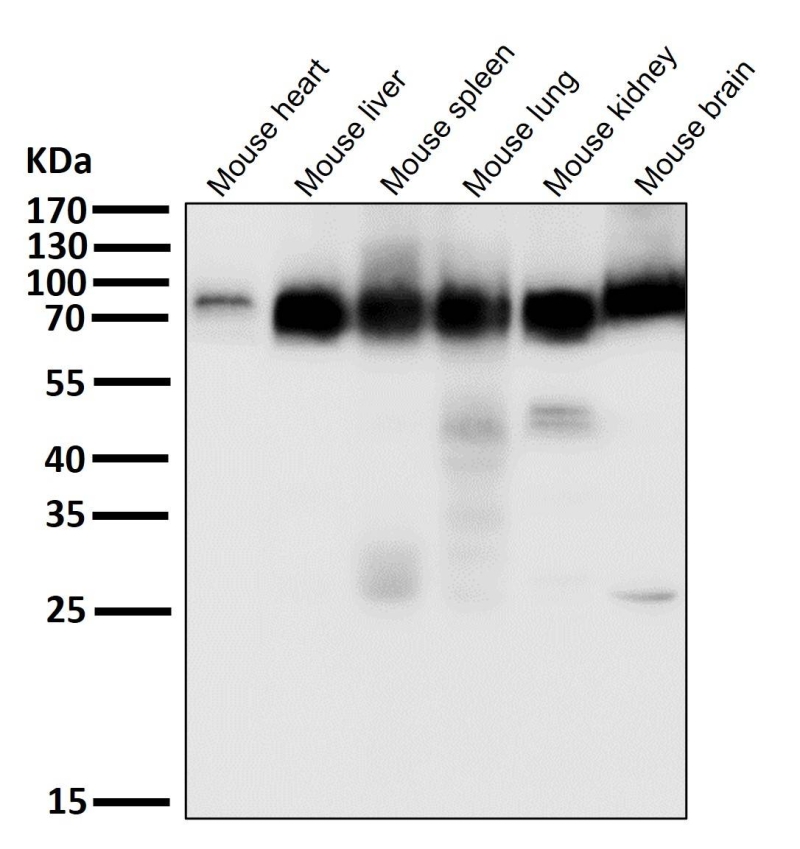
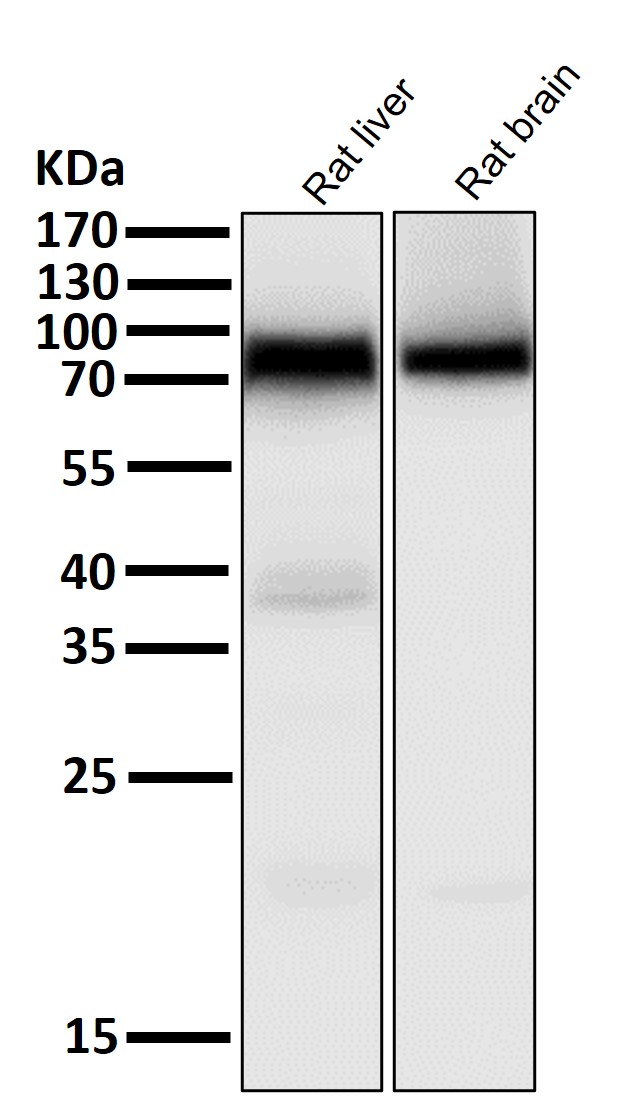
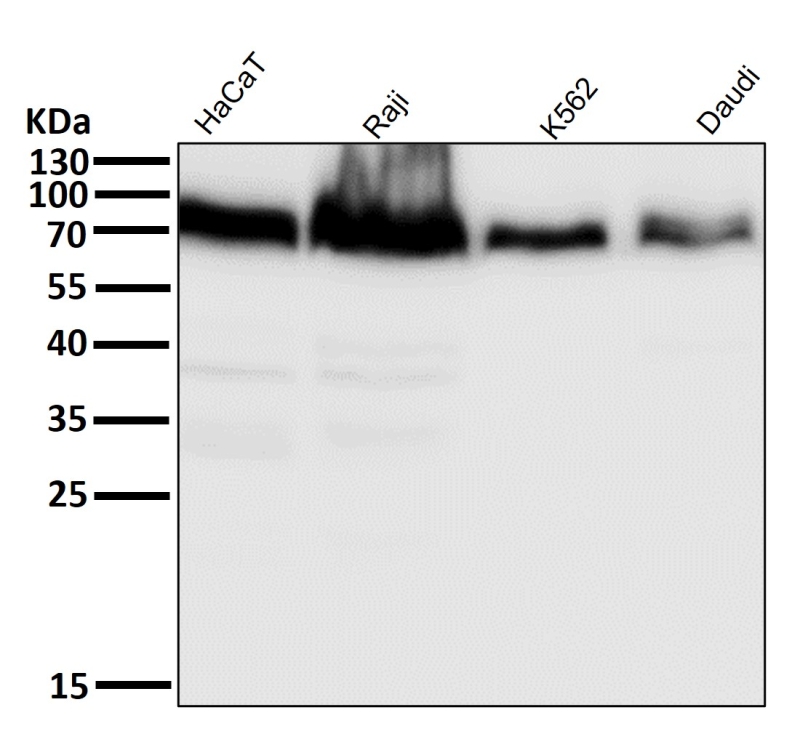
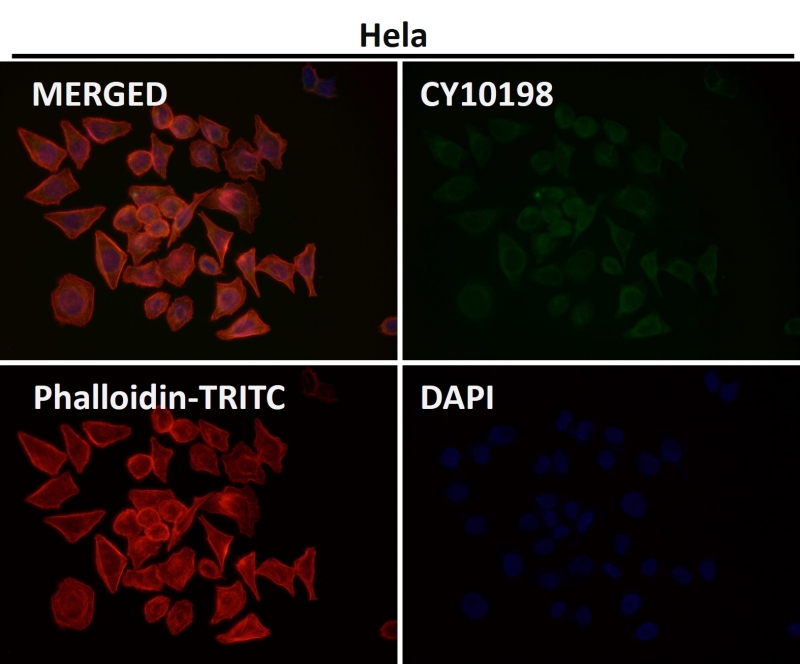
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
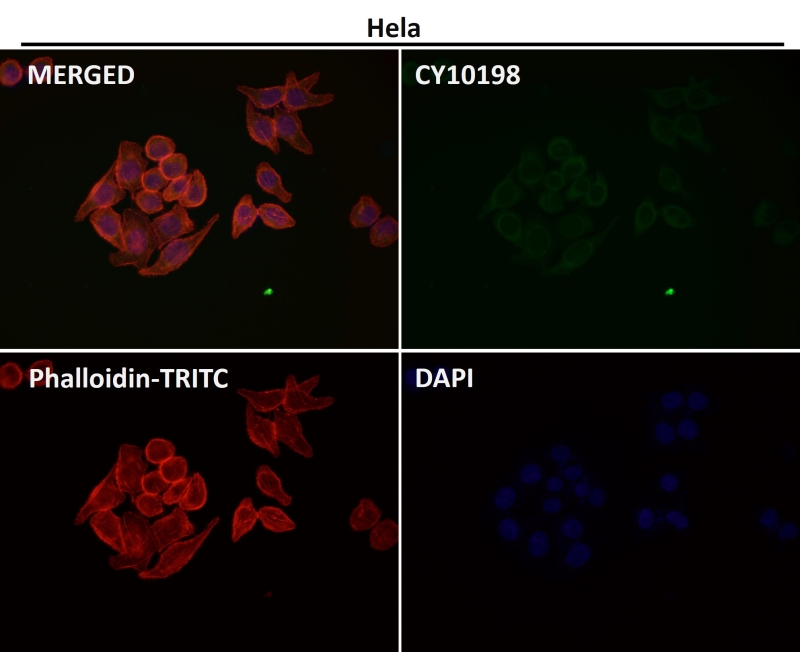
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ACS4; Acsl4; acyl CoA synthetase 4; FACL4; Fatty acid Coenzyme A ligase; LACS4; Long chain 4; long chain fatty acid Coenzyme A ligase 4; MRX63; MRX68;;ACSL4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 79 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ACSL4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ACSL4(可能对应FACL4命名)抗体的参考文献,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: *ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition*
**作者**: Doll, S. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过开发特异性ACSL4抗体,揭示了ACSL4在调控细胞铁死亡(ferroptosis)中的关键作用。实验表明,ACSL4通过促进多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFA)的酯化,影响细胞膜脂质组成,从而决定细胞对铁死亡的敏感性。
