
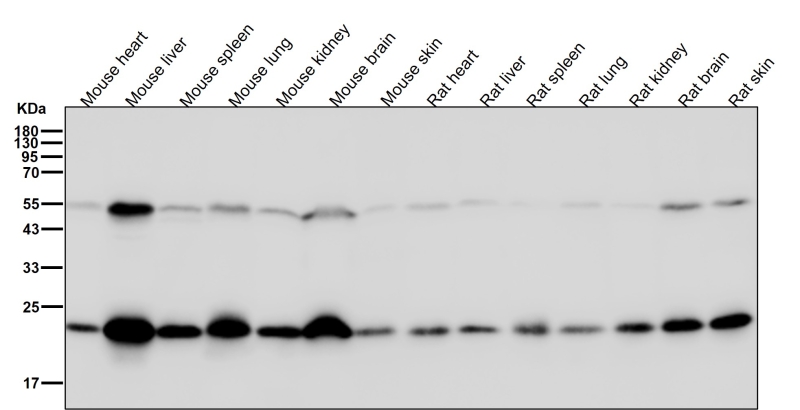
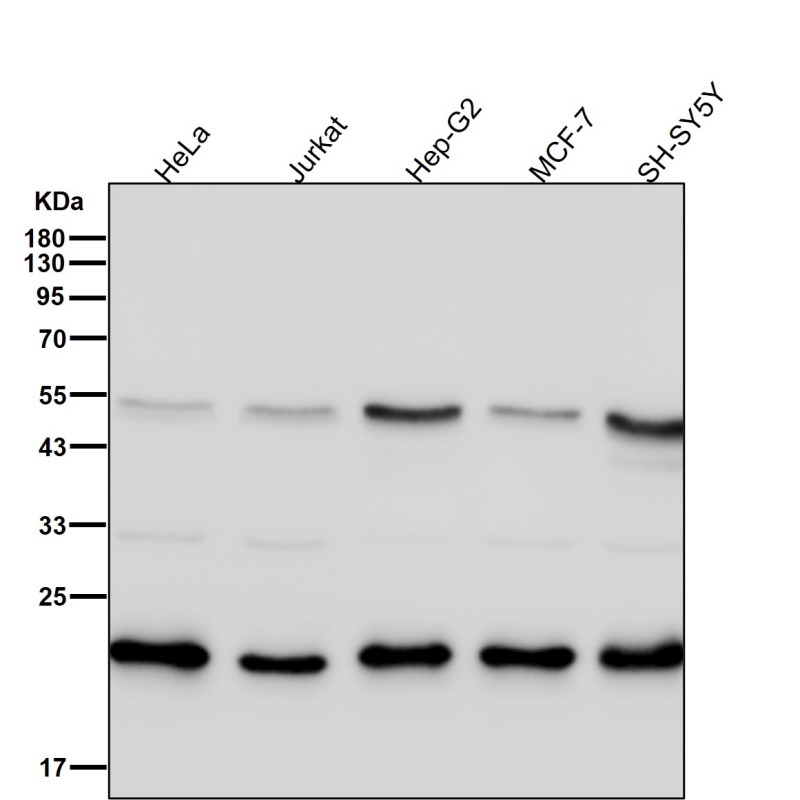
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Aldoketomutase; glo1; GLOD1; Glx I; GLYI;;Lactoylglutathione lyase |
| WB Predicted band size | 21 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Lactoylglutathione lyase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GLO1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: "Glyoxalase 1 Antibody [2B12H12] (Western Blot-Validated)"
**作者**: Bierhaus, A. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种高特异性小鼠单克隆抗体(2B12H12),用于检测人GLO1蛋白的表达。通过Western blot和免疫组化验证,该抗体成功应用于分析糖尿病模型中GLO1的上调及其与氧化应激的关系。
2. **文献名称**: "Overexpression of Glyoxalase 1 in Glioblastoma: A Novel Biomarker Detected by Immunohistochemistry"
**作者**: Santarius, T. et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用GLO1抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现胶质母细胞瘤组织中GLO1显著过表达,且与患者化疗耐药性及预后不良相关。抗体检测结果支持GLO1作为潜在治疗靶点和预后标志物。
3. **文献名称**: "Role of Glyoxalase 1 in Alzheimer’s Disease: Detection of Enzyme Activity with a Novel Antibody Probe"
**作者**: Kuhla, B. et al.
**摘要**: 该文献报道了一种新型抗体探针,用于定量检测脑组织中的GLO1活性。研究发现阿尔茨海默病患者脑内GLO1活性降低,导致甲基乙二醛积累,可能加速神经元损伤和晚期糖基化终产物(AGEs)形成。
以上文献均聚焦于GLO1抗体的开发或应用,涵盖糖尿病、癌症及神经退行性疾病领域的研究。如需具体文献来源,建议通过PubMed或期刊数据库检索标题及作者以获取全文。
The glyoxalase 1 (GLO1) antibody is a research tool targeting the GLO1 enzyme, a critical component of the glyoxalase system responsible for detoxifying methylglyoxal (MG), a cytotoxic byproduct of glycolysis. GLO1 catalyzes the conversion of MG and glutathione into S-D-lactoylglutathione, mitigating cellular damage linked to oxidative stress and advanced glycation end-products (AGEs). Dysregulation of GLO1 has been implicated in metabolic disorders (e.g., diabetes complications), neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), and cancer, where its expression often correlates with drug resistance or tumor progression.
GLO1 antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study protein expression, localization, and regulatory mechanisms in tissues or cell lines. Both monoclonal and polyclonal variants are available, with specificity validated across human, mouse, and rat models due to high sequence homology. Commercial antibodies are typically developed using recombinant GLO1 protein fragments or peptide antigens.
Research leveraging GLO1 antibodies has highlighted its role as a potential therapeutic target. Inhibitors are being explored for cancer treatment, while upregulation strategies aim to address diabetic complications. However, challenges persist, including variability in antibody cross-reactivity and the need for standardized validation protocols. Overall, GLO1 antibodies remain vital for elucidating the enzyme’s pathophysiological contributions and advancing biomarker or drug discovery efforts.
×