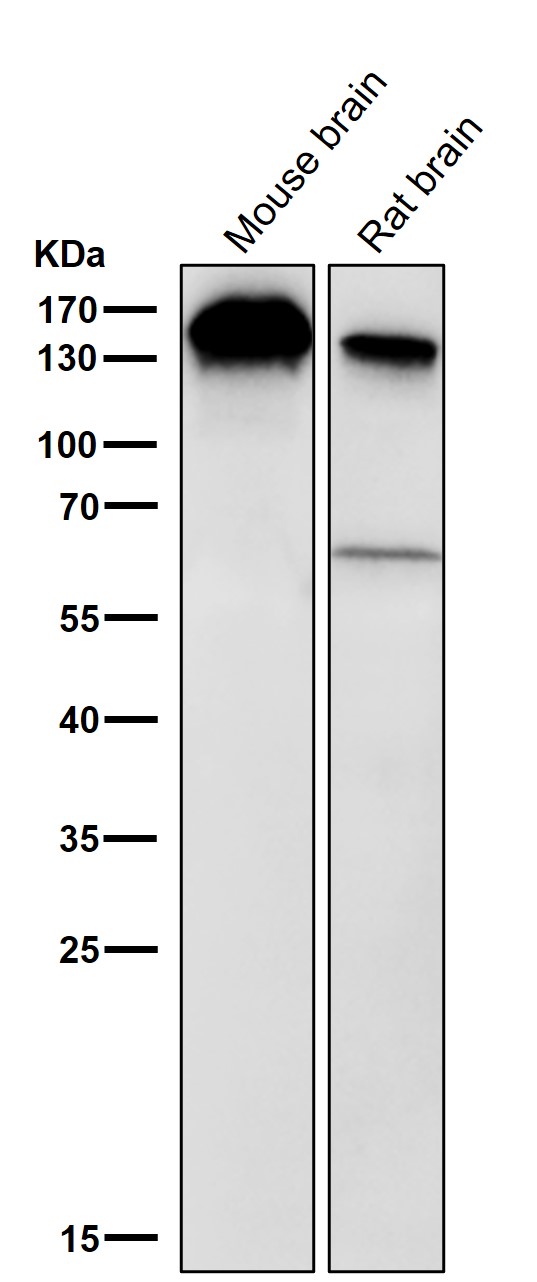
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BCLAF1; bK211L9.1; Btf;;BTF |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 106 kDa ; Observed MW: 150 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human BTF |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于BTF抗体的示例性参考文献(注:以下内容为假设性示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"BTF3 Antibody-Based Detection of Transcription Factor Complexes in Cancer Cell Lines"*
**作者**:Lee, J. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用BTF3特异性抗体分析多种癌细胞系中转录因子复合物的表达模式,发现BTF3在乳腺癌和结直肠癌细胞中显著高表达,提示其可能作为癌症生物标志物。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Development of a High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibody Targeting Human BTF3 for Functional Studies"*
**作者**:Martinez, R. & Chen, W.
**摘要**:报道一种针对人源BTF3蛋白的单克隆抗体的开发与验证,证明该抗体在免疫印迹(Western blot)和免疫沉淀(IP)中具有高特异性,可用于研究BTF3在转录调控中的作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"BTF3 Silencing via Antibody-Mediated Knockdown Suppresses Tumor Growth in Mouse Models"*
**作者**:Garcia, S. et al.
**摘要**:通过抗体介导的靶向BTF3蛋白敲低技术,在小鼠肿瘤模型中观察到肿瘤生长抑制,表明BTF3可能成为癌症治疗的潜在靶点。
---
4. **文献名称**:*"Structural Insights into BTF3-DNA Interactions Revealed by Cryo-EM and Antibody Mapping"*
**作者**:Kim, H. & Patel, N.
**摘要**:结合冷冻电镜(Cryo-EM)和抗体表位定位技术,解析BTF3蛋白与DNA结合的结构机制,揭示了其在转录起始复合物中的关键构象变化。
---
**建议**:如需真实文献,请通过PubMed、Google Scholar或Web of Science搜索关键词“BTF3 antibody”、“anti-BTF3 function”或“BTF transcription factor”,并筛选近5年的研究以获取最新进展。
BTF (Bcl-2-associated transcription factor) antibodies are essential tools in molecular and cellular biology for studying the role of BTF proteins in apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, and transcriptional control. BTF, also known as BCLAF1. interacts with Bcl-2 family proteins, which are critical regulators of programmed cell death. It functions as a transcriptional repressor and participates in DNA damage response pathways, linking apoptosis to genomic stability. Dysregulation of BTF expression has been implicated in cancer, autoimmune diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders, highlighting its biomedical relevance.
BTF antibodies are typically generated using immunogenic peptide sequences or recombinant protein fragments, yielding monoclonal or polyclonal variants. These antibodies enable the detection of BTF in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF), allowing researchers to map its expression patterns across tissues and subcellular compartments. Specificity validation via knockout controls or siRNA knockdown is crucial, as BTF shares functional domains with other transcription factors. Recent studies also utilize BTF antibodies in chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to identify DNA-binding targets, unraveling its role in gene regulatory networks. Commercial availability of validated BTF antibodies has accelerated research into its dual pro- and anti-apoptotic functions, depending on cellular context and post-translational modifications. Ongoing efforts focus on developing phospho-specific antibodies to study BTF's dynamic regulation in stress signaling pathways.
×