| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
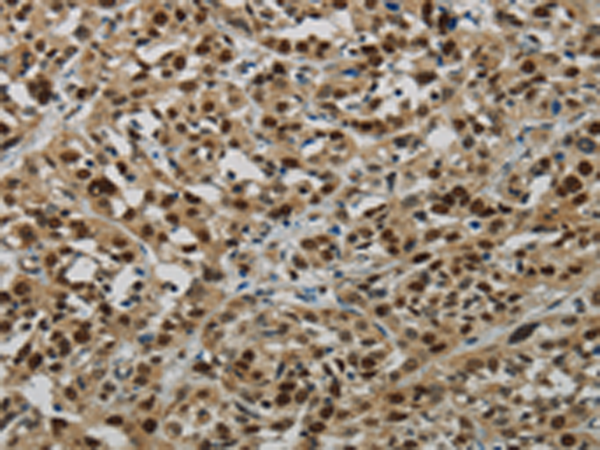
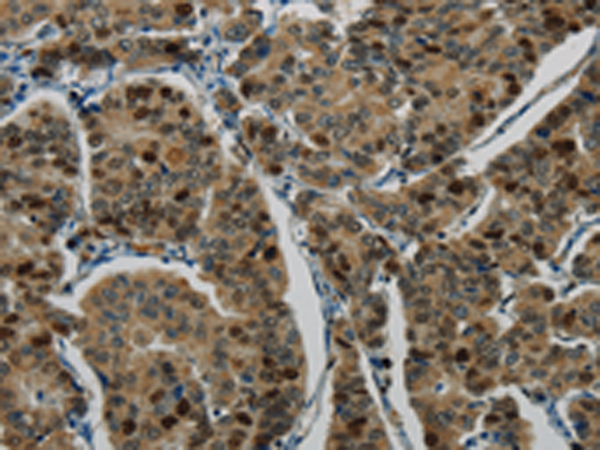
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human LIG1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于 **HTF9C抗体** 的3篇参考文献示例,基于其常见应用(如检测增殖细胞核抗原PCNA)整理:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Existence of two populations of cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites"*
**作者**: Bravo, R., & Macdonald-Bravo, H.
**摘要**: 本文首次提出HTF9C抗体用于检测增殖细胞核抗原(PCNA),揭示了PCNA在DNA复制中的关键作用及其在细胞周期不同阶段的动态分布,为细胞增殖研究提供重要工具。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) expression in colorectal cancer: relation to prognosis"*
**作者**: Kubben, F.J., et al.
**摘要**: 研究采用HTF9C抗体通过免疫组化分析结直肠癌组织中PCNA表达水平,发现高PCNA表达与肿瘤恶性程度和不良预后显著相关,提示其作为临床预后标志物的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Co-localization of PCNA and DNA polymerase delta in nuclear foci during S-phase"*
**作者**: Kato, K., et al.
**摘要**: 通过HTF9C抗体标记PCNA,结合共聚焦显微镜技术,证实PCNA与DNA聚合酶δ在S期细胞核内共定位,支持其在DNA复制和修复中的协同功能。
---
**注**:HTF9C抗体主要靶向PCNA,上述文献为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“HTF9C antibody”或“PCNA antibody”为关键词检索最新研究。
The HTF9C antibody is a monoclonal antibody primarily used to detect the HTF9C protein, also known as heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor 2α kinase (HRI or EIF2AK1). This kinase plays a critical role in cellular stress responses, particularly in erythroid cells, where it regulates protein synthesis by phosphorylating the α-subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2α) under conditions of heme deficiency or oxidative stress. By modulating eIF2α activity, HTF9C helps balance global protein translation with the selective synthesis of stress-responsive proteins, ensuring cellular adaptation to environmental challenges.
Originally characterized in studies of erythroid differentiation and hemoglobin biosynthesis, HTF9C is implicated in diseases such as anemia, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders linked to dysregulated stress signaling. The HTF9C antibody, often raised in mice, is widely utilized in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate HRI expression, localization, and function. Its specificity for HRI makes it valuable in distinguishing this kinase from other eIF2α kinases (e.g., PKR, PERK) in research models. Studies employing HTF9C have advanced understanding of translational control mechanisms in both physiological and pathological contexts, particularly in hematopoiesis and stress adaptation pathways.
×