2. **文献名称**: *Targeting ACSL4 suppresses tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**: Li, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 作者利用ACSL4抗体检测肝癌组织中蛋白表达,发现ACSL4高表达与患者预后不良相关。通过体外实验证实,抑制ACSL4可减少脂质过氧化并抑制肿瘤生长,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**: *Antibody-based profiling of ACSL isoforms in human tissues*
**作者**: Coleman, R.A. et al.
**摘要**: 该文献开发了针对ACSL家族(包括ACSL4)的特异性抗体,并系统分析了其在不同组织中的表达差异。研究发现ACSL4在脑和生殖腺中高表达,提示其组织特异性功能。
4. **文献名称**: *ACSL4 promotes prostate cancer metastasis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling*
**作者**: Wu, X. et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过免疫组化(使用ACSL4抗体)发现,前列腺癌转移灶中ACSL4表达显著上调。机制研究表明,ACSL4通过激活Wnt通路促进肿瘤侵袭和转移。
---
**注意**:部分文献中“FACL4”可能被统称为“ACSL4”,建议结合具体研究背景确认命名一致性。如需全文链接或补充信息,可进一步提供DOI或PMID。
The fatty acid-CoA ligase 4 (FACL4), also known as ACSL4. is a key enzyme in lipid metabolism that activates long-chain fatty acids for synthesis of cellular lipids. It catalyzes the conversion of fatty acids into acyl-CoA esters, critical for membrane formation, energy storage, and signaling pathways. FACL4 is uniquely involved in metabolizing arachidonic acid (AA) and other polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), linking it to inflammatory responses and cell survival. Dysregulation of FACL4 has been implicated in various cancers, including breast, prostate, and hepatocellular carcinoma, where it promotes tumor growth, metastasis, and resistance to therapies like ferroptosis inducers.
FACL4 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in biological systems. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to assess FACL4 levels in tissues or cell lines. Research using these antibodies has revealed FACL4's role in lipid droplet formation, apoptosis regulation, and cancer progression. Additionally, FACL4 antibodies hold diagnostic potential, as elevated FACL4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in certain cancers. Their therapeutic relevance is being explored, particularly in targeting lipid metabolism pathways to combat chemoresistance.
×