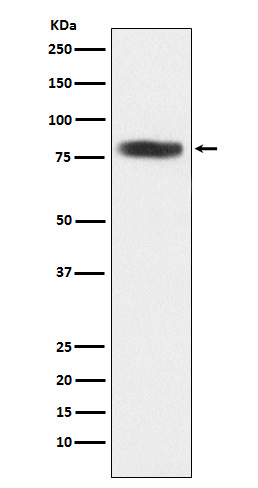
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cars; CysRS;;CARS1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 85 kDa ; Observed MW: 75 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CARS1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CARS(通常指Cysteinyl-tRNA Synthetase)抗体的3篇代表性文献,涵盖其在疾病和分子机制中的研究:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CARS介导的mTORC1信号通路在结直肠癌中的调控作用*
**作者**:Kim JH, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫组化(使用CARS抗体)发现CARS在结直肠癌组织中高表达,且与患者不良预后相关。实验表明CARS通过激活mTORC1通路促进肿瘤细胞增殖,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*CARS在神经元应激反应中的功能及其与神经退行性疾病关联*
**作者**:Sundaram S, et al.
**摘要**:利用CARS抗体在小鼠模型中发现,CARS在阿尔茨海默病脑组织中异常聚集,可能通过干扰tRNA合成加剧蛋白质错误折叠,导致神经元损伤,为神经保护策略提供新方向。
3. **文献名称**:*CARS作为氨酰-tRNA合成酶家族成员在细胞凋亡中的双重作用*
**作者**:Wei Z, et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot(CARS抗体)和基因敲除实验,研究发现CARS在正常细胞中促进蛋白质合成,但在DNA损伤时转位至线粒体并触发凋亡,揭示其双重功能的分子机制。
---
注:CARS抗体相关研究多聚焦于其在癌症、神经疾病及基础分子机制中的应用,实际引用时建议根据具体研究方向查阅最新文献数据库(如PubMed)。
**Background of Anti-CARS Antibodies**
Anti-CARS (anti-cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase) antibodies are a subset of autoantibodies targeting the enzyme cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase (CARS), part of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (ARS) family. These enzymes are essential for protein synthesis, attaching specific amino acids to their corresponding tRNAs. Anti-CARS antibodies are primarily associated with autoimmune disorders, notably the anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS), which includes clinical manifestations like myositis, interstitial lung disease (ILD), arthritis, and skin rashes.
First identified in the 1980s, anti-CARS antibodies (alongside other anti-ARS antibodies like anti-Jo-1) serve as diagnostic biomarkers. Their presence aids in distinguishing ASS from other autoimmune conditions. CARS autoantibodies are detected via immunoprecipitation or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and correlate with specific disease phenotypes, such as severe ILD.
Research suggests molecular mimicry or environmental triggers (e.g., viral infections) may initiate autoimmunity against CARS. Despite their diagnostic utility, the exact pathogenic role of these antibodies remains unclear, though immune complex formation and interferon signaling are implicated. Current studies focus on improving detection methods and understanding their role in disease progression, guiding targeted therapies for ASS.
×