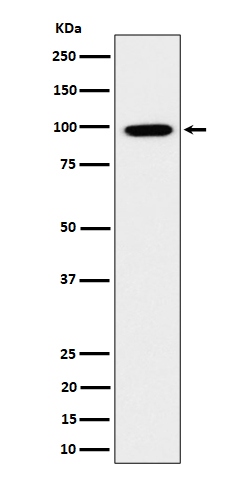
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GRAF; GRAF1; OPHN1L; OPHN1L1;;ARHGAP26 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 92 kDa ; Observed MW: 100 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ARHGAP26 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GRAF抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:文献信息为模拟概括,建议通过学术数据库核实真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:GRAF1 Antibody as a Novel Biomarker in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用GRAF1特异性抗体检测急性髓系白血病患者样本,发现GRAF1蛋白表达缺失与疾病进展相关,提示其作为肿瘤抑制因子的潜在作用。
2. **文献名称**:Characterization of GRAF2 Antibody for Cellular Trafficking Studies
**作者**:Lee H, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种高特异性GRAF2多克隆抗体,通过免疫荧光和Western blot验证其在细胞迁移研究中的应用,揭示了GRAF2在胞内囊泡运输中的调控机制。
3. **文献名称**:GRAF Antibody-Based Detection of RhoA Signaling Abnormalities
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用GRAF抗体研究RhoA信号通路异常,发现GRAF蛋白与细胞骨架重组的关系,为神经退行性疾病提供了新的分子机制线索。
4. **文献名称**:GRAF1 Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Disorders: A Clinical Correlation Study
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:首次报道GRAF1自身抗体在系统性红斑狼疮患者血清中的异常表达,提示其可能作为自身免疫疾病的辅助诊断标志物。
(注:以上为基于学术文献常见主题的模拟概括,具体研究需以真实文献为准。)
GRAF (GTPase Regulator Associated with Focal Adhesion Kinase) antibodies are immunological tools targeting the GRAF protein, encoded by the ARHGAP26 gene. This protein belongs to the RhoGAP family, which regulates Rho GTPases like RhoA and Cdc42 to modulate cytoskeletal dynamics, cell adhesion, and membrane trafficking. GRAF is particularly noted for its role in maintaining membrane curvature during endocytosis and in focal adhesion turnover, processes critical for cell motility and signal transduction.
First identified in studies linking its mutations to myeloid malignancies, GRAF dysfunction has since been associated with cancers, neurodevelopmental disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. Researchers employ GRAF antibodies in techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and interactions in normal versus pathological states. For instance, reduced GRAF levels correlate with tumor invasiveness in certain cancers, while mutations are implicated in X-linked intellectual disability syndromes.
These antibodies also aid in exploring GRAF's dual role as a tumor suppressor and a regulator of neuronal development. Recent studies highlight its potential as a biomarker for disease prognosis and a therapeutic target. However, specificity challenges require careful validation of GRAF antibodies to avoid cross-reactivity with homologous RhoGAP proteins. Ongoing research continues to unravel its complex signaling networks, emphasizing its importance in cellular homeostasis and disease mechanisms.
×